Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
TOLCAPONE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIR concern
Severity Score:4
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- BOXED WARNING
- Because of the risk of potentially fatal, acute fulminant liver failure, TASMAR (tolcapone) should ordinarily be used in patients with Parkinson's disease on l-dopa/carbidopa who are experiencing symptom fluctuations and are not responding satisfactorily to or are not appropriate candidates for other adjunctive therapies (see INDICATIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION sections).
- Because of the risk of liver injury and because TASMAR, when it is effective, provides an observable symptomatic benefit, the patient who fails to show substantial clinical benefit within 3 weeks of initiation of treatment, should be withdrawn from TASMAR.
- TASMAR therapy should not be initiated if the patient exhibits clinical evidence of liver disease or two SGPT/ALT or SGOT/AST values greater than the upper limit of normal. Patients with severe dyskinesia or dystonia should be treated with caution (see PRECAUTIONS: RHABDOMYOLYSIS).
- PATIENTS WHO DEVELOP EVIDENCE OF HEPATOCELLULAR INJURY WHILE ON TASMAR AND ARE WITHDRAWN FROM THE DRUG FOR ANY REASON MAY BE AT INCREASED RISK FOR LIVER INJURY IF TASMAR IS REINTRODUCED. ACCORDINGLY, SUCH PATIENTS SHOULD NOT ORDINARILY BE CONSIDERED FOR RETREATMENT.
- Cases of severe hepatocellular injury, including fulminant liver failure resulting in death, have been reported in postmarketing use. As of May 2005, 3 cases of fatal fulminant hepatic failure have been reported from more than 40,000 patient years of worldwide use. This incidence may be 10- to 100-fold higher than the background incidence in the general population. Underreporting of cases may lead to significant underestimation of the increased risk associated with the use of TASMAR. All 3 cases were reported within the first six months of initiation of treatment with TASMAR. Analysis of the laboratory monitoring data in over 3,400 TASMAR-treated patients participating in clinical trials indicated that increases in SGPT/ALT or SGOT/AST, when present, generally occurred within the first 6 months of treatment with TASMAR.
- A prescriber who elects to use TASMAR in face of the increased risk of liver injury is strongly advised to monitor patients for evidence of emergent liver injury. Patients should be advised of the need for self-monitoring for both the classical signs of liver disease (e.g., clay colored stools, jaundice) and the nonspecific ones (e.g., fatigue, loss of appetite, lethargy).
- Although a program of periodic laboratory monitoring for evidence of hepatocellular injury is recommended, it is not clear that periodic monitoring of liver enzymes will prevent the occurrence of fulminant liver failure. However, it is generally believed that early detection of drug-induced hepatic injury along with immediate withdrawal of the suspect drug enhances the likelihood for recovery. Accordingly, the following liver monitoring program is recommended.
- Before starting treatment with TASMAR, the physician should conduct appropriate tests to exclude the presence of liver disease. In patients determined to be appropriate candidates for treatment with TASMAR, serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT/ALT) and serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT/AST) levels should be determined at baseline and periodically (i.e., every 2 to 4 weeks) for the first 6 months of therapy. After the first six months, periodic monitoring is recommended at intervals deemed clinically relevant. Although more frequent monitoring increases the chances of early detection, the precise schedule for monitoring is a matter of clinical judgment. If the dose is increased to 200 mg tid (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section), liver enzyme monitoring should take place before increasing the dose and then be conducted every 2 to 4 weeks for the following 6 months of therapy. After six months, periodic monitoring is recommended at intervals deemed clinically relevant.
- TASMAR should be discontinued if SGPT/ALT or SGOT/AST levels exceed 2 times the upper limit of normal or if clinical signs and symptoms suggest the onset of hepatic dysfunction (persistent nausea, fatigue, lethargy, anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, pruritus, and right upper quadrant tenderness).
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- TASMAR tablets are contraindicated in patients with liver disease, in patients who were withdrawn from TASMAR because of evidence of TASMAR-induced hepatocellular injury or who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients.
- TASMAR is also contraindicated in patients with a history of nontraumatic rhabdomyolysis or hyperpyrexia and confusion possibly related to medication (see PRECAUTIONS: EVENTS REPORTED WITH DOPAMINERGIC THERAPY).
- WARNINGS
- (see BOXED WARNING) Because of the risk of potentially fatal, acute fulminant liver failure, TASMAR (tolcapone) should ordinarily be used in patients with Parkinson's disease on l-dopa/carbidopa who are experiencing symptom fluctuations and are not responding satisfactorily to or are not appropriate candidates for other adjunctive therapies (see INDICATIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION sections).
- Because of the risk of liver injury and because TASMAR, when it is effective, provides an observable symptomatic benefit, the patient who fails to show substantial clinical benefit within 3 weeks of initiation of treatment, should be withdrawn from TASMAR.
- TASMAR therapy should not be initiated if the patient exhibits clinical evidence of liver disease or two SGPT/ALT or SGOT/AST values greater than the upper limit of normal. Patients with severe dyskinesia or dystonia should be treated with caution (see PRECAUTIONS: RHABDOMYOLYSIS).
- PRECAUTIONS
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Cases of severe rhabdomyolysis, with one case of multi-organ system failure rapidly progressing to death, have been reported. The complicated nature of these cases makes it impossible to determine what role, if any, TASMAR played in their pathogenesis. Severe prolonged motor activity including dyskinesia may account for rhabdomyolysis. Some cases, however, included fever, alteration of consciousness and muscular rigidity. It is possible, therefore, that the rhabdomyolysis may be a result of the syndrome described in Hyperpyrexia and Confusion (see PRECAUTIONS: EVENTS REPORTED WITH DOPAMINERGIC THERAPY).
- SPECIAL POPULATIONS
- TASMAR therapy should not be initiated if the patient exhibits clinical evidence of active liver disease or two SGPT/ALT or SGOT/AST values greater than the upper limit of normal. Patients with severe dyskinesia or dystonia should be treated with caution (see PRECAUTIONS: RHABDOMYOLYSIS). Patients with severe renal impairment should be treated with caution (see INDICATIONS, DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, BOXED WARNING and WARNINGS).
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Because of the risk of potentially fatal, acute fulminant liver failure, TASMAR (tolcapone) should ordinarily be used in patients with Parkinson's disease on l-dopa/carbidopa who are experiencing symptom fluctuations and are not responding satisfactorily to or are not appropriate candidates for other adjunctive therapies (see INDICATIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION sections).
- BECAUSE OF THE RISK OF LIVER INJURY AND BECAUSE TASMAR WHEN IT IS EFFECTIVE PROVIDES AN OBSERVABLE SYMPTOMATIC BENEFIT, THE PATIENT WHO FAILS TO SHOW SUBSTANTIAL CLINICAL BENEFIT WITHIN 3 WEEKS OF INITIATION OF TREATMENT, SHOULD BE WITHDRAWN FROM TASMAR.
- TASMAR therapy should not be initiated if the patient exhibits clinical evidence of liver disease or two SGPT/ALT or SGOT/AST values greater than the upper limit of normal. Patients with severe dyskinesia or dystonia should be treated with caution (see PRECAUTIONS: RHABDOMYOLYSIS).
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
27
42885
Other ADRs
1033
14116246
Odds Ratio = 8.604
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- N04BX01 - tolcapone
- N04BX - Other dopaminergic agents
- N04B - DOPAMINERGIC AGENTS
- N04 - ANTI-PARKINSON DRUGS
- N - NERVOUS SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:tolcapone
Active Ingredient UNII:CIF6334OLY
Drugbank ID:DB00323
PubChem Compound:4659569
CAS Number:134308-13-7
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 450.0 mg/day N04BX01
Chemical Structure: 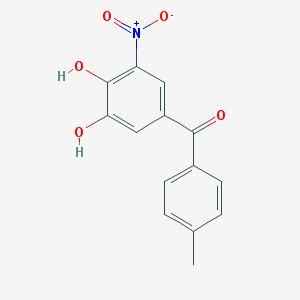

SMILE Code:
CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)C2=CC(=C(C(=C2)O)O)[N+](=O)[O-]
CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)C2=CC(=C(C(=C2)O)O)[N+](=O)[O-]
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: Clinical pharmacology, therapeutic use and potential of COMT inhibitors in Parkinson's disease.
[Kaakkola S]Drugs.2000 Jun;59(6):1233-50. PMID: 10882160
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.