Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
LEVOFLOXACIN
DIR Classification
Classification:Less-DIR concern
Severity Score:1
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Prolongation of the QT Interval
- Some fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin, have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram and infrequent cases of arrhythmia. Rare cases of torsade de pointes have been spontaneously reported during postmarketing surveillance in patients receiving fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin. Levofloxacin should be avoided in patients with known prolongation of the QT interval, patients with uncorrected hypokalemia, and patients receiving Class IA (quinidine, procainamide), or Class III (amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents. Elderly patients may be more susceptible to drug-associated effects on the QT interval [see Adverse Reactions (6.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.5), and Patient Counseling Information (17.3)].
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Prolongation of the QT Interval [seeWarningsandPrecautions(5.10)]
- Cardiac Disorders
- isolated reports of torsade de pointes,electrocardiogram QT prolonged[seeWarnings and Precautions(5.10)]
- PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Prolongation of the QT Interval: Instruct patients to inform their physician of any personal or family history of QT prolongation or proarrhythmic conditions such as hypokalemia, bradycardia, or recent myocardial ischemia; if they are taking any Class IA (quinidine, procainamide), or Class III (amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents. Instruct patients to notify their physician if they have any symptoms of prolongation of the QT interval, including prolonged heart palpitations or a loss of consciousness.
- Musculoskeletal Disorders in Pediatric Patients: Instruct parents to inform their child's physician if the child has a history of joint-related problems before taking this drug. Inform parents of pediatric patients to notify their child's physician of any joint-related problems that occur during or following levofloxacin therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
- Photosensitivity/Phototoxicity: Inform patients that photosensitivity/phototoxicity has been reported in patients receiving fluoroquinolones. Inform patients to minimize or avoid exposure to natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while taking fluoroquinolones. If patients need to be outdoors while using fluoroquinolones, instruct them to wear loose-fitting clothes that protect skin from sun exposure and discuss other sun protection measures with their physician. If a sunburn-like reaction or skin eruption occurs, instruct patients to contact their physician.
- MEDICATION GUIDE
- Serious heart rhythm changes (QT prolongation and torsades de pointes) Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have a change in your heart beat (a fast or irregular heartbeat), or if you faint. Levofloxacin tablets may cause a rare heart problem known as prolongation of the QT interval. This condition can cause an abnormal heartbeat and can be very dangerous. The chances of this happening are higher in people:
- who are elderly
- with a family history of prolonged QT interval
- with low blood potassium (hypokalemia)
- who take certain medicines to control heart rhythm (antiarrhythmics)
- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Elderly patients may be more susceptible to drug-associated effects on the QT interval. Therefore, precaution should be taken when using levofloxacin with concomitant drugs that can result in prolongation of the QT interval (e.g., Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmics) or in patients with risk factors for torsade de pointes (e.g., known QT prolongation, uncorrected hypokalemia) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
166
42746
Other ADRs
31663
14085616
Odds Ratio = 1.728
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- A02BD10 - levofloxacin
- A02BD - Combinations for eradication of Helicobacter pylori
- A02B - DRUGS FOR PEPTIC ULCER AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD)
- A02 - DRUGS FOR ACID RELATED DISORDERS
- A - ALIMENTARY TRACT AND METABOLISM
- J01RA05 - levofloxacin
- J01RA - Combinations of antibacterials
- J01R - COMBINATIONS OF ANTIBACTERIALS
- J01 - ANTIBACTERIALS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- J - ANTIINFECTIVES FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- S01AE05 - levofloxacin
- S01AE -
- S01A - ANTIINFECTIVES
- S01 - OPHTHALMOLOGICALS
- S - SENSORY ORGANS
- J01MA12 - levofloxacin
- J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
- J01M - QUINOLONE ANTIBACTERIALS
- J01 - ANTIBACTERIALS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- J - ANTIINFECTIVES FOR SYSTEMIC USE
Active Ingredient:levofloxacin
Active Ingredient UNII:6GNT3Y5LMF
Drugbank ID:DB01137
PubChem Compound:149096
CAS Number:100986-85-4
Dosage Form(s):solution
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 500.0 mg/day J01MA12
Chemical Structure: 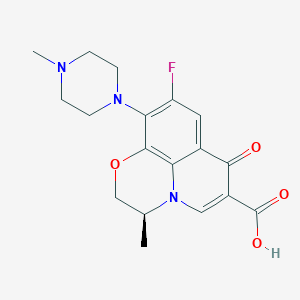

SMILE Code:
C[C@H]1COC2=C3N1C=C(C(=O)C3=CC(=C2N4CCN(CC4)C)F)C(=O)O
C[C@H]1COC2=C3N1C=C(C(=O)C3=CC(=C2N4CCN(CC4)C)F)C(=O)O
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: Legionnaires' Disease Complicated with Rhabdomyolysis and Acute Kidney Injury in an AIDS Patient.
[Seegobin Karan,Maharaj Satish,Baldeo Cherisse,Downes Julio Perez,Reddy Pramod]Case Rep Infect Dis.2017;2017:8051096. doi: 10.1155/2017/8051096. Epub 2017 Oct 4. PMID: 29109879
2: ISMP Adverse Drug Reactions: Levofloxacin-Induced Neuroexcitation and Hallucinations; Statin-Induced Muscle Rupture; Mefloquine-Induced Rhabdomyolysis; Methimazole-Induced Cholestatic Hepatitis; Decitabine-Induced Hand and Foot Syndrome.
[Mancano Michael A]Hosp Pharm.2017 May;52(5):330-333. doi: 10.1177/0018578717715349. Epub 2017 May 1. PMID: 28804147
3: Levofloxacin-induced rhabdomyolysis: a case report.
[John Febin,Oluronbi Ruby,Pitchumoni C S]J Med Case Rep.2016 Aug 24;10(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-1004-6. PMID: 27557756
4: Acute rhabdomyolysis associated with coadministration of levofloxacin and simvastatin in a patient with normal renal function.
[Paparoupa Maria,Pietrzak Sebastian,Gillissen Adrian]Case Rep Med.2014;2014:562929. doi: 10.1155/2014/562929. Epub 2014 Jul 22. PMID: 25140181
5: [Young male with fever and muscle pain after a visit to the dentist].
[de la Guerra Acebal Carla,Moreno Rodrigo Ana,Manterola Martija José María,Madariaga Ordeñana Idoia]Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin.2014 Nov;32(9):612-3. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2014.02.021. Epub 2014 May 9. PMID: 24813927
6: Quantitative evaluation of initial symptoms as predictors to detect adverse drug reactions using Bayes' theory: expansion and evaluation of drug-adverse drug reaction-initial symptom combinations using adverse event reporting system database.
[Kobayashi Daisuke,Hosaka Shigeru,Inoue Emiko,Ohshima Kimie,Kutsuma Nobuaki,Oshima Shinji,Okuno Yasushi]Biol Pharm Bull.2013;36(12):1891-901. PMID: 24292049
7: Levofloxacin-induced rhabdomyolysis in a hemodialysis patient.
[Gupta Ankur,Guron Nita,Harris Michael,Bell Robert]Hemodial Int.2012 Jan;16(1):101-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-4758.2011.00592.x. PMID: 22098607
8: Levofloxacin and rhabdomyolysis in a renal transplant patient.
[Korzets Asher,Gafter Uzi,Dicker Dror,Herman Michal,Ori Yaacov]Nephrol Dial Transplant.2006 Nov;21(11):3304-5. Epub 2006 Sep 12. PMID: 16968728
9: Acute rhabdomyolysis associated with ofloxacin/levofloxacin therapy.
[Hsiao Shu-Hwa,Chang Chia-Ming,Tsao Chao-Jung,Lee Yu-Yun J,Hsu May-Ying,Wu Ta-Jen]Ann Pharmacother.2005 Jan;39(1):146-9. Epub 2004 Nov 23. PMID: 15562138
10: A case of rhabdomyolysis with fatal outcome after a treatment with levofloxacin.
[Petitjeans Fabrice,Nadaud Julien,Perez Jean Paul,Debien Bruno,Olive Frederic,Villevieille Thierry,Pats Bruno]Eur J Clin Pharmacol.2003 Dec;59(10):779-80. Epub 2003 Oct 24. PMID: 14576967
11: Toxic effects of quinolone antibacterial agents on the musculoskeletal system in juvenile rats.
[Kashida Y,Kato M]Toxicol Pathol.1997 Nov-Dec;25(6):635-43. PMID: 9437810
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.