Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
LOXAPINE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIR concern
Severity Score:4
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
- Antipsychotic drugs can cause a potentially fatal symptom complex termed Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS). Clinical manifestations of NMS include hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia). Associated features can include elevated serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) concentration, rhabdomyolysis, elevated serum and urine myoglobin concentration, and renal failure. NMS did not occur in the ADASUVE clinical program.
- The diagnostic evaluation of patients with this syndrome is complicated. It is important to consider the presence of other serious medical conditions (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, heat stroke, primary CNS pathology, central anticholinergic toxicity, extrapyramidal symptoms, or drug fever).
- The management of NMS should include: 1) immediate discontinuation of antipsychotic drugs and other drugs that may contribute to the underlying disorder, 2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring, and 3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for NMS.
- If a patient requires antipsychotic drug treatment after recovery from NMS, the potential reintroduction of drug therapy should be carefully considered. The patient should be carefully monitored, since recurrences of NMS have been reported.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
2
42910
Other ADRs
47
14117232
Odds Ratio = 14.0
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- N05AH01 - loxapine
- N05AH - "Diazepines, oxazepines and thiazepines"
- N05A - ANTIPSYCHOTICS
- N05 - PSYCHOLEPTICS
- N - NERVOUS SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:loxapine
Active Ingredient UNII:LER583670J
Drugbank ID:DB00408
PubChem Compound:3964
CAS Number:1977-10-2
Dosage Form(s):aerosol, powder
Route(s) Of Administrator:respiratory (inhalation)
Daily Dose:
- 100.0 mg/day N05AH01
Chemical Structure: 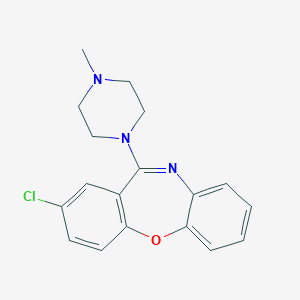

SMILE Code:
CN1CCN(CC1)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3OC4=C2C=C(C=C4)Cl
CN1CCN(CC1)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3OC4=C2C=C(C=C4)Cl
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: Rhabdomyolysis with Acute Renal Failure and Deep Vein Thrombosis Induced by Antipsychotic Drugs: A Case Report.
[Jullian-Desayes I,Roselli A,Lamy C,Alberto-Gondouin M C,Janvier N,Venturi-Maestri G]Pharmacopsychiatry.2015 Nov;48(7):265-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1564088. Epub 2015 Sep 23. PMID: 26398280
2: Marked elevations of serum creatine kinase activity associated with antipsychotic drug treatment.
[Meltzer H Y,Cola P A,Parsa M]Neuropsychopharmacology.1996 Oct;15(4):395-405. PMID: 8887994
3: Amoxapine overdose in a young man: a transient mitochondrial abnormality?
[Mancias P,Kramer L,Butler I J]Pharmacotherapy.1995 Jul-Aug;15(4):528-32. PMID: 7479209
4: Rhabdomyolysis complicating rapid intramuscular neuroleptization.
[Thase M E,Shostak M]J Clin Psychopharmacol.1984 Feb;4(1):46-8. PMID: 6141190
5: Seizures induced by acute loxapine overdose.
[Peterson C D]Am J Psychiatry.1981 Aug;138(8):1089-91. PMID: 7258388
6: Loxapine-associated rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure.
[Tam C W,Olin B R,Ruiz A E]Arch Intern Med.1980 Jul;140(7):975-6. PMID: 6770772
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.