Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
AMOXAPINE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIR concern
Severity Score:4
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- OVERDOSAGE
- Signs and Symptoms
- Toxic manifestations of amoxapine overdosage differ significantly from those of other tricyclic antidepressants. Serious cardiovascular effects are seldom if ever observed. However, CNS effects - particularly grand mal convulsions - occur frequently, and treatment should be directed primarily toward prevention or control of seizures. Status epilepticus may develop and constitutes a neurologic emergency. Coma and acidosis are other serious complications of substantial amoxapine overdosage in some cases. Fatal overdoses with amoxapine have occurred.
- Renal failure may develop two to five days after toxic overdosage in patients who may appear otherwise recovered. Acute tubular necrosis with rhabdomyolysis and myoglobinuria is the most common renal complication in such cases. This reaction probably occurs in less than 5% of overdose cases, and typically in those who have experienced multiple seizures.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
9
42903
Other ADRs
116
14117163
Odds Ratio = 25.53
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- N06AA17 - amoxapine
- N06AA - Non-selective monoamine reuptake inhibitors
- N06A - ANTIDEPRESSANTS
- N06 - PSYCHOANALEPTICS
- N - NERVOUS SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:amoxapine
Active Ingredient UNII:R63VQ857OT
Drugbank ID:DB00543
PubChem Compound:2170
CAS Number:14028-44-5
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 150.0 mg/day N06AA17
Chemical Structure: 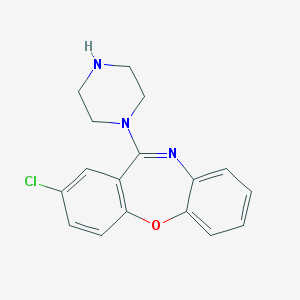

SMILE Code:
C1CN(CCN1)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3OC4=C2C=C(C=C4)Cl
C1CN(CCN1)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3OC4=C2C=C(C=C4)Cl
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: Successful treatment of rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure following amoxapine overdose.
[Shigemura Tatsuro Kuwahara Soichiro Nomura Akimitsu Yokoyama Hideki Uemura J]Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract.2001;5(4):287-90. doi: 10.1080/13651500152733071. PMID: 24921698
2: Amoxapine overdose in a young man: a transient mitochondrial abnormality?
[Mancias P,Kramer L,Butler I J]Pharmacotherapy.1995 Jul-Aug;15(4):528-32. PMID: 7479209
3: [Acute amoxapine poisoning with rhabdomyolysis and acute renal insufficiency].
[Saviuc P,Danel V,Waldner D,Claustre A]J Toxicol Clin Exp.1992 Dec;12(8):487-9. PMID: 1308897
4: Acute renal failure secondary to non-traumatic rhabdomyolysis following amoxapine overdose.
[Frendin T J,Swainson C P]N Z Med J.1985 Aug 28;98(785):690-1. PMID: 3863031
5: Amoxapine-associated acute renal failure.
[Jennings A E,Levey A S,Harrington J T]Arch Intern Med.1983 Aug;143(8):1525-7. PMID: 6870433
6: Amoxapine-associated rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure: case report.
[Abero K,Shelp W D,Kosseff A,Thomas S]J Clin Psychiatry.1982 Oct;43(10):426-7. PMID: 7118837
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.