Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
VANDETANIB
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:5.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- BOXED WARNING
- WARNING: QT PROLONGATION, TORSADES DE POINTES, AND SUDDEN DEATH
- CAPRELSA can prolong the QT interval. Torsades de pointes and sudden death have occurred in patients receiving CAPRELSA. Do not use CAPRELSA in patients with hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or long QT syndrome. Correct hypocalcemia, hypokalemia and/or hypomagnesemia prior to CAPRELSA administration. Monitor electrolytes periodically. Avoid drugs known to prolong the QT interval. Only prescribers and pharmacies certified with the restricted distribution program are able to prescribe and dispense CAPRELSA [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1, 5.16)].
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
- CAPRELSA can prolong the QT interval in a concentration-dependent manner [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.2)]. Torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia and sudden deaths have occurred in patients treated with CAPRELSA.
- Do not start CAPRELSA treatment in patients whose QTcF interval is greater than 450 ms. Do not administer CAPRELSA to patients who have a history of Torsades de pointes, congenital long QT syndrome, bradyarrhythmias or uncompensated heart failure. CAPRELSA has not been studied in patients with ventricular arrhythmias or recent myocardial infarction. Vandetanib exposure is increased in patients with impaired renal function. Reduce the starting dose to 200 mg in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment and monitor QT interval frequently.
- Obtain an ECG and serum potassium, calcium, magnesium and TSH at baseline, 2–4 weeks and 8–12 weeks after starting treatment with CAPRELSA, and every 3 months thereafter. Monitor electrolytes and ECGs more frequently in patients who experience diarrhea. Following any dose reduction for QT prolongation or any dose interruption greater than 2 weeks, conduct QT assessments as described above. Maintain serum potassium levels of 4 mEq/L or higher (within normal range) and maintain serum magnesium and calcium levels within normal ranges to reduce the risk of QT prolongation.
- Avoid using CAPRELSA with drugs known to prolong the QT interval [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.11) and DRUG INTERACTIONS (7.4)]. If such drugs are given to patients already receiving CAPRELSA and no alternative therapy exists, perform ECG monitoring of the QT interval more frequently.
- Stop CAPRELSA in patients who develop a QTcF greater than 500 ms until the QTcF returns to less than 450 ms. Dosing of CAPRELSA can then be resumed at a reduced dose [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.1)].
- [Diarrhea]
- Diarrhea of Grade 3 or greater severity occurred in 11% of patients receiving CAPRELSA in the randomized MTC study. If diarrhea occurs, carefully monitor serum electrolytes and ECGs to reduce the risk and enable early detection of QT prolongation resulting from dehydration [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]. Interrupt CAPRELSA for severe diarrhea. Upon improvement, resume CAPRELSA at a reduced dose [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.1)].
- [Drug Interactions]
- Avoid administration of CAPRELSA with anti-arrhythmic drugs (including but not limited to amiodarone, disopyramide, procainamide, sotalol, dofetilide) and other drugs that may prolong the QT interval (including but not limited to chloroquine, clarithromycin, dolasetron, granisetron, haloperidol, methadone, moxifloxacin, and pimozide) [see DRUG INTERACTIONS (7.4) and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.2)].
- [Renal Impairment]
- Vandetanib exposure is increased in patients with impaired renal function. Reduce the starting dose to 200 mg in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment and monitor the QT interval closely. There is no information available for patients with end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis [see BOXED WARNING, DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.1), USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.6) and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.3)].
- [CAPRELSA REMS (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy) Program]
- Because of the risk of QT prolongation, Torsades de pointes, and sudden death, CAPRELSA is available only through a restricted distribution program called the CAPRELSA REMS Program. Only prescribers and pharmacies certified with the program are able to prescribe and dispense CAPRELSA.
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Drugs that Prolong the QT Interval
- Avoid concomitant use of CAPRELSA with agents that may prolong the QT interval [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.11)].
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Do not use in patients with congenital long QT syndrome [see BOXED WARNING].
- OVERDOSAGE
- In the event of an overdose, monitor patients closely for QTc prolongation. Because of the 19-day half-life, adverse reactions may not resolve quickly.
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Dosage Adjustment
- Interrupt CAPRELSA for the following:
- Corrected QT interval, Fridericia (QTcF) greater than 500 ms: Resume at a reduced dose when the QTcF returns to less than 450 ms.
- CTCAE Grade 3 or greater toxicity: Resume at a reduced dose when the toxicity resolves or improves to CTCAE Grade 1.
- For recurrent toxicities, reduce the dose of CAPRELSA to 100 mg after resolution or improvement to CTCAE Grade 1 severity, if continued treatment is warranted.
- Because of the 19-day half-life, adverse reactions including a prolonged QT interval may not resolve quickly. Monitor appropriately [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1), (5.2), (5.3), (5.4), (5.5), (5.6), (5.7), and (5.9)].
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Clinical Trials Experience
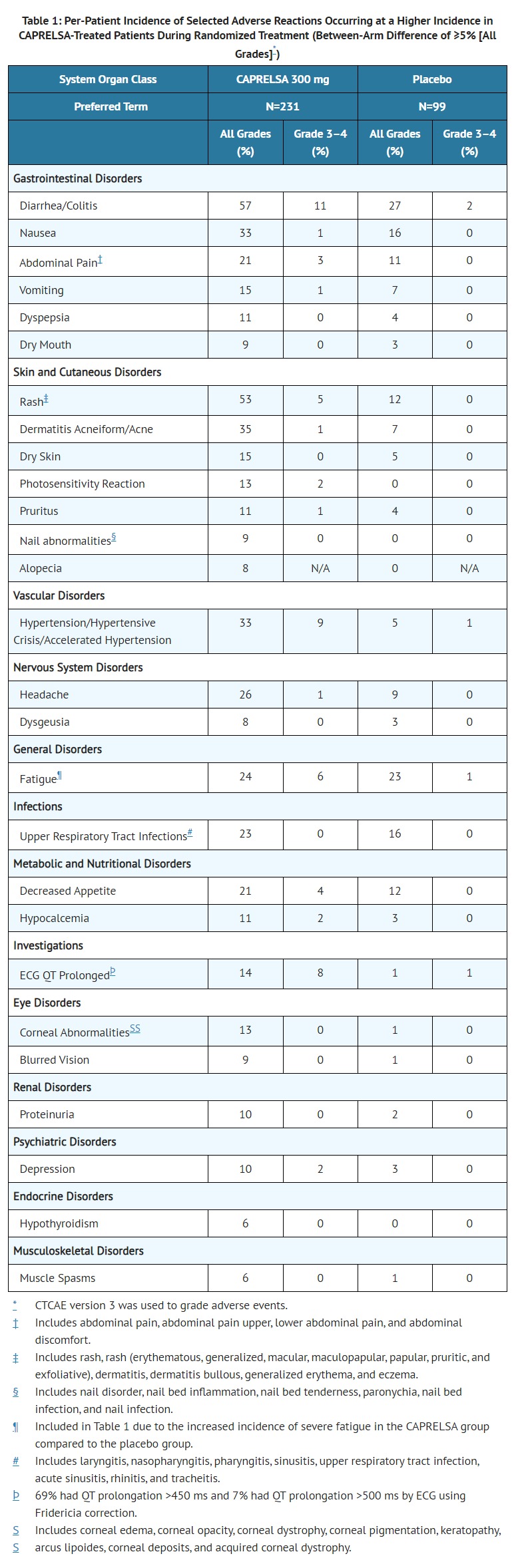
- Among CAPRELSA-treated patients, dose interruption occurred in 109 (47%) and dose reduction occurred in 83 (36%). Adverse reactions led to study treatment discontinuation in 28 of 231 patients (12%) receiving CAPRELSA and in 3 of 99 patients (3.0%) receiving placebo. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation in 2 or more (≥0.9%) patients treated with CAPRELSA were: asthenia (1.7%), rash (1.7%), diarrhea (0.9%), fatigue (0.9%), pyrexia (0.9%), elevated creatinine (0.9%), QT prolongation (0.9%), and hypertension (0.9%).
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- In 231 patients with medullary thyroid cancer randomized to receive CAPRELSA 300 mg once daily in the phase 3 clinical trial. CAPRELSA was associated with sustained plasma concentration-dependent QT prolongation. Based on the exposure-response relationship, the mean (90% CI) QTcF change from baseline (ΔQTcF) was 35 (33–36) ms for the 300 mg dose. The ΔQTcF remained above 30 ms for the duration of the trial (up to 2 years). In addition, 36% of patients experienced greater than 60 ms increase in ΔQTcF and 4.3% of patients had QTcF greater than 500 ms. Cases of Torsades de pointes and sudden death have occurred [see BOXED WARNING and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1), (5.11)].
- PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
- Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider in the event of syncope, pre-syncopal symptoms, and cardiac palpitations. Advise patients that their healthcare provider will monitor their electrolytes and ECGs during treatment [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
- MEDICATION GUIDE
- CAPRELSA can cause a change in the electrical activity of your heart called QT prolongation, which can cause irregular heartbeats and that may lead to death. You should not take CAPRELSA if you have had a condition called long QT syndrome since birth.
- Your healthcare provider should perform tests to check the levels of your blood potassium, calcium, magnesium, and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), as well as the electrical activity of your heart with a test called an electrocardiogram (ECG). You should have these tests:
- Before starting CAPRELSA
- Regularly during CAPRELSA treatment:
- 2 to 4 weeks after starting CAPRELSA
- 8 to 12 weeks after starting CAPRELSA
- every 3 months thereafter
- if your healthcare provider changes your dose of CAPRELSA
- if you start taking medicine that causes QT prolongation
- as instructed by your healthcare provider
- Your healthcare provider may stop your CAPRELSA treatment for a while and restart you at a lower dose if you have QT prolongation.
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you feel faint, light-headed, or feel your heart beating irregularly while taking CAPRELSA. These may be symptoms related to QT prolongation.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
86
24006
Other ADRs
3463
38378124
Odds Ratio = 39.702
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- L01EX04 - vandetanib
- L01EX -
- L01E -
- L01 - ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS
- L - ANTINEOPLASTIC AND IMMUNOMODULATING AGENTS
Active Ingredient:VANDETANIB
Active Ingredient UNII:YO460OQ37K
Drugbank ID:DB05294
PubChem Compound:3081361
CTD ID:C452423
PharmGKB:PA166118341
CAS Number:443913-73-3
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
Chemical Structure: 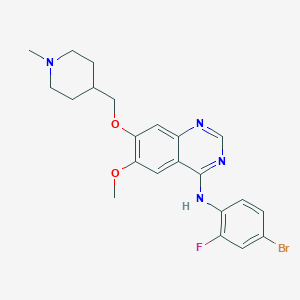

SMILE Code:
COC1=C(OCC2CCN(C)CC2)C=C2N=CN=C(NC3=C(F)C=C(Br)C=C3)C2=C1
COC1=C(OCC2CCN(C)CC2)C=C2N=CN=C(NC3=C(F)C=C(Br)C=C3)C2=C1
Reference
1: Thyroid cancer and COVID-19: experience at one single thyroid disease referral center.
[Prete Alessandro,Falcone Marco,Bottici Valeria,Giani Carlotta,Tiseo Giusy,Agate Laura,Matrone Antonio,Cappagli Virginia,Valerio Laura,Lorusso Loredana,Minaldi Elisa,Molinaro Eleonora,Elisei Rossella]Endocrine,2021 Feb 27;1-8. PMID: 33638758
2: Comparative efficacy and safety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for thyroid cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
[Oba Takaaki,Chino Tatsunori,Soma Ai,Shimizu Tadafumi,Ono Mayu,Ito Tokiko,Kanai Toshiharu,Maeno Kazuma,Ito Ken-Ichi]Endocr J,2020 Dec 28;67(12):1215-1226. PMID: 32814730
3: Evaluating vandetanib in the treatment of medullary thyroid cancer: patient-reported outcomes.
[Fallahi Poupak,Ferrari Silvia Martina,Elia Giusy,Ragusa Francesca,Paparo Sabrina Rosaria,Ruffilli Ilaria,Patrizio Armando,Materazzi Gabriele,Antonelli Alessandro]Cancer Manag Res,2019 Aug 21;11:7893-7907. PMID: 31686907
4: Vandetanib photoinduced cutaneous toxicities.
[Doan Hung Q,Hu Mimi I,Goldstein Jennifer,Piha-Paul Sarina A,Subbiah Vivek,Patel Anisha B]Cutis,2019 May;103(5):E24-E29. PMID: 31233590
5: Safety and efficacy of two starting doses of vandetanib in advanced medullary thyroid cancer.
[Hu Mimi I,Elisei Rossella,Dedecjus Marek,Popovtzer Aron,Druce Maralyn,Kapiteijn Ellen,Pacini Furio,Locati Laura,Krajewska Jolanta,Weiss Richard,Gagel Robert F]Endocr Relat Cancer,2019 Feb 1;26(2):241-250. PMID: 30557850
6: Management of treatment-related toxicities in advanced medullary thyroid cancer.
[Brose Marcia S,Bible Keith C,Chow Laura Q M,Gilbert Jill,Grande Carolyn,Worden Francis,Haddad Robert]Cancer Treat Rev,2018 May;66:64-73. PMID: 29704768
7: Vandetanib in patients with previously treated RET-rearranged advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (LURET): an open-label, multicentre phase 2 trial.
[Yoh Kiyotaka,Seto Takashi,Satouchi Miyako,Nishio Makoto,Yamamoto Noboru,Murakami Haruyasu,Nogami Naoyuki,Matsumoto Shingo,Kohno Takashi,Tsuta Koji,Tsuchihara Katsuya,Ishii Genichiro,Nomura Shogo,Sato Akihiro,Ohtsu Atsushi,Ohe Yuichiro,Goto Koichi]Lancet Respir Med,2017 Jan;5(1):42-50. PMID: 27825616
8: SAFETY AND TOLERABILITY OF VANDETANIB IN JAPANESE PATIENTS WITH MEDULLARY THYROID CANCER: A PHASE I/II OPEN-LABEL STUDY.
[Uchino Keita,Komoda Masato,Tomomatsu Junichi,Okamoto Takahiro,Horiuchi Kiyomi,Tsuji Akihito,Ito Yasuhiro,Todo Takuya,Rito Ki,Takahashi Shunji]Endocr Pract,2017 Feb;23(2):149-156. PMID: 27819766
9: Vandetanib in pretreated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer-harboring RET rearrangement: a phase II clinical trial.
[Lee S-H,Lee J-K,Ahn M-J,Kim D-W,Sun J-M,Keam B,Kim T M,Heo D S,Ahn J S,Choi Y-L,Min H-S,Jeon Y K,Park K]Ann Oncol,2017 Feb 1;28(2):292-297. PMID: 27803005
10: The safety and efficacy of vandetanib in the treatment of progressive medullary thyroid cancer.
[Fallahi Poupak,Ferrari Silvia Martina,Baldini Enke,Biricotti Marco,Ulisse Salvatore,Materazzi Gabriele,Miccoli Paolo,Antonelli Alessandro]Expert Rev Anticancer Ther,2016 Nov;16(11):1109-1118. PMID: 27650489
11: Treatment compliance and severe adverse events limit the use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in refractory thyroid cancer.
[Chrisoulidou Alexandra,Mandanas Stylianos,Margaritidou Efterpi,Mathiopoulou Lemonia,Boudina Maria,Georgopoulos Konstantinos,Pazaitou-Panayiotou Kalliopi]Onco Targets Ther,2015 Sep 3;8:2435-42. PMID: 26366098
12: Selective use of vandetanib in the treatment of thyroid cancer.
[Fallahi Poupak,Di Bari Flavia,Ferrari Silvia Martina,Spisni Roberto,Materazzi Gabriele,Miccoli Paolo,Benvenga Salvatore,Antonelli Alessandro]Drug Des Devel Ther,2015 Jul 3;9:3459-70. PMID: 26170630
13: Meta-analysis of the risks of hypertension and QTc prolongation in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer who were receiving vandetanib.
[Liu Ying,Liu Yi,Fan Zai-Wen,Li Jian,Xu Guo-Gang]Eur J Clin Pharmacol,2015 May;71(5):541-7. PMID: 25753291
14: QTc interval prolongation with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
[Ghatalia P,Je Y,Kaymakcalan M D,Sonpavde G,Choueiri T K]Br J Cancer,2015 Jan 20;112(2):296-305. PMID: 25349964
15: Vandetanib for the treatment of medullary thyroid carcinoma.
[Cooper Maryann R,Yi Soo Yun,Alghamdi Wael,Shaheen Daniel J,Steinberg Michael]Ann Pharmacother,2014 Mar;48(3):387-94. PMID: 24259657
16: Vandetanib for the treatment of medullary thyroid cancer.
[Chau Nicole G,Haddad Robert I]Clin Cancer Res,2013 Feb 1;19(3):524-9. PMID: 23231950
17: Vandetanib and the management of advanced medullary thyroid cancer.
[Campbell Michael J,Seib Carolyn D,Gosnell Jessica]Curr Opin Oncol,2013 Jan;25(1):39-43. PMID: 23202050
18: Chemotherapy plus Vandetanib or chemotherapy alone in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of four randomised controlled trials.
[Xiao Yong-Ying,Zhan Ping,Yuan Dong-Mei,Liu Hong-Bing,Lv Tang-Feng,Shi Yi,Song Yong]Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol),2013 Jan;25(1):e7-e15. PMID: 23177099
19: Vandetanib therapy in medullary thyroid cancer.
[Grabowski P,Briest F,Baum R P,Zaknun J J,Kulkarni H R,Zeitz M,Hörsch D]Drugs Today (Barc),2012 Nov;48(11):723-33. PMID: 23170308
20: Vandetanib in locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 trial.
[Leboulleux Sophie,Bastholt Lars,Krause Thomas,de la Fouchardiere Christelle,Tennvall Jan,Awada Ahmad,Gómez José Manuel,Bonichon Françoise,Leenhardt Laurence,Soufflet Christine,Licour Muriel,Schlumberger Martin J]Lancet Oncol,2012 Sep;13(9):897-905. PMID: 22898678
21: Phase I study of cetuximab, irinotecan, and vandetanib (ZD6474) as therapy for patients with previously treated metastastic colorectal cancer.
[Meyerhardt Jeffrey A,Ancukiewicz Marek,Abrams Thomas A,Schrag Deborah,Enzinger Peter C,Chan Jennifer A,Kulke Matthew H,Wolpin Brian M,Goldstein Michael,Blaszkowsky Lawrence,Zhu Andrew X,Elliott Meaghan,Regan Eileen,Jain Rakesh K,Duda Dan G]PLoS One,2012;7(6):e38231. PMID: 22701615
22: Vandetanib for the treatment of symptomatic or progressive medullary thyroid cancer in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease: U.S. Food and Drug Administration drug approval summary.
[Thornton Katherine,Kim Geoffrey,Maher V Ellen,Chattopadhyay Somesh,Tang Shenghui,Moon Young Jin,Song Pengfei,Marathe Anshu,Balakrishnan Suchitra,Zhu Hao,Garnett Christine,Liu Qi,Booth Brian,Gehrke Brenda,Dorsam Robert,Verbois Leigh,Ghosh Debasis,Wilson Wendy,Duan John,Sarker Haripada,Miksinski Sarah Pope,Skarupa Lisa,Ibrahim Amna,Justice Robert,Murgo Anthony,Pazdur Richard]Clin Cancer Res,2012 Jul 15;18(14):3722-30. PMID: 22665903
23: [Vandetanib treatment in refractory advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients: five cases and review of literature].
[Guo Lili,Tang Junfang,Meng Qiyi,Zhu Yunzhong,Xu Liyan,Shi Heling,Liu Zhe]Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi,2012 Feb;15(2):122-6. PMID: 22336242
24: A phase I study of Vandetanib in combination with vinorelbine/cisplatin or gemcitabine/cisplatin as first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
[Blackhall Fiona H,O'brien Mary,Schmid Peter,Nicolson Marianne,Taylor Paul,Milenkova Tsveta,Kennedy Sarah J,Thatcher Nick]J Thorac Oncol,2010 Aug;5(8):1285-8. PMID: 20661087
25: Vandetanib (ZD6474), a dual inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinases: current status and future directions.
[Morabito Alessandro,Piccirillo Maria Carmela,Falasconi Fabiano,De Feo Gianfranco,Del Giudice Antonia,Bryce Jane,Di Maio Massimo,De Maio Ermelinda,Normanno Nicola,Perrone Francesco]Oncologist,2009 Apr;14(4):378-90. PMID: 19349511
26: An open-label study of vandetanib with pemetrexed in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer.
[de Boer R,Humblet Y,Wolf J,Nogová L,Ruffert K,Milenkova T,Smith R,Godwood A,Vansteenkiste J]Ann Oncol,2009 Mar;20(3):486-91. PMID: 19088171
27: A randomized, double-blind, phase IIa dose-finding study of Vandetanib (ZD6474) in Japanese patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
[Kiura Katsuyuki,Nakagawa Kazuhiko,Shinkai Tetsu,Eguchi Kenji,Ohe Yuichiro,Yamamoto Nobuyuki,Tsuboi Masahiro,Yokota Soichiro,Seto Takashi,Jiang Haiyi,Nishio Kazuto,Saijo Nagahiro,Fukuoka Masahiro]J Thorac Oncol,2008 Apr;3(4):386-93. PMID: 18379357
28: Phase II study of vandetanib or placebo in small-cell lung cancer patients after complete or partial response to induction chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy: National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR.20.
[Arnold Andrew M,Seymour Lesley,Smylie Michael,Ding Keyue,Ung Yee,Findlay Brian,Lee Christopher W,Djurfeldt Marina,Whitehead Marlo,Ellis Peter,Goss Glenwood,Chan Adrien,Meharchand Jacinta,Alam Yasmin,Gregg Richard,Butts Charles,Langmuir Peter,Shepherd Frances,National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR.20]J Clin Oncol,2007 Sep 20;25(27):4278-84. PMID: 17878480
29: Vandetanib, a novel multitargeted kinase inhibitor, in cancer therapy.
[Sathornsumetee Sith,Rich Jeremy N]Drugs Today (Barc),2006 Oct;42(10):657-70. PMID: 17136225
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.