Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
DISOPYRAMIDE PHOSPHATE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS
- MORTALITY
- In the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute's Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST), a long-term, multi-center, randomized, double-blind study in patients with asymptomatic non-life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias who had had a myocardial infarction more than 6 days but less than 2 years previously, an excessive mortality or non-fatal cardiac arrest rate (7.7%) was seen in patients treated with encainide or flecainide compared with that seen in patients assigned to carefully matched placebo-treated groups (3.0%). The average duration of treatment with encainide or flecainide in this study was 10 months.
- The applicability of the CAST results to other populations (e.g., those without recent myocardial infarction) is uncertain. Considering the known proarrhythmic properties of Norpace or Norpace CR and the lack of evidence of improved survival for any antiarrhythmic drug in patients without life-threatening arrhythmias, the use of Norpace or Norpace CR as well as other antiarrhythmic agents should be reserved for patients with life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
- [Q-T Prolongation]
- As with other Type 1 antiarrhythmic drugs, prolongation of the Q-T interval (corrected) and worsening of the arrhythmia, including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, may occur. Patients who have evidenced prolongation of the Q-T interval in response to quinidine may be at particular risk. As with other Type 1A antiarrhythmics, disopyramide phosphate has been associated with torsade de pointes.
- If a Q-T prolongation of greater than 25% is observed and if ectopy continues, the patient should be monitored closely, and consideration given to discontinuing Norpace or Norpace CR.
- [Concomitant Antiarrhythmic Therapy]
- The concomitant use of Norpace or Norpace CR with other Type 1A antiarrhythmic agents (such as quinidine or procainamide), Type 1C antiarrhythmics (such as encainide, flecainide or propafenone), and/or propranolol should be reserved for patients with life-threatening arrhythmias who are demonstrably unresponsive to single-agent antiarrhythmic therapy. Such use may produce serious negative inotropic effects, or may excessively prolong conduction. This should be considered particularly in patients with any degree of cardiac decompensation or those with a prior history thereof. Patients receiving more than one antiarrhythmic drug must be carefully monitored.
- PRECAUTIONS
- Drug Interactions
- If phenytoin or other hepatic enzyme inducers are taken concurrently with Norpace or Norpace CR, lower plasma levels of disopyramide may occur. Monitoring of disopyramide plasma levels is recommended in such concurrent use to avoid ineffective therapy. Other antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g., quinidine, procainamide, lidocaine, propranolol) have occasionally been used concurrently with Norpace. Excessive widening of the QRS complex and/or prolongation of the Q-T interval may occur in these situations (see WARNINGS). In healthy subjects, no significant drug-drug interaction was observed when Norpace was coadministered with either propranolol or diazepam. Concomitant administration of Norpace and quinidine resulted in slight increases in plasma disopyramide levels and slight decreases in plasma quinidine levels. Norpace does not increase serum digoxin levels.
- Until data on possible interactions between verapamil and disopyramide phosphate are obtained, disopyramide should not be administered within 48 hours before or 24 hours after verapamil administration.
- Although potent inhibitors of cytochrome P450 3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole) have not been studied clinically, in vitro studies have shown that erythromycin and oleandomycin inhibit the metabolism of disopyramide. Cases of life-threatening interactions have been reported for disopyramide when given with clarithromycin and erythromycin indicating that coadministration of disopyramide with inhibitors of cytochrome 3A4 could result in potentially fatal interaction.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Norpace and Norpace CR are contraindicated in the presence of cardiogenic shock, preexisting second-or third-degree AV block (if no pacemaker is present), congenital Q-T prolongation, or known hypersensitivity to the drug.
- OVERDOSAGE
- Symptoms
- Deliberate or accidental overdosage of oral disopyramide may be followed by apnea, loss of consciousness, cardiac arrhythmias, and loss of spontaneous respiration. Death has occurred following overdosage.
- Toxic plasma levels of disopyramide produce excessive widening of the QRS complex and Q-T interval, worsening of congestive heart failure, hypotension, varying kinds and degrees of conduction disturbance, bradycardia, and finally asystole. Obvious anticholinergic effects are also observed.
- The approximate oral LD50 of disopyramide phosphate is 580 and 700 mg/kg for rats and mice, respectively.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
18
24074
Other ADRs
1171
38380416
Odds Ratio = 24.507
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- C01BA03 - disopyramide phosphate
- C01BA - "Antiarrhythmics, class Ia"
- C01B - "ANTIARRHYTHMICS, CLASS I AND III"
- C01 - CARDIAC THERAPY
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:DISOPYRAMIDE PHOSPHATE
Active Ingredient UNII:N6BOM1935W
Drugbank ID:DB00280
PubChem Compound:3114
CTD ID:D004206
PharmGKB:PA449373
CAS Number:3737-09-5
Dosage Form(s):capsule, extended release; capsule, gelatin coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 400.0 mg/day C01BA03
Chemical Structure: 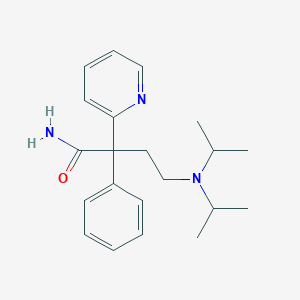

SMILE Code:
CC(C)N(CCC(C(N)=O)(C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=NC=CC=C1)C(C)C
CC(C)N(CCC(C(N)=O)(C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=NC=CC=C1)C(C)C
Reference
1: Concurrent use of quinidine and disopyramide: evaluation of serum concentrations and electrocardiographic effects.
[Baker B J,Gammill J,Massengill J,Schubert E,Karin A,Doherty J E]Am Heart J,1983 Jan;105(1):12-5. PMID: 6849225
2: Disopyramide-induced Torsade de Pointes.
[Tzivoni D,Keren A,Stern S,Gottlieb S]Arch Intern Med,1981 Jun;141(7):946-7. PMID: 7235820
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.