Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
FLUVOXAMINE MALEATE
DIR Classification
Classification:Less-DIR concern
Severity Score:1
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Potential Thioridazine Interaction
- The effect of fluvoxamine (25 mg b.i.d. for one week) on thioridazine steady-state concentrations was evaluated in 10 male inpatients with schizophrenia. Concentrations of thioridazine and its two active metabolites, mesoridazine and sulforidazine, increased three-fold following coadministration of fluvoxamine.
- Thioridazine administration produces a dose-related prolongation of the QTc interval, which is associated with serious ventricular arrhythmias, such as torsades de pointes-type arrhythmias, and sudden death. It is likely that this experience underestimates the degree of risk that might occur with higher doses of thioridazine. Moreover, the effect of fluvoxamine may be even more pronounced when it is administered at higher doses.
- Therefore, fluvoxamine and thioridazine should not be coadministered [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4.1)].
- [Potential Pimozide Interaction]
- Pimozide is metabolized by the cytochrome P4503A4 isoenzyme, and it has been demonstrated that ketoconazole, a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, blocks the metabolism of this drug, resulting in increased plasma concentrations of parent drug. An increased plasma concentration of pimozide causes QT prolongation and has been associated with torsades de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia, sometimes fatal. As noted below, a substantial pharmacokinetic interaction has been observed for fluvoxamine in combination with alprazolam, a drug that is known to be metabolized by CYP3A4. Although it has not been definitively demonstrated that fluvoxamine is a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor, it is likely to be, given the substantial interaction of fluvoxamine with alprazolam. Consequently, it is recommended that fluvoxamine not be used in combination with pimozide [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4.1)].
- [Post-Marketing Reports]
- Voluntary reports of adverse reactions in patients taking fluvoxamine maleate that have been received since market introduction and are of unknown causal relationship to fluvoxamine maleate use include: acute renal failure, agranulocytosis, amenorrhea, anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, aplastic anemia, bullous eruption, Henoch-Schoenlein purpura, hepatitis, ileus, pancreatitis, porphyria, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, vasculitis, and ventricular tachycardia (including torsades de pointes).
- OVERDOSAGE
- Commonly (greater than or equal to 5%) observed adverse events associated with fluvoxamine maleate overdose include gastrointestinal complaints (nausea, vomiting and diarrhea), coma, hypokalemia, hypotension, respiratory difficulties, somnolence, and tachycardia. Other notable signs and symptoms seen with fluvoxamine maleate overdose (single or multiple drugs) include bradycardia, ECG abnormalities (such as heart arrest, QT interval prolongation, first degree atrioventricular block, bundle branch block, and junctional rhythm), convulsions, dizziness, liver function disturbances, tremor, and increased reflexes.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
46
42866
Other ADRs
2783
14114496
Odds Ratio = 5.443
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- N06AB08 - fluvoxamine maleate
- N06AB - Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- N06A - ANTIDEPRESSANTS
- N06 - PSYCHOANALEPTICS
- N - NERVOUS SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:fluvoxamine maleate
Active Ingredient UNII:5LGN83G74V
Drugbank ID:DB00176
PubChem Compound:3404
CAS Number:54739-18-3
Dosage Form(s):capsule, extended release
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 100.0 mg/day N06AB08
Chemical Structure: 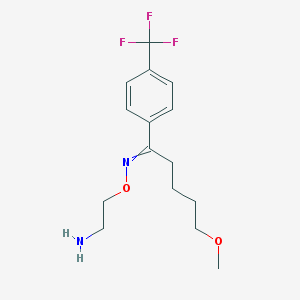

SMILE Code:
COCCCCC(=NOCCN)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(F)(F)F
COCCCCC(=NOCCN)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(F)(F)F
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
N/ADisclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.