Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
MIRTAZAPINE
DIR Classification
Classification:Less-DIR concern
Severity Score:1
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
- The effect of mirtazapine on QTc interval was assessed in a clinical randomized trial with placebo and positive (moxifloxacin) controls involving 54 healthy volunteers using exposure response analysis. This trial showed a positive relationship between mirtazapine concentrations and prolongation of the QTc interval. However, the degree of QT prolongation observed with both 45 mg and 75 mg (1.67 times the maximum recommended daily dose) doses of mirtazapine was not at a level generally considered to be clinically meaningful. During postmarketing use of mirtazapine, cases of QT prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden death, have been reported [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1, 6.2)]. The majority of reports occurred in association with overdose or in patients with other risk factors for QT prolongation, including concomitant use of QTc-prolonging medicines [see DRUG INTERACTIONS (7) and OVERDOSAGE (10)]. Exercise caution when mirtazapine is prescribed in patients with known cardiovascular disease or family history of QT prolongation, and in concomitant use with other drugs thought to prolong the QTc interval.
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- >>10ea9d83-19c3-4f3b-a1cc-cfc48b42507f.jpeg
- OVERDOSAGE
- Human Experience
- Based on postmarketing reports, serious outcomes (including fatalities) may occur at dosages higher than the recommended doses, especially with mixed overdoses. In these cases, QT prolongation and Torsades de Pointes have also been reported [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5), ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.2), and DRUG INTERACTIONS (7)].
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The following adverse reactions are described in more detail in other sections of the prescribing information:
- QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5)]
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- The effect of mirtazapine on QTc interval was assessed in healthy subjects. At a dose of 75 mg (1.67 times the maximum recommended dosage), mirtazapine does not prolong the QTc interval to a clinically meaningful extent.
- [Pharmacokinetics]
- QTc-Prolonging Drugs
- The risk of QT prolongation and/or ventricular arrhythmias (e.g., Torsades de Pointes) may be increased with concomitant use of medicines which prolong the QTc interval (e.g., some antipsychotics and antibiotics) and in mirtazapine overdose [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5), ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1, 6.2), Drug Interactions (7), and Overdosage (10)].
- PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- QTc Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
- Inform patients to consult their physician immediately if they feel faint, lose consciousness, or have heart palpitations [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5), DRUG INTERACTIONS (7), OVERDOSAGE (10)]. Advise patients to inform physicians that they are taking mirtazapine before any new drug is taken.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
197
42715
Other ADRs
13303
14103976
Odds Ratio = 4.89
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- N06AX11 - mirtazapine
- N06AX - Other antidepressants
- N06A - ANTIDEPRESSANTS
- N06 - PSYCHOANALEPTICS
- N - NERVOUS SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:mirtazapine
Active Ingredient UNII:A051Q2099Q
Drugbank ID:DB00370
PubChem Compound:4205
CAS Number:85650-52-8
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 30.0 mg/day N06AX11
Chemical Structure: 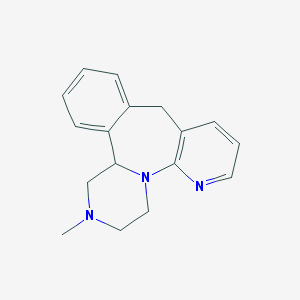

SMILE Code:
CN1CCN2C(C1)C3=CC=CC=C3CC4=C2N=CC=C4
CN1CCN2C(C1)C3=CC=CC=C3CC4=C2N=CC=C4
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: Serotonin Syndrome Induced by Combined Use of Mirtazapine and Olanzapine Complicated with Rhabdomyolysis, Acute Renal Failure, and Acute Pulmonary Edema-A Case Report.
[Wu Chi-Shun,Tong Show-Hwa,Ong Cheung-Ter,Sung Sheng-Feng]Acta Neurol Taiwan.2015 Dec;24(4):117-21. PMID: 27333965
2: Mirtazapine: rhabdomyolysis.
Prescrire Int.2014 May;23(149):129. PMID: 24926518
3: A case of pulmonary thromboembolism and rhabdomyolysis during therapy with mirtazapine and risperidone.
[Zink Mathias,Knopf Udo,Argiriou Sotiria,Kuwilsky Anna]J Clin Psychiatry.2006 May;67(5):835. PMID: 16841636
4: Non-lethal mirtazapine overdose with rhabdomyolysis.
[Kuliwaba Andrew]Aust N Z J Psychiatry.2005 Apr;39(4):312-3. PMID: 15777372
5: Possible mirtazapine-induced rhabdomyolysis.
[Khandat Amaresh B,Nurnberger John I,Shekhar Anantha]Ann Pharmacother.2004 Jul-Aug;38(7-8):1321. Epub 2004 Jun 8. PMID: 15187213
6: Non-fatal mirtazapine overdose.
[Retz W,Maier S,Maris F,Rösler M]Int Clin Psychopharmacol.1998 Nov;13(6):277-9. PMID: 9861579
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.