Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
EZETIMIBE
DIR Classification
Classification:Less-DIR concern
Severity Score:1
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis
- In clinical trials, there was no excess of myopathy or rhabdomyolysis associated with ZETIA compared with the relevant control arm (placebo or statin alone). However, myopathy and rhabdomyolysis are known adverse reactions to statins and other lipid-lowering drugs. In clinical trials, the incidence of creatine phosphokinase (CPK) >10 × ULN was 0.2% for ZETIA vs. 0.1% for placebo, and 0.1% for ZETIA coadministered with a statin vs. 0.4% for statins alone. Risk for skeletal muscle toxicity increases with higher doses of statin, advanced age (>65), hypothyroidism, renal impairment, and depending on the statin used, concomitant use of other drugs.
- In post-marketing experience with ZETIA, cases of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis have been reported. Most patients who developed rhabdomyolysis were taking a statin prior to initiating ZETIA. However, rhabdomyolysis has been reported with ZETIA monotherapy and with the addition of ZETIA to agents known to be associated with increased risk of rhabdomyolysis, such as fibrates. ZETIA and any statin or fibrate that the patient is taking concomitantly should be immediately discontinued if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. The presence of muscle symptoms and a CPK level >10 × the ULN indicates myopathy.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- - Liver enzyme abnormalities [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)]
- - Rhabdomyolysis and myopathy [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.3)]
- Post-Marketing Experience
- Because the reactions below are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ZETIA:
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and urticaria; erythema multiforme; arthralgia; myalgia; elevated creatine phosphokinase; myopathy/rhabdomyolysis [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.3)]; elevations in liver transaminases; hepatitis; abdominal pain; thrombocytopenia; pancreatitis; nausea; dizziness; paresthesia; depression; headache; cholelithiasis; cholecystitis.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
420
42492
Other ADRs
11578
14105701
Odds Ratio = 12.043
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- C10BA02 - ezetimibe
- C10BA - HMG CoA reductase inhibitors in combination with other lipid modifying agents
- C10B - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- C10BA05 - ezetimibe
- C10BA - HMG CoA reductase inhibitors in combination with other lipid modifying agents
- C10B - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- C10BA06 - ezetimibe
- C10BA - HMG CoA reductase inhibitors in combination with other lipid modifying agents
- C10B - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- C10AX09 - ezetimibe
- C10AX - Other lipid modifying agents
- C10A - "LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, PLAIN"
- C10 - LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:ezetimibe
Active Ingredient UNII:EOR26LQQ24
Drugbank ID:DB00973
PubChem Compound:150311
CAS Number:163222-33-1
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 10.0 mg/day C10AX09
Chemical Structure: 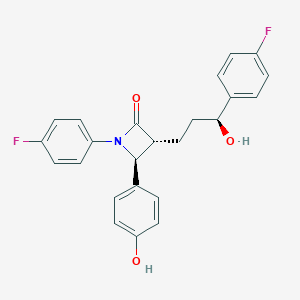

SMILE Code:
C1=CC(=CC=C1[C@@H]2[C@H](C(=O)N2C3=CC=C(C=C3)F)CC[C@@H](C4=CC=C(C=C4)F)O)O
C1=CC(=CC=C1[C@@H]2[C@H](C(=O)N2C3=CC=C(C=C3)F)CC[C@@H](C4=CC=C(C=C4)F)O)O
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: Statin Intolerance and Risk of Coronary Heart Events and All-Cause Mortality Following Myocardial Infarction.
[Serban Maria-Corina,Colantonio Lisandro D,Manthripragada Angelika D,Monda Keri L,Bittner Vera A,Banach Maciej,Chen Ligong,Huang Lei,Dent Ricardo,Kent Shia T,Muntner Paul,Rosenson Robert S]J Am Coll Cardiol.2017 Mar 21;69(11):1386-1395. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.12.036. PMID: 28302290
2: Colchicine triggered severe rhabdomyolysis after long-term low-dose simvastatin therapy: a case report.
[Frydrychowicz Clara,Pasieka Bastian,Pierer Matthias,Mueller Wolf,Petros Sirak,Weidhase Lorenz]J Med Case Rep.2017 Jan 4;11(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-1169-z. PMID: 28049514
3: Algorithms to Identify Statin Intolerance in Medicare Administrative Claim Data.
[Colantonio Lisandro D,Kent Shia T,Huang Lei,Chen Ligong,Monda Keri L,Serban Maria-Corina,Manthripragada Angelika,Kilgore Meredith L,Rosenson Robert S,Muntner Paul]Cardiovasc Drugs Ther.2016 Oct;30(5):525-533. PMID: 27389413
4: Efficacy and Tolerability of Evolocumab vs Ezetimibe in Patients With Muscle-Related Statin Intolerance: The GAUSS-3 Randomized Clinical Trial.
[Nissen Steven E,Stroes Erik,Dent-Acosta Ricardo E,Rosenson Robert S,Lehman Sam J,Sattar Naveed,Preiss David,Bruckert Eric,Ceška Richard,Lepor Norman,Ballantyne Christie M,Gouni-Berthold Ioanna,Elliott Mary,Brennan Danielle M,Wasserman Scott M,Somaratne Ransi,Scott Rob,Stein Evan A,GAUSS-3 Investigators]JAMA.2016 Apr 19;315(15):1580-90. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.3608. PMID: 27039291
5: Statin-related myotoxicity.
[Fernandes Vera,Santos Maria Joana,Pérez Antonio]Endocrinol Nutr.2016 May;63(5):239-49. doi: 10.1016/j.endonu.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Mar 19. PMID: 27005745
6: Statin intolerance.
[Laufs Ulrich,Scharnagl Hubert,März Winfried]Curr Opin Lipidol.2015 Dec;26(6):492-501. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000236. PMID: 26780003
7: Risk identification and possible countermeasures for muscle adverse effects during statin therapy.
[Magni Paolo,Macchi Chiara,Morlotti Beatrice,Sirtori Cesare R,Ruscica Massimiliano]Eur J Intern Med.2015 Mar;26(2):82-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 29. PMID: 25640999
8: Design and rationale of the GAUSS-2 study trial: a double-blind, ezetimibe-controlled phase 3 study of the efficacy and tolerability of evolocumab (AMG 145) in subjects with hypercholesterolemia who are intolerant of statin therapy.
[Cho Leslie,Rocco Michael,Colquhoun David,Sullivan David,Rosenson Robert S,Dent Ricardo,Xue Allen,Scott Rob,Wasserman Scott M,Stroes Erik]Clin Cardiol.2014 Mar;37(3):131-9. doi: 10.1002/clc.22248. Epub 2014 Jan 29. PMID: 24477778
9: Lipid-lowering agents for nephrotic syndrome.
[Kong Xiangyu,Yuan Hao,Fan Junming,Li Zi,Wu Taixiang,Jiang Lanhui]Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2013 Dec 10;(12):CD005425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005425.pub2. PMID: 24327265
10: Comparative efficacy and adverse effects of the addition of ezetimibe to statin versus statin titration in chronic kidney disease patients.
[Suzuki Hiromichi,Watanabe Yusuke,Kumagai Hiroo,Shuto Hiroshi]Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis.2013 Dec;7(6):306-15. doi: 10.1177/1753944713513222. Epub 2013 Nov 26. PMID: 24280596
11: Treatment of dyslipidemia in chronic kidney disease: Effectiveness and safety of statins.
[Scarpioni Roberto,Ricardi Marco,Albertazzi Vittorio,Melfa Luigi]World J Nephrol.2012 Dec 6;1(6):184-94. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v1.i6.184. PMID: 24175258
12: HPS2-THRIVE randomized placebo-controlled trial in 25 673 high-risk patients of ER niacin/laropiprant: trial design, pre-specified muscle and liver outcomes, and reasons for stopping study treatment.
[HPS2-THRIVE Collaborative Group]Eur Heart J.2013 May;34(17):1279-91. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht055. Epub 2013 Feb 26. PMID: 23444397
13: Risk of hospitalized rhabdomyolysis associated with lipid-lowering drugs in a real-world clinical setting.
[Cziraky Mark J,Willey Vincent J,McKenney James M,Kamat Siddhesh A,Fisher Maxine D,Guyton John R,Jacobson Terry A,Davidson Michael H]J Clin Lipidol.2013 Mar-Apr;7(2):102-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2012.06.006. Epub 2012 Jul 3. PMID: 23415428
14: Retrospective study on antihyperlipidemic efficacy and safety of simvastatin, ezetimibe and their combination in Korean adults.
[Lee Young-Hee,Kim Mi-Jeong,Choi Chang-Ik,Bae Jung-Woo,Jang Choon-Gon,Lee Seok-Yong]Arch Pharm Res.2011 Aug;34(8):1331-7. doi: 10.1007/s12272-011-0813-9. Epub 2011 Sep 11. PMID: 21910055
15: Managing the underestimated risk of statin-associated myopathy.
[Rallidis Loukianos S,Fountoulaki Katerina,Anastasiou-Nana Maria]Int J Cardiol.2012 Sep 6;159(3):169-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.07.048. Epub 2011 Aug 2. PMID: 21813193
16: Statin myopathy: significant problem with minimal awareness by clinicians and no emphasis by clinical investigators.
[Whayne Thomas F]Angiology.2011 Jul;62(5):415-21. doi: 10.1177/0003319710395560. Epub 2011 Mar 18. PMID: 21421631
17: Ezetimibe is effective in the treatment of persistent hyperlipidemia of renal allograft recipients.
[Savvidaki E,Koukoulaki M,Benou A,Roumeliotou M,Fourtounas C,Kalliakmani P,Papachristou E,Vlachojannis J G,Goumenos D]Clin Nephrol.2011 Feb;75(2):107-12. PMID: 21255539
18: Ezetimibe and reactive oxygen species.
[Yamaoka-Tojo Minako,Tojo Taiki,Takahira Naonobu,Masuda Takashi,Izumi Tohru]Curr Vasc Pharmacol.2011 Jan;9(1):109-20. PMID: 21044015
19: [Statins and muscular side-effects].
[Brosteaux Christine,Ruiz Juan,Buclin Thierry,Kuntzer Thierry,Rodondi Nicolas]Rev Med Suisse.2010 Mar 10;6(239):510, 512-4, 516-7. PMID: 20373698
20: Rosuvastatin-associated adverse effects and drug-drug interactions in the clinical setting of dyslipidemia.
[Kostapanos Michael S,Milionis Haralampos J,Elisaf Moses S]Am J Cardiovasc Drugs.2010;10(1):11-28. doi: 10.2165/13168600-000000000-00000. PMID: 20104931
21: Effects of ezetimibe add-on therapy for high-risk patients with dyslipidemia.
[Yamaoka-Tojo Minako,Tojo Taiki,Kosugi Rie,Hatakeyama Yuko,Yoshida Yuki,Machida Yoji,Aoyama Naoyoshi,Masuda Takashi,Izumi Tohru]Lipids Health Dis.2009 Oct 12;8:41. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-8-41. PMID: 19821987
22: Narrative review: statin-related myopathy.
[Joy Tisha R,Hegele Robert A]Ann Intern Med.2009 Jun 16;150(12):858-68. PMID: 19528564
23: Renal failure and rhabdomyolysis associated with sitagliptin and simvastatin use.
[Kao D P,Kohrt H E,Kugler J]Diabet Med.2008 Oct;25(10):1229-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02536.x. PMID: 19046202
24: The efficacy and safety of ezetimibe for treatment of dyslipidemia after heart transplantation.
[Crespo-Leiro M G,Paniagua M J,Marzoa R,Grille Z,Naya C,Flores X,Rodriguez J A,Mosquera V,Franco R,Castro-Beiras A]Transplant Proc.2008 Nov;40(9):3060-2. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2008.09.007. PMID: 19010194
25: Safety and efficacy of ezetimibe in a sample of cardiac transplant patients.
[Guisado Rasco A,Lage Gallé E,Sobrino Márquez J M,Sánchez Brotons J A,Mogollón Jiménez M V,Borrego Domínguez J M,Martínez Martínez A]Transplant Proc.2008 Nov;40(9):3058-9. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2008.09.048. PMID: 19010193
26: Long-term (48-week) safety of ezetimibe 10 mg/day coadministered with simvastatin compared to simvastatin alone in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia.
[Bays Harold,Sapre Aditi,Taggart William,Liu Ji,Capece Rachel,Tershakovec Andrew]Curr Med Res Opin.2008 Oct;24(10):2953-66. doi: 10.1185/03007990802365094 . Epub 2008 Sep 8. PMID: 18782465
27: Rhabdomyolysis and pancreatitis associated with coadministration of danazol 600 mg/d and lovastatin 40 mg/d.
[Hsieh Cheng-Yang,Chen Chih-Hung]Clin Ther.2008 Jul;30(7):1330-5. PMID: 18691993
28: Combination drug products: an indication for medication reconciliation and pharmacist counseling.
[Stroup Jeffrey,Stephens Johnny]J Am Pharm Assoc (2003).2008 Jul-Aug;48(4):541-3. doi: 10.1331/JAPhA.2008.07058. PMID: 18653432
29: Rhabdomyolysis resulting from pharmacologic interaction between erlotinib and simvastatin.
[Veeraputhiran Muthu,Sundermeyer Mark]Clin Lung Cancer.2008 Jul;9(4):232-4. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2008.n.036. PMID: 18650173
30: Toward "pain-free" statin prescribing: clinical algorithm for diagnosis and management of myalgia.
[Jacobson Terry A]Mayo Clin Proc.2008 Jun;83(6):687-700. doi: 10.4065/83.6.687. PMID: 18533086
31: Rhabdomyolysis after ezetimibe/simvastatin therapy in an HIV-infected patient.
[Chanson Noemie,Bossi Philippe,Schneider Luminita,Bourry Edward,Izzedine Hassane]NDT Plus.2008 Jun;1(3):157-61. doi: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfn012. PMID: 25983864
32: Review of side-effect profile of combination ezetimibe and statin therapy in randomized clinical trials.
[Kashani Amir,Sallam Tamer,Bheemreddy Swarna,Mann Douglas L,Wang Yun,Foody JoAnne M]Am J Cardiol.2008 Jun 1;101(11):1606-13. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.01.041. Epub 2008 Apr 9. PMID: 18489938
33: Ezetimibe-associated adverse effects: what the clinician needs to know.
[Florentin M,Liberopoulos E N,Elisaf M S]Int J Clin Pract.2008 Jan;62(1):88-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01592.x. PMID: 18173814
34: [Type 1 diabetes: what are the alternatives for lowering cholesterol levels with statins?].
[Krone W,Berthold J]Dtsch Med Wochenschr.2007 Nov;132(44):2344. PMID: 17957603
35: [Rhabdomyolysis associated to combined ezetimibe-statin treatment].
[Piedra León M,García Unzueta M T,Otero Martínez M,Amado Señaris J A]Rev Clin Esp.2007 Sep;207(8):425-6. PMID: 17688879
36: Safety of aggressive lipid management.
[Davidson Michael H,Robinson Jennifer G]J Am Coll Cardiol.2007 May 1;49(17):1753-62. Epub 2007 Apr 16. PMID: 17466224
37: Safety considerations with gastrointestinally active lipid-lowering drugs.
[Jacobson Terry A,Armani Annemarie,McKenney James M,Guyton John R]Am J Cardiol.2007 Mar 19;99(6A):47C-55C. Epub 2006 Nov 29. PMID: 17368279
38: Myopathy associated with atorvastatin-ezetimibe combination therapy.
[Weffald Linda A,Flach Lynn A]Pharmacotherapy.2007 Feb;27(2):309-11. PMID: 17253923
39: Fenofibrate: a review of its use in primary dyslipidaemia, the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
[Keating Gillian M,Croom Katherine F]Drugs.2007;67(1):121-53. PMID: 17209672
40: Rhabdomyolysis associated with pomegranate juice consumption.
[Sorokin Alexey V,Duncan Brett,Panetta Randolph,Thompson Paul D]Am J Cardiol.2006 Sep 1;98(5):705-6. Epub 2006 Jul 14. PMID: 16923466
41: Pharmacologic options for aggressive low-density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering: benefits versus risks.
[McKenney James M]Am J Cardiol.2005 Aug 22;96(4A):60E-66E. PMID: 16098846
42: [Selective cholesterol absorption inhibition as a new prospect in treatment of hypercholesterolemia].
[Lima Joan,Fonollosa Vicent,Chacón Pilar]Med Clin (Barc).2005 Jun 4;125(1):16-23. PMID: 15960941
43: [Innovation instead of imitation -- news in drug therapy -- regarding the contribution in DMW 13/2005].
[Thesen R]Dtsch Med Wochenschr.2005 May 20;130(20):1280. PMID: 15889335
44: Simvastatin plus ezetimibe: combination therapy for the management of dyslipidaemia.
[Toth Peter P,Davidson Michael H]Expert Opin Pharmacother.2005 Jan;6(1):131-9. PMID: 15709890
45: [Ezetimibe (Ezetrol): the statins' partner].
[Ducobu J,Sternon J]Rev Med Brux.2004 Oct;25(5):456-61. PMID: 15584647
46: Simvastatin: a review.
[Pedersen Terje R,Tobert Jonathan A]Expert Opin Pharmacother.2004 Dec;5(12):2583-96. PMID: 15571475
47: Long-term safety and tolerability profile of ezetimibe and atorvastatin coadministration therapy in patients with primary hypercholesterolaemia.
[Ballantyne C M,Lipka L J,Sager P T,Strony J,Alizadeh J,Suresh R,Veltri E P]Int J Clin Pract.2004 Jul;58(7):653-8. PMID: 15311720
48: Hypolipidemic therapy and cholesterol absorption.
[Manhas Amit,Farmer John A]Curr Atheroscler Rep.2004 Mar;6(2):89-93. PMID: 15023291
49: [The best of 2001. Clinical pharmacology].
[Ambrosi P,Gayet J L,Andréjak M]Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss.2002 Jan;95 Spec No 1(5 Spec 1):33-8. PMID: 11901897
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.