Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
CIPROFLOXACIN
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Prolongation of the QT Interval
- Some fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram and cases of arrhythmia. Cases of torsade de pointes have been reported during postmarketing surveillance in patients receiving fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin.
- Avoid ciprofloxacin in patients with known prolongation of the QT interval, risk factors for QT prolongation or torsade de pointes (for example, congenital long QT syndrome, uncorrected electrolyte imbalance, such as hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia and cardiac disease, such as heart failure, myocardial infarction, or bradycardia), and patients receiving Class IA antiarrhythmic agents (quinidine, procainamide), or Class III antiarrhythmic agents (amiodarone, sotalol), tricyclic antidepressants, macrolides, and antipsychotics. Elderly patients may also be more susceptible to drug-associated effects on the QT interval [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.2), USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.5)].
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The following serious and otherwise important adverse drug reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of labeling:
- Prolongation of the QT Interval [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.12)]
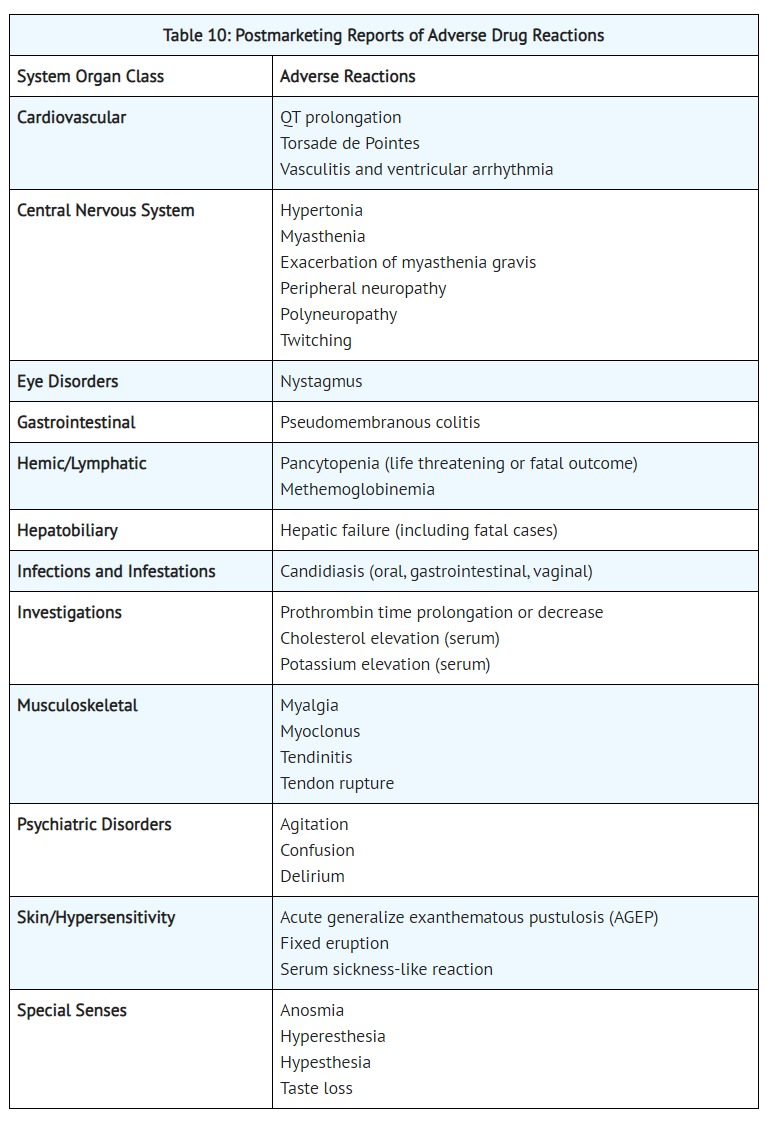
- [Postmarketing Experience]
- PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Prolongation of the QT Interval: Instruct patients to inform their physician of any personal or family history of QT prolongation or proarrhythmic conditions such as hypokalemia, bradycardia, or recent myocardial ischemia; if they are taking any Class IA (quinidine, procainamide), or Class III (amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents. Instruct patients to notify their physician if they have any symptoms of prolongation of the QT interval, including prolonged heart palpitations or a loss of consciousness.
- Serious heart rhythm changes (QT prolongation and torsade de pointes). Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have a change in your heart beat (a fast or irregular heartbeat), or if you faint. Ciprofloxacin tablets may cause a rare heart problem known as prolongation of the QT interval. This condition can cause an abnormal heartbeat and can be very dangerous. The chances of this event are higher in people:
- who are elderly
- with a family history of prolonged QT interval
- with low blood potassium (hypokalemia)
- who take certain medicines to control heart rhythm (antiarrhythmics)
- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Geriatric Use
- In general, elderly patients may be more susceptible to drug-associated effects on the QT interval. Therefore, precaution should be taken when using ciprofloxacin with concomitant drugs that can result in prolongation of the QT interval (for example, class IA or class III antiarrhythmics) or in patients with risk factors for torsade de pointes (for example, known QT prolongation, uncorrected hypokalemia) [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.12)].
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
213
23879
Other ADRs
128160
38253427
Odds Ratio = 2.663
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- J01MA02 - ciprofloxacin
- J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
- J01M - QUINOLONE ANTIBACTERIALS
- J01 - ANTIBACTERIALS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- J - ANTIINFECTIVES FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- S01AE03 - ciprofloxacin
- S01AE -
- S01A - ANTIINFECTIVES
- S01 - OPHTHALMOLOGICALS
- S - SENSORY ORGANS
- S02AA15 - ciprofloxacin
- S02AA - Antiinfectives
- S02A - ANTIINFECTIVES
- S02 - OTOLOGICALS
- S - SENSORY ORGANS
- S03AA07 - ciprofloxacin
- S03AA - Antiinfectives
- S03A - ANTIINFECTIVES
- S03 - OPHTHALMOLOGICAL AND OTOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS
- S - SENSORY ORGANS
Active Ingredient:CIPROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE
Active Ingredient UNII:4BA73M5E37
Drugbank ID:DB00537
PubChem Compound:2764
CTD ID:D002939
PharmGKB:PA449009
CAS Number:85721-33-1
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 1000.0 mg/day J01MA02
Chemical Structure: 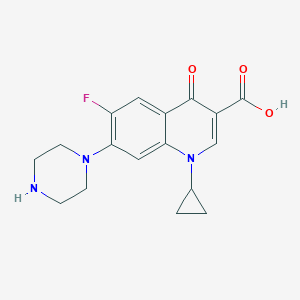

SMILE Code:
OC(=O)C1=CN(C2CC2)C2=CC(N3CCNCC3)=C(F)C=C2C1=O
OC(=O)C1=CN(C2CC2)C2=CC(N3CCNCC3)=C(F)C=C2C1=O
Reference
1: Effect of ciprofloxacin vs levofloxacin on QTc-interval and dysglycemia in diabetic and non-diabetic patients.
[Saad Nada A,Elberry Ahmed A,Samy Matar Hazem,Hussein Raghda R S]Int J Clin Pract,2021 May;75(5):e14072. PMID: 33559294
2: {'#text': 'Lethal Arrhythmia () in COVID-19: An Event Synergistically Induced by Viral Associated Cardiac Injury, Hyperinflammatory Response, and Treatment Drug?', 'i': 'Torsade de Pointes'}
[Yasmin Kusumawardhani Nuraini,Huang Ian,Martanto Erwan,Sihite Teddy Arnold,Nugraha Eka Surya,Prodjosoewojo Susantina,Hamijoyo Laniyati,Hartantri Yovita]Clin Med Insights Case Rep,2020 Dec 14;13:1179547620972397. PMID: 33402858
3: QTc interval prolongation associated with inpatient azithromycin therapy for pneumonia.
[Dela Cruz Maricel,Ershad Muhammed,Mostafa Ahmed]J Osteopath Med,2021 Jan 1;121(1):5-9. PMID: 33044496
4: Adverse Drug Events in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Multiple Drug Interactions and Polypharmacy.
[Sommer Julia,Seeling Andreas,Rupprecht Harald]Drugs Aging,2020 May;37(5):359-372. PMID: 32056163
5: Descriptive study of drug-drug interactions attributed to prescriptions written upon discharge from the emergency department.
[Jawaro Tara,Bridgeman Patrick J,Mele Jude,Wei Grant]Am J Emerg Med,2019 May;37(5):924-927. PMID: 30880039
6: Assessment of the risk of QT-interval prolongation associated with potential drug-drug interactions in patients admitted to Intensive Care Units.
[Fernandes Flávia Medeiros,da Silva Paulino Aryelle Mayara,Sedda Bruna Camelo,da Silva Eliane Pereira,Martins Rand Randall,Oliveira Antonio Gouveia]Saudi Pharm J,2019 Feb;27(2):229-234. PMID: 30766434
7: {'#text': 'Validation and Clinical Utility of the hERG IC50:C Ratio to Determine the Risk of Drug-Induced Torsades de Pointes: A Meta-Analysis.', 'sub': 'max'}
[Lehmann David F,Eggleston William D,Wang Dongliang]Pharmacotherapy,2018 Mar;38(3):341-348. PMID: 29380488
8: Ciprofloxacin does not Prolong the QTc Interval: A Clinical Study in ICU Patients and Review of the Literature.
[Heemskerk Charlotte,Woldman Evelien,Pereboom Marieke,Van der Hoeven Ruud,Mantel-Teeuwisse Aukje,Van Gemeren Claudia,Becker Matthijs Lambertus]J Pharm Pharm Sci,2017;20(1):360-364. PMID: 29145929
9: QTc prolongation during ciprofloxacin and fluconazole combination therapy: prevalence and associated risk factors.
[Berger Florine A,Monadian Nico,de Groot Natasja M S,Santbergen Bart,van der Sijs Heleen,Becker Matthijs L,Broers Annoek E C,van Gelder Teun,van den Bemt Patricia M L A]Br J Clin Pharmacol,2018 Feb;84(2):369-378. PMID: 29057492
10: Appraisal of the cardiovascular risks of azithromycin: an observational analysis.
[Sutton S Scott,Hyche Stephanie,Magagnoli Joseph,Hardin James W]J Comp Eff Res,2017 Sep;6(6):509-517. PMID: 28960092
11: Drug safety of macrolide and quinolone antibiotics in a tertiary care hospital: administration of interacting co-medication and QT prolongation.
[Niedrig David,Maechler Sarah,Hoppe Liesa,Corti Natascia,Kovari Helen,Russmann Stefan]Eur J Clin Pharmacol,2016 Jul;72(7):859-67. PMID: 27023463
12: Weighing the adverse cardiac effects of fluoroquinolones: A risk perspective.
[Mehrzad Raman,Barza Michael]J Clin Pharmacol,2015 Nov;55(11):1198-206. PMID: 26011799
13: Changes in medication preceding out-of-hospital cardiac arrest where resuscitation was attempted.
[Holmgren Christina M,Abdon Nils J,Bergfeldt Lennart B,Edvardsson Nils G,Herlitz Johan D,Karlsson Thomas,Svensson Leif G,Åstrand Bengt H]J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,2014 Jun;63(6):497-503. PMID: 24390174
14: The FLT3 inhibitor quizartinib inhibits ABCG2 at pharmacologically relevant concentrations, with implications for both chemosensitization and adverse drug interactions.
[Bhullar Jasjeet,Natarajan Karthika,Shukla Suneet,Mathias Trevor J,Sadowska Mariola,Ambudkar Suresh V,Baer Maria R]PLoS One,2013 Aug 14;8(8):e71266. PMID: 23967177
15: Negative electro-mechanical windows are required for drug-induced Torsades de Pointes in the anesthetized guinea pig.
[Guns P-J,Johnson D M,Weltens E,Lissens J]J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods,2012 Sep;66(2):125-34. PMID: 22516473
16: QT prolongation and torsade de pointes induced by fluoroquinolones: infrequent side effects from commonly used medications.
[Briasoulis Alexandros,Agarwal Vikram,Pierce Walter J]Cardiology,2011;120(2):103-10. PMID: 22156660
17: The electro-mechanical window in anaesthetized guinea pigs: a new marker in screening for Torsade de Pointes risk.
[Guns P-J,Johnson D M,Van Op den Bosch J,Weltens E,Lissens J]Br J Pharmacol,2012 May;166(2):689-701. PMID: 22122450
18: Ciprofloxacin in critically ill children.
[Sideri G,Kafetzis D A,Vouloumanou E K,Papadatos J H,Papadimitriou M,Falagas M E]Anaesth Intensive Care,2011 Jul;39(4):635-9. PMID: 21823382
19: Ciprofloxacin-induced torsade de pointes.
[Ibrahim Morhaf,Omar Bassam]Am J Emerg Med,2012 Jan;30(1):252.e5-9. PMID: 21075583
20: Ciprofloxacin-induced torsades de pointes in a methadone-dependent patient.
[Nair Murali K,Patel Krunal,Starer Perry J]Addiction,2008 Dec;103(12):2062-4. PMID: 19469750
21: Ciprofloxacin induced acquired long QT syndrome in a patient under class III antiarrhythmic therapy.
[Keivanidou Anastasia,Arnaoutoglou Christos,Krommydas Argyrios,Papanikolaou Georgios,Tsiptses Konstantinos,Chrisopoulos Charalampos,Kirpizidis Christos]Cardiol J,2009;16(2):172-4. PMID: 19387967
22: Proarrhythmia as a class effect of quinolones: increased dispersion of repolarization and triangulation of action potential predict torsades de pointes.
[Milberg Peter,Hilker Ekkehard,Ramtin Shahram,Cakir Yilmaz,Stypmann Jörg,Engelen Markus A,Mönnig Gerold,Osada Nani,Breithardt Günter,Haverkamp Wilhelm,Eckardt Lars]J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol,2007 Jun;18(6):647-54. PMID: 17388913
23: Arrhythmias associated with fluoroquinolone therapy.
[Falagas Matthew E,Rafailidis Petros I,Rosmarakis Evangelos S]Int J Antimicrob Agents,2007 Apr;29(4):374-9. PMID: 17241772
24: The use of systemic fluoroquinolones.
[Committee on Infectious Diseases]Pediatrics,2006 Sep;118(3):1287-92. PMID: 16951028
25: QT PRODACT: sensitivity and specificity of the canine telemetry assay for detecting drug-induced QT interval prolongation.
[Miyazaki Hiroyasu,Watanabe Hiroyuki,Kitayama Tetsuya,Nishida Masahiro,Nishi Yasuhiro,Sekiya Koji,Suganami Hideki,Yamamoto Keiji]J Pharmacol Sci,2005;99(5):523-9. PMID: 16493192
26: QT PRODACT: in vivo QT assay in the conscious dog for assessing the potential for QT interval prolongation by human pharmaceuticals.
[Toyoshima Shigeki,Kanno Akihiro,Kitayama Tetsuya,Sekiya Koji,Nakai Keiko,Haruna Masao,Mino Terumasa,Miyazaki Hiroyasu,Yano Koji,Yamamoto Keiji]J Pharmacol Sci,2005;99(5):459-71. PMID: 16493187
27: Effects of three fluoroquinolones on QT analysis after standard treatment courses.
[Tsikouris James P,Peeters Michael J,Cox Craig D,Meyerrose Gary E,Seifert Charles F]Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol,2006 Jan;11(1):52-6. PMID: 16472283
28: Effect of ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin on the QT interval: is this a significant "clinical" event?
[Makaryus Amgad N,Byrns Kory,Makaryus Mary N,Natarajan Usha,Singer Carol,Goldner Bruce]South Med J,2006 Jan;99(1):52-6. PMID: 16466123
29: Drug-induced QT prolongation.
[Wooten James M]South Med J,2006 Jan;99(1):16. PMID: 16466115
30: Ciprofloxacin-induced torsade de pointes.
[Flanagan M Casey,Mitchell Eric S,Haigney Mark C P]Int J Cardiol,2006 Nov 10;113(2):239-41. PMID: 16386810
31: Drug-induced QT interval prolongation after ciprofloxacin administration in a patient receiving olanzapine.
[Letsas Konstantinos P,Sideris Antonios,Kounas Stavros P,Efremidis Michalis,Korantzopoulos Panagiotis,Kardaras Fotios]Int J Cardiol,2006 May 10;109(2):273-4. PMID: 15935493
32: Ciprofloxacin-induced acquired long QT syndrome.
[Prabhakar Manu,Krahn Andrew D]Heart Rhythm,2004 Nov;1(5):624-6. PMID: 15851230
33: QT prolongation with antimicrobial agents: understanding the significance.
[Owens Robert C]Drugs,2004;64(10):1091-124. PMID: 15139788
34: Ciprofloxacin- and hypocalcemia-induced torsade de pointes triggered by hemodialysis.
[Daya Samantapudi K,Gowda Ramesh M,Khan Ijaz A]Am J Ther,Jan-Feb 2004;11(1):77-9. PMID: 14704599
35: Quinolones: cardioprotective or cardiotoxic.
[Katritsis Demosthenes,Camm A John]Pacing Clin Electrophysiol,2003 Dec;26(12):2317-20. PMID: 14675020
36: Moxifloxacin: new preparation. A me-too with more cardiac risks.
Prescrire Int,2002 Dec;11(62):168-9. PMID: 12469694
37: Clinical toxicological aspects of fluoroquinolones.
[Stahlmann Ralf]Toxicol Lett,2002 Feb 28;127(1-3):269-77. PMID: 12052667
38: Ciprofloxacin-induced QTc prolongation.
[Singh H,Kishore K,Gupta M S,Khetarpal S,Jain S,Mangla M]J Assoc Physicians India,2002 Mar;50:430-1. PMID: 11922236
39: Rates of torsades de pointes associated with ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, gatifloxacin, and moxifloxacin.
[Frothingham R]Pharmacotherapy,2001 Dec;21(12):1468-72. PMID: 11765299
40: Evidence of different profiles of side effects and drug-drug interactions among the quinolones--the pharmacokinetic standpoint.
[Lode H]Chemotherapy,2001;47 Suppl 3:24-31; discussion 44-8. PMID: 11549786
41: A risk-benefit assessment of levofloxacin in respiratory, skin and skin structure, and urinary tract infections.
[Martin S J,Jung R,Garvin C G]Drug Saf,2001;24(3):199-222. PMID: 11347723
42: Interactions of a series of fluoroquinolone antibacterial drugs with the human cardiac K+ channel HERG.
[Kang J,Wang L,Chen X L,Triggle D J,Rampe D]Mol Pharmacol,2001 Jan;59(1):122-6. PMID: 11125032
43: Effects of sparfloxacin, grepafloxacin, moxifloxacin, and ciprofloxacin on cardiac action potential duration.
[Patmore L,Fraser S,Mair D,Templeton A]Eur J Pharmacol,2000 Oct 20;406(3):449-52. PMID: 11040352
44: Effects of fluoroquinolones on HERG currents.
[Bischoff U,Schmidt C,Netzer R,Pongs O]Eur J Pharmacol,2000 Oct 20;406(3):341-3. PMID: 11040340
45: Comparative tolerability of the newer fluoroquinolone antibacterials.
[Ball P,Mandell L,Niki Y,Tillotson G]Drug Saf,1999 Nov;21(5):407-21. PMID: 10554054
46: The effect of ciprofloxacin on the pharmacokinetic and ECG parameters of quinidine.
[Bleske B E,Carver P L,Annesley T M,Bleske J R,Morady F]J Clin Pharmacol,1990 Oct;30(10):911-5. PMID: 2229451
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.