Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
OFLOXACIN
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- PRECAUTIONS
- Torsade de Pointes
- Some quinolones, including ofloxacin, have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram and infrequent cases of arrhythmia. Rare cases of torsade de pointes have been spontaneously reported during postmarketing surveillance in patients receiving quinolones, including ofloxacin. Ofloxacin should be avoided in patients with known prolongation of the QT interval, patients with uncorrected hypokalemia, and patients receiving Class IA (quinidine, procainamide), or Class III (amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents.
- [Other Information]
- Patients should be advised:
- that convulsions have been reported in patients taking quinolones, including ofloxacin, and to notify their physician before taking this drug if there is a history of this condition;
- to inform their physician of any personal or family history of QTc prolongation or proarrhythmic conditions such as hypokalemia, bradycardia, or recent myocardial ischemia; if they are taking any class IA (quinidine, procainamide), or class III (amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents. Patients should notify their physicians if they have any symptoms of prolongation of the QTc interval including prolonged heart palpitations or a loss of consciousness.
- [Drug Interactions]
- Elderly patients may be more sensitive to drug-associated effects on the QT interval. Therefore, precaution should be taken when using ofloxacin with concomitant drugs that can result in prolongation of the QT interval (e.g. Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmics) or in patients with risk factors for torsade de pointes (e.g. known QT prolongation, uncorrected hypokalemia) (see PRECAUTIONS, GENERAL, TORSADE DE POINTES).
- MEDICATION GUIDE
- Other serious side effects of ofloxacin tablets include:
- Serious heart rhythm changes (QT prolongation and torsade de pointes)
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have a change in your heart beat (a fast or irregular heartbeat), or if you faint. Ofloxacin tablets may cause a rare heart problem known as prolongation of the QT interval. This condition can cause an abnormal heartbeat and can be very dangerous. The chances of this happening are higher in people:
- who are elderly
- with a family history of prolonged QT interval
- with low blood potassium (hypokalemia)
- who take certain medicines to control heart rhythm (antiarrhythmics)
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
5
24087
Other ADRs
4697
38376890
Odds Ratio = 1.697
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- J01MA01 - ofloxacin
- J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
- J01M - QUINOLONE ANTIBACTERIALS
- J01 - ANTIBACTERIALS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- J - ANTIINFECTIVES FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- S01AE01 - ofloxacin
- S01AE -
- S01A - ANTIINFECTIVES
- S01 - OPHTHALMOLOGICALS
- S - SENSORY ORGANS
- S02AA16 - ofloxacin
- S02AA - Antiinfectives
- S02A - ANTIINFECTIVES
- S02 - OTOLOGICALS
- S - SENSORY ORGANS
Active Ingredient:OFLOXACIN
Active Ingredient UNII:A4P49JAZ9H
Drugbank ID:DB01165
PubChem Compound:4583
CTD ID:D015242
PharmGKB:PA450684
CAS Number:82419-36-1
Dosage Form(s):tablet, coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 400.0 mg/day J01MA01
Chemical Structure: 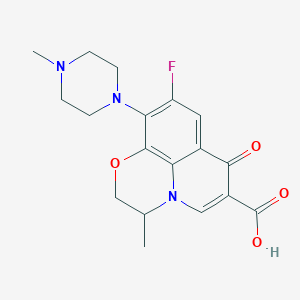

SMILE Code:
CC1COC2=C3N1C=C(C(O)=O)C(=O)C3=CC(F)=C2N1CCN(C)CC1
CC1COC2=C3N1C=C(C(O)=O)C(=O)C3=CC(F)=C2N1CCN(C)CC1
Reference
1: Relationship between antofloxacin concentration and QT prolongation and estimation of the possible false-positive rate.
[Liang Li-Yu,He Ying-Chun,Li Yun-Fei,Yang Juan,Xu Feng-Yan,Li Lu-Jin,Huang Ji-Han,Wang Kun,Zheng Qing-Shan]Biomed Pharmacother,2020 Oct;130:110619. PMID: 32795925
2: Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin and levofloxacin for prevention and treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in children.
[Thee S,Garcia-Prats A J,McIlleron H M,Wiesner L,Castel S,Norman J,Draper H R,van der Merwe P L,Hesseling A C,Schaaf H S]Antimicrob Agents Chemother,2014 May;58(5):2948-51. PMID: 24550337
3: A case of levofloxacin-induced anaphylaxis with elevated serum tryptase levels.
[Lee Ji-Ho,Lee Won Yeon,Yong Suk Joong,Shin Kye Chul,Lee Myoung Kyu,Kim Chong Whan,Kim Sang-Ha]Allergy Asthma Immunol Res,2013 Mar;5(2):113-5. PMID: 23450078
4: Effect of combined fluoroquinolone and azole use on QT prolongation in hematology patients.
[Zeuli John D,Wilson John W,Estes Lynn L]Antimicrob Agents Chemother,2013 Mar;57(3):1121-7. PMID: 23229485
5: QT prolongation and torsade de pointes induced by fluoroquinolones: infrequent side effects from commonly used medications.
[Briasoulis Alexandros,Agarwal Vikram,Pierce Walter J]Cardiology,2011;120(2):103-10. PMID: 22156660
6: Analysis of Relationship between Levofloxacin and Corrected QT Prolongation Using a Clinical Data Warehouse.
[Park Man Young,Kim Eun Yeob,Lee Young Ho,Kim Woojae,Kim Ku Sang,Sheen Seung Soo,Lim Hong Seok,Park Rae Woong]Healthc Inform Res,2011 Mar;17(1):58-66. PMID: 21818458
7: [A multi-center, randomized, controlled, double blind and double dummy clinical trial of antofloxacin hydrochloride tablet versus levofloxacin tablet for the treatment of acute bacterial infections].
[Xiao Yong-hong,Cui Hong,Xue Feng,Huang Wen-xiang,Xiu Qing-yu,Li De-tian,Chen Ping,Jia Zheng-ping,Wen Ai-dong,Yang Guo-ping,Mao Guo-guang]Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi,2011 Mar;50(3):225-9. PMID: 21600087
8: Proarrhythmia as a class effect of quinolones: increased dispersion of repolarization and triangulation of action potential predict torsades de pointes.
[Milberg Peter,Hilker Ekkehard,Ramtin Shahram,Cakir Yilmaz,Stypmann Jörg,Engelen Markus A,Mönnig Gerold,Osada Nani,Breithardt Günter,Haverkamp Wilhelm,Eckardt Lars]J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol,2007 Jun;18(6):647-54. PMID: 17388913
9: Arrhythmias associated with fluoroquinolone therapy.
[Falagas Matthew E,Rafailidis Petros I,Rosmarakis Evangelos S]Int J Antimicrob Agents,2007 Apr;29(4):374-9. PMID: 17241772
10: Effects of three fluoroquinolones on QT analysis after standard treatment courses.
[Tsikouris James P,Peeters Michael J,Cox Craig D,Meyerrose Gary E,Seifert Charles F]Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol,2006 Jan;11(1):52-6. PMID: 16472283
11: Effect of ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin on the QT interval: is this a significant "clinical" event?
[Makaryus Amgad N,Byrns Kory,Makaryus Mary N,Natarajan Usha,Singer Carol,Goldner Bruce]South Med J,2006 Jan;99(1):52-6. PMID: 16466123
12: Drug-induced QT prolongation.
[Wooten James M]South Med J,2006 Jan;99(1):16. PMID: 16466115
13: A randomized trial comparing the cardiac rhythm safety of moxifloxacin vs levofloxacin in elderly patients hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia.
[Morganroth Joel,Dimarco John P,Anzueto Antonio,Niederman Michael S,Choudhri Shurjeel,CAPRIE Study Group]Chest,2005 Nov;128(5):3398-406. PMID: 16304291
14: QTc prolongation associated with combination therapy of levofloxacin, imipramine, and fluoxetine.
[Nykamp Diane L,Blackmon Casey L,Schmidt Paul E,Roberson Andrea G]Ann Pharmacother,2005 Mar;39(3):543-6. PMID: 15687478
15: Fluconazole- and levofloxacin-induced torsades de pointes in an intensive care unit patient.
[Gandhi Pritesh J,Menezes Pearl A,Vu Hien T,Rivera Amy L,Ramaswamy Karthik]Am J Health Syst Pharm,2003 Dec 1;60(23):2479-83. PMID: 14686224
16: Prescription of QT-prolonging drugs in a cohort of about 5 million outpatients.
[Curtis Lesley H,Østbye Truls,Sendersky Veronica,Hutchison Steve,Allen LaPointe Nancy M,Al-Khatib Sana M,Usdin Yasuda Sally,Dans Peter E,Wright Alan,Califf Robert M,Woosley Raymond L,Schulman Kevin A]Am J Med,2003 Feb 1;114(2):135-41. PMID: 12586234
17: Moxifloxacin: new preparation. A me-too with more cardiac risks.
Prescrire Int,2002 Dec;11(62):168-9. PMID: 12469694
18: Clinical toxicological aspects of fluoroquinolones.
[Stahlmann Ralf]Toxicol Lett,2002 Feb 28;127(1-3):269-77. PMID: 12052667
19: Rates of torsades de pointes associated with ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, gatifloxacin, and moxifloxacin.
[Frothingham R]Pharmacotherapy,2001 Dec;21(12):1468-72. PMID: 11765299
20: Latest industry information on the safety profile of levofloxacin in the US.
[Kahn J B]Chemotherapy,2001;47 Suppl 3:32-7; discussion 44-8. PMID: 11549787
21: Comparison of side effects of levofloxacin versus other fluoroquinolones.
[Carbon C]Chemotherapy,2001;47 Suppl 3:9-14; discussion 44-8. PMID: 11549784
22: History of quinolones and their side effects.
[Rubinstein E]Chemotherapy,2001;47 Suppl 3:3-8; discussion 44-8. PMID: 11549783
23: A risk-benefit assessment of levofloxacin in respiratory, skin and skin structure, and urinary tract infections.
[Martin S J,Jung R,Garvin C G]Drug Saf,2001;24(3):199-222. PMID: 11347723
24: Interactions of a series of fluoroquinolone antibacterial drugs with the human cardiac K+ channel HERG.
[Kang J,Wang L,Chen X L,Triggle D J,Rampe D]Mol Pharmacol,2001 Jan;59(1):122-6. PMID: 11125032
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.