Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
NIACIN
DIR Classification
Classification:Moderate-DIR concern
Severity Score:3
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS
- Skeletal Muscle
- Rare cases of rhabdomyolysis have been associated with concomitant administration of lipid-altering doses (≥1 g/day) of nicotinic acid and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Physicians contemplating combined therapy with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and nicotinic acid should carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks and should carefully monitor patients for any signs and symptoms of muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, particularly during the initial months of therapy and during any periods of upward dosage titration of either drug. Periodic serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and potassium determinations should be considered in such situations, but there is no assurance that such monitoring will prevent the occurrence of severe myopathy.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
55
42857
Other ADRs
36517
14080762
Odds Ratio = 0.495
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- C10BA01 - niacin
- C10BA - HMG CoA reductase inhibitors in combination with other lipid modifying agents
- C10B - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- C10AD52 - niacin
- C10AD - Nicotinic acid and derivatives
- C10A - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, PLAIN"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- C04AC01 - niacin
- C04AC - Nicotinic acid and derivatives
- C04A - PERIPHERAL VASODILATORS
- C04 - PERIPHERAL VASODILATORS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- C10AD02 - niacin
- C10AD - Nicotinic acid and derivatives
- C10A - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, PLAIN"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:niacin
Active Ingredient UNII:2679MF687A
Drugbank ID:DB00627
PubChem Compound:938
CAS Number:59-67-6
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
Chemical Structure: 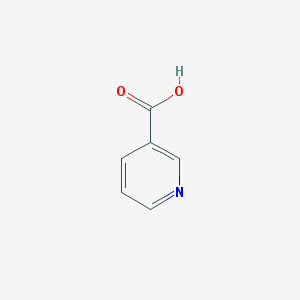

SMILE Code:
C1=CC(=CN=C1)C(=O)O
C1=CC(=CN=C1)C(=O)O
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: HPS2-THRIVE randomized placebo-controlled trial in 25 673 high-risk patients of ER niacin/laropiprant: trial design, pre-specified muscle and liver outcomes, and reasons for stopping study treatment.
[HPS2-THRIVE Collaborative Group]Eur Heart J.2013 May;34(17):1279-91. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht055. Epub 2013 Feb 26. PMID: 23444397
2: Risk of hospitalized rhabdomyolysis associated with lipid-lowering drugs in a real-world clinical setting.
[Cziraky Mark J,Willey Vincent J,McKenney James M,Kamat Siddhesh A,Fisher Maxine D,Guyton John R,Jacobson Terry A,Davidson Michael H]J Clin Lipidol.2013 Mar-Apr;7(2):102-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2012.06.006. Epub 2012 Jul 3. PMID: 23415428
3: Statin-associated rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure complicated by intradialytic NSTEMI: a review of lipid management considerations.
[Kar Subrata,Chockalingam Anand]Am J Ther.2013 Jan;20(1):57-60. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181ff7c79. PMID: 21192242
4: Managing dyslipidemia in chronic kidney disease.
[Harper Charles R,Jacobson Terry A]J Am Coll Cardiol.2008 Jun 24;51(25):2375-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.03.025. PMID: 18565393
5: Management of mixed dyslipidemia in patients with or at risk for cardiovascular disease: a role for combination fibrate therapy.
[Fazio Sergio]Clin Ther.2008 Feb;30(2):294-306. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.02.004. PMID: 18343268
6: Safety of aggressive lipid management.
[Davidson Michael H,Robinson Jennifer G]J Am Coll Cardiol.2007 May 1;49(17):1753-62. Epub 2007 Apr 16. PMID: 17466224
7: Safety of lovastatin/extended release niacin compared with lovastatin alone, atorvastatin alone, pravastatin alone, and simvastatin alone (from the United States Food and Drug Administration adverse event reporting system).
[Alsheikh-Ali Alawi A,Karas Richard H]Am J Cardiol.2007 Feb 1;99(3):379-81. Epub 2006 Dec 8. PMID: 17261402
8: Statin safety: an assessment using an administrative claims database.
[Cziraky Mark J,Willey Vincent J,McKenney James M,Kamat Siddhesh A,Fisher Maxine D,Guyton John R,Jacobson Terry A,Davidson Michael H]Am J Cardiol.2006 Apr 17;97(8A):61C-68C. Epub 2006 Jan 30. PMID: 16581331
9: Pharmacologic options for aggressive low-density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering: benefits versus risks.
[McKenney James M]Am J Cardiol.2005 Aug 22;96(4A):60E-66E. PMID: 16098846
10: Relative impact of CYP3A genotype and concomitant medication on the severity of atorvastatin-induced muscle damage.
[Wilke Russell A,Moore Jason H,Burmester James K]Pharmacogenet Genomics.2005 Jun;15(6):415-21. PMID: 15900215
11: Prevalence of potentially severe drug-drug interactions in ambulatory patients with dyslipidaemia receiving HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor therapy.
[Rätz Bravo Alexandra E,Tchambaz Lydia,Krähenbühl-Melcher Anita,Hess Lorenzo,Schlienger Raymond G,Krähenbühl Stephan]Drug Saf.2005;28(3):263-75. PMID: 15733030
12: Simvastatin plus ezetimibe: combination therapy for the management of dyslipidaemia.
[Toth Peter P,Davidson Michael H]Expert Opin Pharmacother.2005 Jan;6(1):131-9. PMID: 15709890
13: Niacin aids cholesterol control. But choose "extended release" to minimize "flushing" risk.
Heart Advis.2003 Jul;6(7):3. PMID: 12921040
14: Advances in the understanding and management of dyslipidemia: using niacin-based therapies.
[Ito Matthew K]Am J Health Syst Pharm.2003 Jul 1;60(13 Suppl 2):S15-21; quiz S25. PMID: 12901026
15: Risk for myopathy with statin therapy in high-risk patients.
[Ballantyne Christie M,Corsini Alberto,Davidson Michael H,Holdaas Hallvard,Jacobson Terry A,Leitersdorf Eran,März Winfried,Reckless John P D,Stein Evan A]Arch Intern Med.2003 Mar 10;163(5):553-64. PMID: 12622602
16: Pharmaceutical initiatives to combat atherosclerosis--what to do with the good, the bad, and the ugly lipoproteins.
[Samson Russell H]Semin Vasc Surg.2002 Dec;15(4):204-15. PMID: 12478495
17: Safety of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: focus on atorvastatin.
[Bernini F,Poli A,Paoletti R]Cardiovasc Drugs Ther.2001;15(3):211-8. PMID: 11713888
18: Cerivastatin and gemfibrozil-associated rhabdomyolysis.
[Bruno-Joyce J,Dugas J M,MacCausland O E]Ann Pharmacother.2001 Sep;35(9):1016-9. PMID: 11573847
19: Statin-fibrate combination therapy.
[Shek A,Ferrill M J]Ann Pharmacother.2001 Jul-Aug;35(7-8):908-17. PMID: 11485144
20: Does differing metabolism by cytochrome p450 have clinical importance?
[Davidson M H]Curr Atheroscler Rep.2000 Jan;2(1):14-9. PMID: 11122720
21: Combination drug therapy for combined hyperlipidemia.
[Guyton J R]Curr Cardiol Rep.1999 Sep;1(3):244-50. PMID: 10980849
22: Case of the month: February 1999--54 year old man with severe muscle weakness.
[Hill M D,Bilbao J M]Brain Pathol.1999 Jul;9(3):607-8. PMID: 10416996
23: Treatment of hyperlipidemia with combined niacin-statin regimens.
[Guyton J R,Capuzzi D M]Am J Cardiol.1998 Dec 17;82(12A):82U-84U; discussion 85-86U. PMID: 9915667
24: Atorvastatin in the treatment of primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemias.
[Yee H S,Fong N T]Ann Pharmacother.1998 Oct;32(10):1030-43. PMID: 9793596
25: [Rhabdomyolysis in patients with preexisting myopathy, treated with antilipemic agents].
[Franc S,Bruckert E,Giral P,Turpin G]Presse Med.1997 Dec 6;26(38):1855-8. PMID: 9569908
26: Currently available hypolipidaemic drugs and future therapeutic developments.
[Farmer J A,Gotto A M]Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab.1995 Oct;9(4):825-47. PMID: 8593127
27: Rhabdomyolysis from the coadministration of lovastatin and the antifungal agent itraconazole.
[Lees R S,Lees A M]N Engl J Med.1995 Sep 7;333(10):664-5. PMID: 7637734
28: Interactions with hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors.
[Garnett W R]Am J Health Syst Pharm.1995 Aug 1;52(15):1639-45. PMID: 7583826
29: Antihyperlipidaemic agents. Drug interactions of clinical significance.
[Farmer J A,Gotto A M]Drug Saf.1994 Nov;11(5):301-9. PMID: 7873090
30: Fluvastatin with and without niacin for hypercholesterolemia.
[Jacobson T A,Chin M M,Fromell G J,Jokubaitis L A,Amorosa L F]Am J Cardiol.1994 Jul 15;74(2):149-54. PMID: 8023779
31: Combination therapy with fluvastatin and niacin in hypercholesterolemia: a preliminary report on safety.
[Jacobson T A,Amorosa L F]Am J Cardiol.1994 May 26;73(14):25D-29D. PMID: 8198020
32: Lovastatin, nicotinic acid, and rhabdomyolysis.
[Reaven P,Witztum J L]Ann Intern Med.1988 Oct 1;109(7):597-8. PMID: 3421570
33: [Crush syndrome caused by isoniazid poisoning].
[HAND G,WUNDER M,FERENBACH H]Medizinische.1954 May 8;19:683-5. PMID: 13175989
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.