Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
TERBINAFINE
DIR Classification
Classification:Less-DIR concern
Severity Score:1
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse events have been identified during postapproval use of terbinafine tablets. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, severe neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5)]
- Immune system disorders: Serious hypersensitivity reactions e.g angioedema and allergic reactions (including anaphylaxis), precipitation and exacerbation of cutaneous and systemic lupus erythematosus [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.7)], serum sickness-like reaction.
- Psychiatric disorders: Anxiety and Depressive symptoms independent of taste disturbance have been reported with use of terbinafine tablets. In some cases, depressive symptoms have been reported to subside with discontinuance of therapy and to recur with reinstitution of therapy [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.4)]
- Nervous system disorders: Cases of taste disturbance, including taste loss, have been reported with the use of terbinafine tablets. It can be severe enough to result in decreased food intake, weight loss, anxiety, and depressive symptoms. Cases of smell disturbance, including smell loss, have been reported with the use of terbinafine tablets [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2 and 5.3)]. Cases of paresthesia and hypoesthesia have been reported with the use of terbinafine Tablets.
- Eye disorders: Visual field defects, reduced visual acuity
- Ear and labyrinth disorders: Hearing impairment, vertigo, tinnitus
- Vascular disorders: Vasculitis
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Pancreatitis, vomiting
- Hepatobiliary disorders: Cases of liver failure some leading to liver transplant or death [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)], idiosyncratic and symptomatic hepatic injury. Cases of hepatitis, cholestasis, and increased hepatic enzymes [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)] have been seen with the use of terbinafine Tablets.
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Serious skin reactions [e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, and bullous dermatitis, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome] [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.6)], acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, psoriasiform eruptions or exacerbation of psoriasis, photosensitivity reactions, hair loss
- Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Rhabdomyolysis, arthralgia, myalgia
- General disorders and administration site conditions: Malaise, fatigue, influenza-like illness, pyrexia
- Investigations: Altered prothrombin time (prolongation and reduction) in patients concomitantly treated with warfarin and increased blood creatine phosphokinase have been reported.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
165
42747
Other ADRs
10838
14106441
Odds Ratio = 5.024
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- D01BA02 - terbinafine
- D01BA - Antifungals for systemic use
- D01B - ANTIFUNGALS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- D01 - ANTIFUNGALS FOR DERMATOLOGICAL USE
- D - DERMATOLOGICALS
- D01AE15 - terbinafine
- D01AE - Other antifungals for topical use
- D01A - ANTIFUNGALS FOR TOPICAL USE
- D01 - ANTIFUNGALS FOR DERMATOLOGICAL USE
- D - DERMATOLOGICALS
Active Ingredient:terbinafine hydrochloride
Active Ingredient UNII:012C11ZU6G
Drugbank ID:DB00857
PubChem Compound:1549008
CAS Number:91161-71-6
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 250.0 mg/day D01BA02
Chemical Structure: 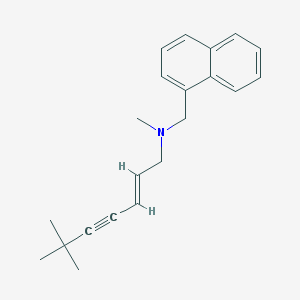

SMILE Code:
CC(C)(C)C#C/C=C/CN(C)CC1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21
CC(C)(C)C#C/C=C/CN(C)CC1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: Statin-associated rhabdomyolysis triggered by drug-drug interaction with itraconazole.
[Dybro Anne Mette,Damkier Per,Rasmussen Torsten Bloch,Hellfritzsch Maja]BMJ Case Rep.2016 Sep 7;2016. pii: bcr2016216457. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2016-216457. PMID: 27605198
2: Quantitative evaluation of initial symptoms as predictors to detect adverse drug reactions using Bayes' theory: expansion and evaluation of drug-adverse drug reaction-initial symptom combinations using adverse event reporting system database.
[Kobayashi Daisuke,Hosaka Shigeru,Inoue Emiko,Ohshima Kimie,Kutsuma Nobuaki,Oshima Shinji,Okuno Yasushi]Biol Pharm Bull.2013;36(12):1891-901. PMID: 24292049
3: [Rhabdomyolisis and terbinafine].
[Gallego Peris Aurora,Sanfélix Gimeno Gabriel,Palop Larrea Vicente,Sanfélix Genovés José]Med Clin (Barc).2006 Nov 25;127(20):799. PMID: 17198674
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.