Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
AMINOPHYLLINE
DIR Classification
Classification:Less-DIR concern
Severity Score:1
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
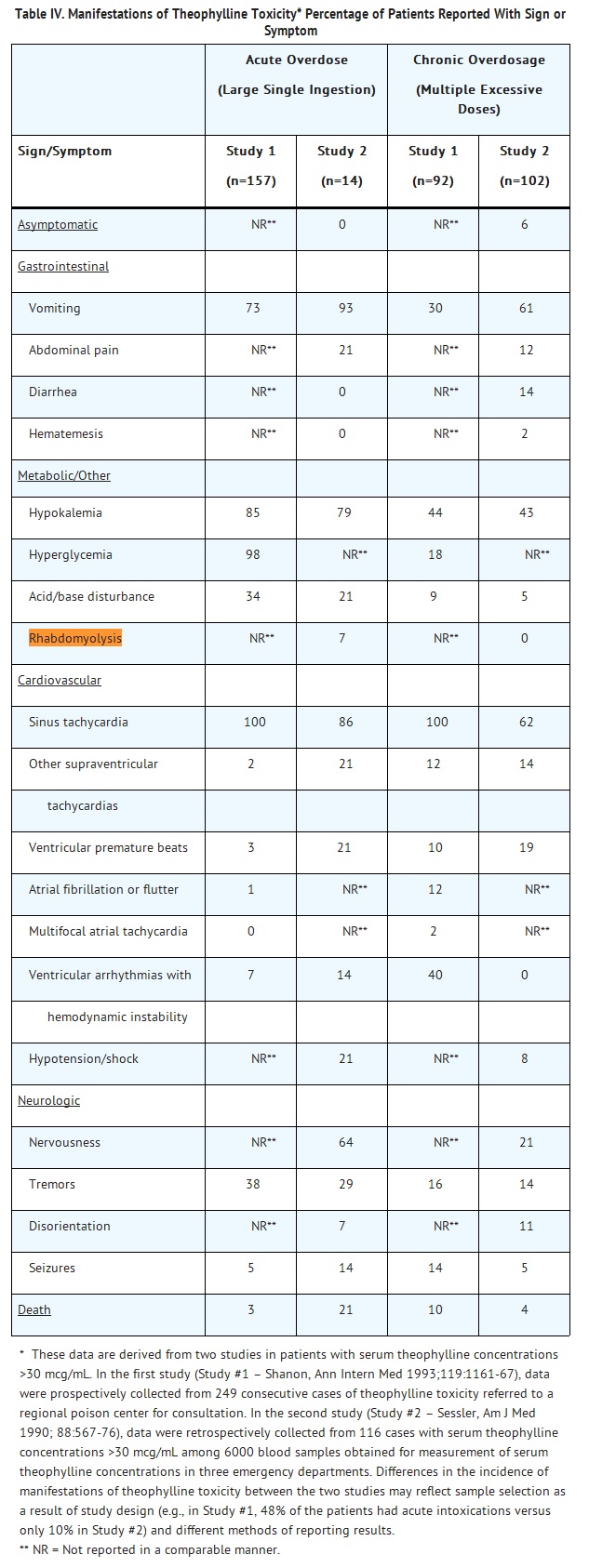
- Adverse reactions associated with theophylline are generally mild when peak serum theophylline concentrations are <20 mcg/mL and mainly consist of transient caffeine-like adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, headache, and insomnia. When peak serum theophylline concentrations exceed 20 mcg/mL, however, theophylline produces a wide range of adverse reactions including persistent vomiting, cardiac arrhythmias, and intractable seizures which can be lethal (see OVERDOSAGE).
- Other adverse reactions that have been reported at serum theophylline concentrations <20 mcg/mL include diarrhea, irritability, restlessness, fine skeletal muscle tremors, and transient diuresis. In patients with hypoxia secondary to COPD, multifocal atrial tachycardia and flutter have been reported at serum theophylline concentrations ≥15 mcg/mL. There have been a few isolated reports of seizures at serum theophylline concentrations <20 mcg/mL in patients with an underlying neurological disease or in elderly patients. The occurrence of seizures in elderly patients with serum theophylline concentrations <20 mcg/mL may be secondary to decreased protein binding resulting in a larger proportion of the total serum theophylline concentration in the pharmacologically active unbound form. The clinical characteristics of the seizures reported in patients with serum theophylline concentrations <20 mcg/mL have generally been milder than seizures associated with excessive serum theophylline concentrations resulting from an overdose (i.e., they have generally been transient, often stopped without anticonvulsant therapy, and did not result in neurological residua).
- Products containing aminophylline may rarely produce severe allergic reactions of the skin, including exfoliative dermatitis, after systemic administration in a patient who has been previously sensitized by topical application of a substance containing ethylenediamine. In such patients skin patch tests are positive for ethylenediamine, a component of aminophylline, and negative for theophylline. Pharmacists and other individuals who experience repeated skin exposure while physically handling aminophylline may develop a contact dermatitis due to the ethylenediamine component.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
0
42912
Other ADRs
130
14117149
Odds Ratio = N/A
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- R03DA55 - aminophylline
- R03DA - Xanthines
- R03D - OTHER SYSTEMIC DRUGS FOR OBSTRUCTIVE AIRWAY DISEASES
- R03 - DRUGS FOR OBSTRUCTIVE AIRWAY DISEASES
- R - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
- R03DB05 - aminophylline
- R03DB - Xanthines and adrenergics
- R03D - OTHER SYSTEMIC DRUGS FOR OBSTRUCTIVE AIRWAY DISEASES
- R03 - DRUGS FOR OBSTRUCTIVE AIRWAY DISEASES
- R - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
- R03DA05 - aminophylline
- R03DA - Xanthines
- R03D - OTHER SYSTEMIC DRUGS FOR OBSTRUCTIVE AIRWAY DISEASES
- R03 - DRUGS FOR OBSTRUCTIVE AIRWAY DISEASES
- R - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:aminophylline
Active Ingredient UNII:27Y3KJK423
Drugbank ID:DB01223
PubChem Compound:9433
CAS Number:317-34-0
Dosage Form(s):injection, solution
Route(s) Of Administrator:intravenous
Daily Dose:
- 600.0 mg/day R03DA05
Chemical Structure: 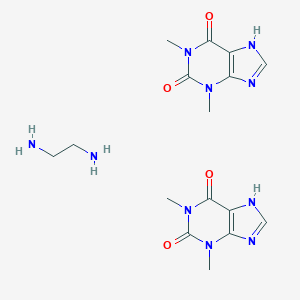

SMILE Code:
CN1C2=C(C(=O)N(C1=O)C)NC=N2.CN1C2=C(C(=O)N(C1=O)C)NC=N2.C(CN)N
CN1C2=C(C(=O)N(C1=O)C)NC=N2.CN1C2=C(C(=O)N(C1=O)C)NC=N2.C(CN)N
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: Rhabdomyolysis following status asthmaticus.
[Bando T,Fujimura M,Noda Y,Ohta G,Matsuda T]Respiration.1996;63(5):309-11. PMID: 8885005
2: Rhabdomyolysis following life-threatening acute asthma attack.
[Visetti E,Costa P]Anaesthesia.1993 Oct;48(10):887-8. PMID: 8238832
3: [A case of theophylline-induced rhabdomyolysis following therapy of bronchial asthma].
[Aoshima M,Kameyama S,Murai Y,Yamazaki M,Kamiya T,Miyazaki T]Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi.1991 Aug;29(8):1064-9. PMID: 1753524
4: Acute renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis following self-poisoning with aminophylline.
[Stevens P E,De Verteuil J A,Rainford D J]J R Army Med Corps.1988 Jun;134(2):79-80. PMID: 3418610
5: Rhabdomyolysis with hyperkalaemia after aminophylline overdose.
[Wight J P,Laurence J,Holt S,Forrest A R]Med Sci Law.1987 Apr;27(2):103-5. PMID: 3586933
6: Theophylline-induced protection in myoglobinuric acute renal failure: further characterization.
[Bidani A K,Churchill P C,Packer W]Can J Physiol Pharmacol.1987 Jan;65(1):42-5. PMID: 3567718
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.