Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
SUCCINYLCHOLINE CHLORIDE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIR concern
Severity Score:4
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- BOXED WARNING
- RISK OF CARDIAC ARREST FROM HYPERKALEMIC RHABDOMYOLYSIS
- There have been rare reports of acute rhabdomyolysis with hyperkalemia followed by ventricular dysrhythmias, cardiac arrest, and death after the administration of succinylcholine to apparently healthy children who were subsequently found to have undiagnosed skeletal muscle myopathy, most frequently Duchenne's muscular dystrophy.
- This syndrome often presents as peaked T-waves and sudden cardiac arrest within minutes after the administration of the drug in healthy appearing children (usually, but not exclusively, males, and most frequently 8 years of age or younger). There have also been reports in adolescents.
- Therefore, when a healthy appearing infant or child develops cardiac arrest soon after administration of succinylcholine not felt to be due to inadequate ventilation, oxygenation, or anesthetic overdose, immediate treatment for hyperkalemia should be instituted. This should include administration of intravenous calcium, bicarbonate, and glucose with insulin, with hyperventilation. Due to the abrupt onset of this syndrome, routine resuscitative measures are likely to be unsuccessful. However, extraordinary and prolonged resuscitative efforts have resulted in successful resuscitation in some reported cases. In addition, in the presence of signs of malignant hyperthermia, appropriate treatment should be instituted concurrently.
- Since there may be no signs or symptoms to alert the practitioner to which patients are at risk, it is recommended that the use of succinylcholine in children should be reserved for emergency intubation or instances where immediate securing of the airway is necessary, e.g. laryngospasm, difficult airway, full stomach, or for intramuscular use when a suitable vein is inaccessible (see PRECAUTIONS: PEDIATRIC USE and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
Rhabdomyolysis
25
42887
Other ADRs
598
14116681
Odds Ratio = 13.761
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- M03AB01 - succinylcholine chloride
- M03AB - Choline derivatives
- M03A - "MUSCLE RELAXANTS, PERIPHERALLY ACTING AGENTS"
- M03 - MUSCLE RELAXANTS
- M - MUSCULO-SKELETAL SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:succinylcholine chloride
Active Ingredient UNII:I9L0DDD30I
Drugbank ID:DB00202
PubChem Compound:5314
CAS Number:306-40-1
Dosage Form(s):injection, solution
Route(s) Of Administrator:intramuscular; intravenous; parenteral
Daily Dose:
Chemical Structure: 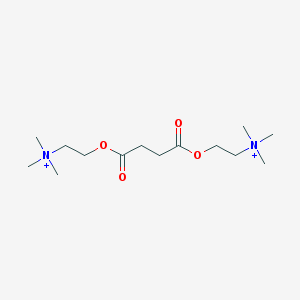

SMILE Code:
C[N+](C)(C)CCOC(=O)CCC(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C
C[N+](C)(C)CCOC(=O)CCC(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C
Reference
COHORT STUDY:
N/AOTHER REFERENCE(S):
1: [Rhabdomyolysis induced by succinylcholine chloride and sevoflurane in an elderly man].
[Takamatsu F,Taoda M,Uchihashi Y,Satoh T]Masui.1996 Nov;45(11):1406-9. PMID: 8953878
2: [Rhabdomyolysis with myoglobinuric acute renal failure following the use of succinylcholine chloride and enflurane in a mentally-retarded patient: a case report].
[Lee S C,Furutani M,Yoshitake K,Sato T,Lin Y S,Shong K L,Wang M H]Ma Zui Xue Za Zhi.1987 Jun;25(2):97-102. PMID: 3669958
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of rhabdomyolysis is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The views presented in this website do not necessarily reflect current or future opinion or policy of the US Food and Drug Administration. Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.