Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
PRAVASTATIN SODIUM
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIR concern
Severity Score:4
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS
- Skeletal Muscle
- Rare cases of rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria have been reported with pravastatin and other drugs in this class. Uncomplicated myalgia has also been reported in pravastatin-treated patients (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). Myopathy, defined as muscle aching or muscle weakness in conjunction with increases in creatine phosphokinase (CPK) values to greater than 10 times the upper limit of normal, was rare (<0.1%) in pravastatin clinical trials. Myopathy should be considered in any patient with diffuse myalgias, muscle tenderness or weakness, and/or marked elevation of CPK. Patients should be advised to report promptly unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness, particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever. Pravastatin therapy should be discontinued if markedly elevated CPK levels occur or myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. Pravastatin therapy should also be temporarily withheld in any patient experiencing an acute or serious condition predisposing to the development of renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis, e.g., sepsis; hypotension; major surgery; trauma; severe metabolic, endocrine, or electrolyte disorders; or uncontrolled epilepsy.
- The risk of myopathy during treatment with another HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor is increased with concurrent therapy with either erythromycin, cyclosporine, niacin, or fibrates. However, neither myopathy nor significant increases in CPK levels have been observed in three reports involving a total of 100 post-transplant patients (24 renal and 76 cardiac) treated for up to two years concurrently with pravastatin 10-40 mg and cyclosporine. Some of these patients also received other concomitant immunosuppressive therapies. Further, in clinical trials involving small numbers of patients who were treated concurrently with pravastatin and niacin, there were no reports of myopathy. Also, myopathy was not reported in a trial of combination pravastatin (40 mg/day) and gemfibrozil (1200 mg/day), although 4 of 75 patients on the combination showed marked CPK elevations versus one of 73 patients receiving placebo. There was a trend toward more frequent CPK elevations and patient withdrawals due to musculoskeletal symptoms in the group receiving combined treatment as compared with the groups receiving placebo, gemfibrozil, or pravastatin monotherapy (see PRECAUTIONS: DRUG INTERACTIONS). The use of fibrates alone may occasionally be associated with myopathy. The combined use of pravastatin and fibrates should be avoided unless the benefit of further alterations in lipid levels is likely to outweigh the increased risk of this drug combination.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Postmarketing Experience
- In addition to the events reported above, as with other drugs in this class, the following events have been reported rarely during postmarketing experience with Pravastatin Sodium Tablets, regardless of causality assessment:
- Musculoskeletal: myopathy, rhabdomyolysis.
- Nervous System: dysfunction of certain cranial nerves (including alteration of taste, impairment of extraocular movement, facial paresis), peripheral nerve palsy.
- Hypersensitivity: anaphylaxis, angioedema, lupus erythematosus-like syndrome, polymyalgia rheumatica, dermatomyositis, vasculitis, purpura, hemolytic anemia, positive ANA, ESR increase, arthritis, arthralgia, asthenia, photosensitivity, chills, malaise, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- Gastrointestinal: pancreatitis, hepatitis, including chronic active hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice, fatty change in liver, cirrhosis, fulminant hepatic necrosis, hepatoma.
- Dermatologic: a variety of skin changes (e.g., nodules, discoloration, dryness of mucous membranes, changes to hair/nails).
- Reproductive: gynecomastia.
- Laboratory Abnormalities: Liver Function Test abnormalities, thyroid function abnormalities.
- Concomitant Therapy
- Pravastatin has been administered concurrently with cholestyramine, colestipol, nicotinic acid, probucol and gemfibrozil. Preliminary data suggest that the addition of either probucol or gemfibrozil to therapy with lovastatin or pravastatin is not associated with greater reduction in LDL-cholesterol than that achieved with lovastatin or pravastatin alone. No adverse reactions unique to the combination or in addition to those previously reported for each drug alone have been reported. Myopathy and rhabdomyolysis (with or without acute renal failure) have been reported when another HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor was used in combination with immunosuppressive drugs, gemfibrozil, erythromycin, or lipid-lowering doses of nicotinic acid. Concomitant therapy with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and these agents is generally not recommended. (See WARNINGS: SKELETAL MUSCLE and PRECAUTIONS: DRUG INTERACTIONS.)
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
440
42472
Other ADRs
7590
14109689
Odds Ratio = 19.259
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- C10AA03 - pravastatin sodium
- C10AA - HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
- C10A - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, PLAIN"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- C10BX02 - pravastatin sodium
- C10BX - "HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, other combinations"
- C10B - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- C10BA03 - pravastatin sodium
- C10BA - HMG CoA reductase inhibitors in combination with other lipid modifying agents
- C10B - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:pravastatin sodium
Active Ingredient UNII:3M8608UQ61
Drugbank ID:DB00175
PubChem Compound:54687
CAS Number:81093-37-0
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 30.0 mg/day C10AA03
Chemical Structure: 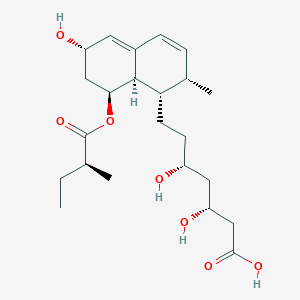

SMILE Code:
CC[C@H](C)C(=O)O[C@H]1C[C@@H](C=C2[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](C=C2)C)CC[C@H](C[C@H](CC(=O)O)O)O)O
CC[C@H](C)C(=O)O[C@H]1C[C@@H](C=C2[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](C=C2)C)CC[C@H](C[C@H](CC(=O)O)O)O)O
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
N/ADisclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.