Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
VORICONAZOLE
DIR Classification
Classification:Moderate-DIR concern
Severity Score:3
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Arrhythmias and QT Prolongation
- Some azoles, including voriconazole, have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram. During clinical development and post-marketing surveillance, there have been rare cases of arrhythmias, (including ventricular arrhythmias such as torsade de pointes), cardiac arrests and sudden deaths in patients taking voriconazole. These cases usually involved seriously ill patients with multiple confounding risk factors, such as history of cardiotoxic chemotherapy, cardiomyopathy, hypokalemia and concomitant medications that may have been contributory.
- Voriconazole should be administered with caution to patients with potentially proarrhythmic conditions, such as:
- Congenital or acquired QT prolongation
- Cardiomyopathy, in particular when heart failure is present
- Sinus bradycardia
- Existing symptomatic arrhythmias
- Concomitant medicinal product that is known to prolong QT interval [see contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
- Rigorous attempts to correct potassium, magnesium and calcium should be made before starting and during voriconazole therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- >>16a80777-f1f3-45bb-a312-998b07767fe3-1.jpeg
- >>16a80777-f1f3-45bb-a312-998b07767fe3-2.jpeg
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Coadministration of cisapride, pimozide or quinidine with voriconazole tablets is contraindicated because increased plasma concentrations of these drugs can lead to QT prolongation and rare occurrences of torsade de pointes [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Cardiovascular: atrial arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, AV block complete, bigeminy, bradycardia, bundle branch block, cardiomegaly, cardiomyopathy, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral ischemia, cerebrovascular accident, congestive heart failure, deep thrombophlebitis, endocarditis, extrasystoles, heart arrest, hypertension, hypotension, myocardial infarction, nodal arrhythmia, palpitation, phlebitis, postural hypotension, pulmonary embolus, QT interval prolonged, supraventricular extrasystoles, supraventricular tachycardia, syncope, thrombophlebitis, vasodilatation, ventricular arrhythmia, ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia (including torsade de pointes) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- A placebo-controlled, randomized, crossover study to evaluate the effect on the QT interval of healthy male and female subjects was conducted with three single oral doses of voriconazole and ketoconazole. Serial ECGs and plasma samples were obtained at specified intervals over a 24-hour post dose observation period. The placebo-adjusted mean maximum increases in QTc from baseline after 800, 1200, and 1600 mg of voriconazole and after ketoconazole 800 mg were all <10 msec. Females exhibited a greater increase in QTc than males, although all mean changes were <10 msec. Age was not found to affect the magnitude of increase in QTc. No subject in any group had an increase in QTc of ≥60 msec from baseline. No subject experienced an interval exceeding the potentially clinically relevant threshold of 500 msec. However, the QT effect of voriconazole combined with drugs known to prolong the QT interval is unknown [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7)].
- [Pharmacokinetics]
- Cisapride, pimozide and quinidine (CYP3A4 substrates)–Although not studied in vitro or in vivo, concomitant administration of voriconazole with cisapride, pimozide or quinidine may result in inhibition of the metabolism of these drugs. Increased plasma concentrations of these drugs can lead to QT prolongation and rare occurrences of torsade de pointes. Coadministration of voriconazole, cisapride, pimozide and quinidine is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
- Methadone (CYP3A4, CYP2C19, CYP2C9 substrate)–Repeat dose administration of oral voriconazole (400 mg every 12 hours for 1 day, then 200 mg every 12 hours for 4 days) increased the Cmax and AUCτ of pharmacologically active Rmethadone by 31% (90% CI: 22%, 40%) and 47% (90% CI: 38%, 57%), respectively, in subjects receiving a methadone maintenance dose (30-100 mg every 24 hours). The Cmax and AUC of (S)-methadone increased by 65% (90% CI: 53%, 79%) and 103% (90% CI: 85%, 124%), respectively. Increased plasma concentrations of methadone have been associated with toxicity including QT prolongation. Frequent monitoring for adverse events and toxicity related to methadone is recommended during coadministration. Dose reduction of methadone may be needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
76
42836
Other ADRs
7337
14109942
Odds Ratio = 3.413
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- J02AC03 - voriconazole
- J02AC - Triazole derivatives
- J02A - ANTIMYCOTICS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- J02 - ANTIMYCOTICS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- J - ANTIINFECTIVES FOR SYSTEMIC USE
Active Ingredient:voriconazole
Active Ingredient UNII:JFU09I87TR
Drugbank ID:DB00582
PubChem Compound:71616
CAS Number:137234-62-9
Dosage Form(s):powder, for suspension
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 400.0 mg/day J02AC03
Chemical Structure: 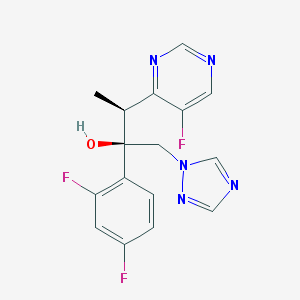

SMILE Code:
C[C@@H](C1=NC=NC=C1F)[C@](CN2C=NC=N2)(C3=C(C=C(C=C3)F)F)O
C[C@@H](C1=NC=NC=C1F)[C@](CN2C=NC=N2)(C3=C(C=C(C=C3)F)F)O
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: [Rhabdomyolysis caused by voriconazole in treatment of severe hepatitis complicated by pulmonary fungal infection: a case report].
[Li M,He W,Ma J,He B,Li N P,Tang W,Yuan T,Li W,Jiang Y F]Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi.2017 Jan 20;25(1):50-51. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.01.013. PMID: 28297781
2: Short term treatment with clarithromycin resulting in colchicine-induced rhabdomyolysis.
[McKinnell James,Tayek John A]J Clin Rheumatol.2009 Sep;15(6):303-5. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e3181bbbcd7. PMID: 19734738
3: Pharmacokinetic interaction between voriconazole and efavirenz at steady state in healthy male subjects.
[Liu Ping,Foster Grover,LaBadie Robert R,Gutierrez Maria J,Sharma Amarnath]J Clin Pharmacol.2008 Jan;48(1):73-84. Epub 2007 Nov 19. PMID: 18025525
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.