Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
ARIPIPRAZOLE
DIR Classification
Classification:Moderate-DIQT concern
Severity Score:2.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- OVERDOSAGE
- Human Experience
- In clinical trials and in postmarketing experience, adverse reactions of deliberate or accidental overdosage with oral aripiprazole have been reported worldwide. These include overdoses with oral aripiprazole alone and in combination with other substances. No fatality was reported with aripiprazole alone. The largest known dose with a known outcome involved acute ingestion of 1260 mg of oral aripiprazole (42 times the maximum recommended daily dose) by a patient who fully recovered. Deliberate or accidental overdosage was also reported in children (age 12 and younger) involving oral aripiprazole ingestions up to 195 mg with no fatalities.
- Common adverse reactions (reported in at least 5% of all overdose cases) reported with oral aripiprazole overdosage (alone or in combination with other substances) include vomiting, somnolence, and tremor. Other clinically important signs and symptoms observed in one or more patients with aripiprazole overdoses (alone or with other substances) include acidosis, aggression, aspartate aminotransferase increased, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, coma, confusional state, convulsion, blood creatine phosphokinase increased, depressed level of consciousness, hypertension, hypokalemia, hypotension, lethargy, loss of consciousness, QRS complex prolonged, QT prolonged, pneumonia aspiration, respiratory arrest, status epilepticus, and tachycardia.
- [Management of Overdosage]
- No specific information is available on the treatment of overdose with aripiprazole. An electrocardiogram should be obtained in case of overdosage and if QT interval prolongation is present, cardiac monitoring should be instituted. Otherwise, management of overdose should concentrate on supportive therapy, maintaining an adequate airway, oxygenation and ventilation, and management of symptoms. Close medical supervision and monitoring should continue until the patient recovers.
- Charcoal: In the event of an overdose of aripiprazole, an early charcoal administration may be useful in partially preventing the absorption of aripiprazole. Administration of 50 g of activated charcoal, one hour after a single 15 mg oral dose of aripiprazole, decreased the mean AUC and C max of aripiprazole by 50%.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Clinical Trials Experience
- Investigations:
- frequent - weight decreased, infrequent - hepatic enzyme increased, blood glucose increased, blood lactate dehydrogenase increased, gamma glutamyl transferase increased; rare – blood prolactin increased, blood urea increased, blood creatinine increased, blood bilirubin increased, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, glycosylated hemoglobin increased
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
307
23785
Other ADRs
154354
38227233
Odds Ratio = 3.197
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- N05AX12 - aripiprazole
- N05AX - Other antipsychotics
- N05A - ANTIPSYCHOTICS
- N05 - PSYCHOLEPTICS
- N - NERVOUS SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:ARIPIPRAZOLE
Active Ingredient UNII:82VFR53I78
Drugbank ID:DB01238
PubChem Compound:60795
CTD ID:D000068180
PharmGKB:PA10026
CAS Number:129722-12-9
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 15.0 mg/day N05AX12
Chemical Structure: 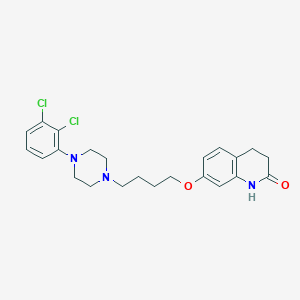

SMILE Code:
ClC1=CC=CC(N2CCN(CCCCOC3=CC4=C(CCC(=O)N4)C=C3)CC2)=C1Cl
ClC1=CC=CC(N2CCN(CCCCOC3=CC4=C(CCC(=O)N4)C=C3)CC2)=C1Cl
Reference
1: Antipsychotics in routine treatment are minor contributors to QT prolongation compared to genetics and age.
[Hommers Leif,Scherf-Clavel Maike,Stempel Roberta,Roth Julian,Falter Matthias,Deckert Jürgen,Mattheisen Manuel,Unterecker Stefan,Gawlik Micha]J Psychopharmacol,2021 Mar 28;2698811211003477. PMID: 33779379
2: [Brexpiprazole for treatment of schizophrenia: a critical literature study].
[Spoelstra S K,Baas C A J,Knegtering H]Tijdschr Psychiatr,2021;63(1):48-55. PMID: 33537974
3: Gastrointestinal absorption of pimozide is enhanced by inhibition of P-glycoprotein.
[Morishita Hiroki,Okawa Kozue,Ishii Misaki,Mizoi Kenta,Ito Masa-Aki,Arakawa Hiroshi,Yano Kentaro,Ogihara Takuo]PLoS One,2020 Oct 29;15(10):e0232438. PMID: 33119612
4: Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions During Antipsychotic Treatment: Results of AMSP, A Drug Surveillance Program Between 1993 and 2013.
[Friedrich Michaela-Elena,Winkler Dietmar,Konstantinidis Anastasios,Huf Wolfgang,Engel Rolf,Toto Sermin,Grohmann Renate,Kasper Siegfried]Int J Neuropsychopharmacol,2020 Feb 1;23(2):67-75. PMID: 31504560
5: Antipsychotics for patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome.
[Nutting Sean,Martin Christopher,Prensner Richard,Francis Andrew,Bellon Alfredo]Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses,2019 Jan 3. PMID: 30649911
6: ISMP Adverse Drug Reactions: Lithium-Induced Cardiomyopathy Fixed Drug Eruption Due to Cetirizine, Levocetirizine, and Hydroxyzine Nivolumab-Induced Myasthenia Gravis Nivolumab-Induced Cholangitic Liver Disease Torsade de Pointes Caused by Psychiatric Polypharmacy Trichotillomania Associated With Aripiprazole.
[Mancano Michael A,Bulow Jacqueline Emily Von,Ro Myungsun]Hosp Pharm,2018 Dec;53(6):371-375. PMID: 30559522
7: Clozapine-related Sudden Pericarditis in a Patient Taking Long Acting Aripiprazole and Valproate: A Case Report.
[De Berardis Domenico,Fornaro Michele,Orsolini Laura,Olivieri Luigi,Nappi Francesco,Rapini Gabriella,Vellante Federica,Napoletano Cosimo,Serroni Nicola,Giannantonio Massimo Di]Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci,2018 Nov 30;16(4):505-507. PMID: 30466225
8: Effects of atypical antipsychotic drugs on QT interval in patients with mental disorders.
[Aronow Wilbert S,Shamliyan Tatyana A]Ann Transl Med,2018 Apr;6(8):147. PMID: 29862236
9: QTc prolongation in short-term treatment of schizophrenia patients: effects of different antipsychotics and genetic factors.
[Spellmann Ilja,Reinhard Matthias A,Veverka Diana,Zill Peter,Obermeier Michael,Dehning Sandra,Schennach Rebecca,Müller Norbert,Möller Hans-Jürgen,Riedel Michael,Musil Richard]Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci,2018 Jun;268(4):383-390. PMID: 29429138
10: QT Prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, and Psychotropic Medications: A 5-Year Update.
[Beach Scott R,Celano Christopher M,Sugrue Alan M,Adams Caitlin,Ackerman Michael J,Noseworthy Peter A,Huffman Jeff C]Psychosomatics,Mar-Apr 2018;59(2):105-122. PMID: 29275963
11: Prevalence and correlates of QTc prolongation in Italian psychiatric care: cross-sectional multicentre study.
[Nosè M,Bighelli I,Castellazzi M,Martinotti G,Carrà G,Lucii C,Ostuzzi G,Sozzi F,Barbui C,STAR NETWORK GROUP]Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci,2016 Dec;25(6):532-540. PMID: 26467074
12: Antipsychotic Dose Mediates the Association between Polypharmacy and Corrected QT Interval.
[Barbui Corrado,Bighelli Irene,Carrà Giuseppe,Castellazzi Mariasole,Lucii Claudio,Martinotti Giovanni,Nosè Michela,Ostuzzi Giovanni,STAR NETWORK INVESTIGATORS]PLoS One,2016 Feb 3;11(2):e0148212. PMID: 26840602
13: Effects of aripiprazole on the QTc: a case report.
[Karz Adam J,McGonigle Daniel P,Goldberg Joseph F,Kellner Charles H,Calenda Brandon S]J Clin Psychiatry,2015 Dec;76(12):1648-9. PMID: 26717525
14: The Contribution of National Spontaneous Reporting Systems to Detect Signals of Torsadogenicity: Issues Emerging from the ARITMO Project.
[Raschi Emanuel,Poluzzi Elisabetta,Salvo Francesco,Koci Ariola,Suling Marc,Antoniazzi Stefania,Perina Luisella,Hazell Lorna,Moretti Ugo,Sturkenboom Miriam,Garbe Edeltraut,Pariente Antoine,De Ponti Fabrizio]Drug Saf,2016 Jan;39(1):59-68. PMID: 26446144
15: The cardiac safety of aripiprazole treatment in patients at high risk for torsade: a systematic review with a meta-analytic approach.
[Polcwiartek Christoffer,Sneider Benjamin,Graff Claus,Taylor David,Meyer Jonathan,Kanters Jørgen K,Nielsen Jimmi]Psychopharmacology (Berl),2015 Sep;232(18):3297-308. PMID: 26231497
16: Implications of atypical antipsychotic prescribing in the intensive care unit.
[Kram Bridgette L,Kram Shawn J,Brooks Kelli R]J Crit Care,2015 Aug;30(4):814-8. PMID: 25887805
17: Prolonged QT Risk Assessment in Antipsychotic Overdose Using the QT Nomogram.
[Berling Ingrid,Isbister Geoffrey K]Ann Emerg Med,2015 Aug;66(2):154-64. PMID: 25639523
18: Antipsychotics-associated serious adverse events in children: an analysis of the FAERS database.
[Kimura Goji,Kadoyama Kaori,Brown J B,Nakamura Tsutomu,Miki Ikuya,Nisiguchi Kohshi,Sakaeda Toshiyuki,Okuno Yasushi]Int J Med Sci,2015 Jan 5;12(2):135-40. PMID: 25589889
19: Corrected QT changes during antipsychotic treatment of children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials.
[Jensen Karsten Gjessing,Juul Klaus,Fink-Jensen Anders,Correll Christoph U,Pagsberg Anne Katrine]J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry,2015 Jan;54(1):25-36. PMID: 25524787
20: Management of psychosis and agitation in medical-surgical patients who have or are at risk for prolonged QT interval.
[Ries Rose,Sayadipour Amirali]J Psychiatr Pract,2014 Sep;20(5):338-44. PMID: 25226194
21: Aripiprazole-associated QTc prolongation in a geriatric patient.
[Hategan Ana,Bourgeois James A]J Clin Psychopharmacol,2014 Dec;34(6):766-8. PMID: 25203469
22: Cardiometabolic risks of blonanserin and perospirone in the management of schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
[Kishi Taro,Matsuda Yuki,Iwata Nakao]PLoS One,2014 Feb 4;9(2):e88049. PMID: 24505373
23: Quetiapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia.
[Asmal Laila,Flegar Srnka J,Wang Jikun,Rummel-Kluge Christine,Komossa Katja,Leucht Stefan]Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2013 Nov 18;(11):CD006625. PMID: 24249315
24: ECG parameters in children and adolescents treated with aripiprazole and risperidone.
[Germanò Eva,Italiano Domenico,Lamberti Marco,Guerriero Laura,Privitera Carmen,D'Amico Gessica,Siracusano Rosamaria,Ingrassia Massimo,Spina Edoardo,Calabrò Maria Pia,Gagliano Antonella]Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry,2014 Jun 3;51:23-7. PMID: 24211841
25: Validation of a population-based method to assess drug-induced alterations in the QT interval: a self-controlled crossover study.
[Iribarren Carlos,Round Alfred D,Peng Jonathan A,Lu Meng,Zaroff Jonathan G,Holve Taylor J,Prasad Amit,Stang Paul]Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf,2013 Nov;22(11):1222-32. PMID: 23857878
26: Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis.
[Leucht Stefan,Cipriani Andrea,Spineli Loukia,Mavridis Dimitris,Orey Deniz,Richter Franziska,Samara Myrto,Barbui Corrado,Engel Rolf R,Geddes John R,Kissling Werner,Stapf Marko Paul,Lässig Bettina,Salanti Georgia,Davis John M]Lancet,2013 Sep 14;382(9896):951-62. PMID: 23810019
27: Changes in QT interval after switching to quetiapine in Japanese patients with schizophrenia.
[Suzuki Yutaro,Sugai Takuro,Fukui Naoki,Watanabe Junzo,Ono Shin,Tsuneyama Nobuto,Saito Mami,Someya Toshiyuki]Hum Psychopharmacol,2013 Jan;28(1):94-6. PMID: 23161621
28: Safety of antipsychotics in the setting of QTc prolongation: the utility of the JT index.
[Mukherji Emily H,Bauer Leah K,Leskov Ilya,Januzzi James Louis,Tanev Kaloyan S]Am J Psychiatry,2011 Sep;168(9):990-1. PMID: 21890808
29: Cardiovascular safety of aripiprazole and pimozide in young patients with Tourette syndrome.
[Gulisano Mariangela,Calì Paola V,Cavanna Andrea E,Eddy Clare,Rickards Hugh,Rizzo Renata]Neurol Sci,2011 Dec;32(6):1213-7. PMID: 21732066
30: Aripiprazole as a viable alternative for treating delusions of parasitosis.
[Ladizinski Barry,Busse Kristine L,Bhutani Tina,Koo John Y M]J Drugs Dermatol,2010 Dec;9(12):1531-2. PMID: 21120263
31: Quetiapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia.
[Komossa Katja,Rummel-Kluge Christine,Schmid Franziska,Hunger Heike,Schwarz Sandra,Srisurapanont Manit,Kissling Werner,Leucht Stefan]Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2010 Jan 20;(1):CD006625. PMID: 20091600
32: Asenapine monotherapy in the acute treatment of both schizophrenia and bipolar I disorder.
[Bishara Delia,Taylor David]Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat,2009;5:483-90. PMID: 19851515
33: Aripiprazole versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia.
[Komossa Katja,Rummel-Kluge Christine,Schmid Franziska,Hunger Heike,Schwarz Sandra,El-Sayeh Hany George G,Kissling Werner,Leucht Stefan]Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2009 Oct 7;(4):CD006569. PMID: 19821375
34: Update on neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia: antipsychotic use.
[Kalapatapu Raj K,Schimming Corbett]Geriatrics,2009 May;64(5):10-8. PMID: 19435390
35: Sertindole versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia.
[Komossa Katja,Rummel-Kluge Christine,Hunger Heike,Schwarz Sandra,Schmidt Franziska,Lewis Ruth,Kissling Werner,Leucht Stefan]Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2009 Apr 15;(2):CD006752. PMID: 19370652
36: Asymptomatic QTc prolongation during coadministration of aripiprazole and haloperidol.
[Leo Roberto,Razzini Cinzia,Di Lorenzo Giorgio,Bianchi Francesco,Tesauro Manfredi,Zanasi Marco,Siracusano Alberto,Romeo Francesco]J Clin Psychiatry,2008 Feb;69(2):327-8. PMID: 18363460
37: Treatment of bipolar disorder: the evolving role of atypical antipsychotics.
[Perlis Roy H]Am J Manag Care,2007 Nov;13(7 Suppl):S178-88. PMID: 18041879
38: Aripiprazole in the treatment of acute manic or mixed episodes in patients with bipolar I disorder: a 3-week placebo-controlled study.
[Sachs Gary,Sanchez Raymond,Marcus Ronald,Stock Elyse,McQuade Robert,Carson William,Abou-Gharbia Neveen,Impellizzeri Cheryl,Kaplita Stephen,Rollin Linda,Iwamoto Taro,Aripiprazole Study Group]J Psychopharmacol,2006 Jul;20(4):536-46. PMID: 16401666
39: Aripiprazole: new drug. Just another neuroleptic.
Prescrire Int,2005 Oct;14(79):163-7. PMID: 16285069
40: Overdose of aripiprazole, a new type of antipsychotic.
[Carstairs Shaun D,Williams Saralyn R]J Emerg Med,2005 Apr;28(3):311-313. PMID: 15769575
41: Clinical experience with aripiprazole treatment in ten elderly patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder: retrospective case studies.
[Madhusoodanan Subramoniam,Brenner Ronald,Gupta Sanjay,Reddy Harsha,Bogunovic Olivera]CNS Spectr,2004 Nov;9(11):862-7. PMID: 15520608
42: Dopamine partial agonists: a new class of antipsychotic.
[Lieberman Jeffrey A]CNS Drugs,2004;18(4):251-67. PMID: 15015905
43: Using antipsychotic agents in older patients.
[Alexopoulos George S,Streim Joel,Carpenter Daniel,Docherty John P,Expert Consensus Panel for Using Antipsychotic Drugs in Older Patients]J Clin Psychiatry,2004;65 Suppl 2:5-99; discussion 100-102; quiz 103-4. PMID: 14994733
44: Open labeled, randomized, switch-over study of two fixed doses (10/15mg) of aripiprazole : to evaluate its safety and efficacy in the treatment of Indian patients of schizophrenia.
[Sarin A,Nagpal J,Bohra N K,Jiloha R C,Rao G P,Sharma S K,Vaishnav M,Vaya L,Karan R S,Patel N K,Patel R]Indian J Psychiatry,2004 Jan;46(1):64-71. PMID: 21206777
45: A placebo-controlled, double-blind study of the efficacy and safety of aripiprazole in patients with acute bipolar mania.
[Keck Paul E,Marcus Ronald,Tourkodimitris Stavros,Ali Mirza,Liebeskind Amy,Saha Anutosh,Ingenito Gary,Aripiprazole Study Group]Am J Psychiatry,2003 Sep;160(9):1651-8. PMID: 12944341
46: Aripiprazole: a partial dopamine D2 receptor agonist antipsychotic.
[Keck Paul E,McElroy Susan L]Expert Opin Investig Drugs,2003 Apr;12(4):655-62. PMID: 12665420
47: Aripiprazole.
[McGavin Jane K,Goa Karen L]CNS Drugs,2002;16(11):779-86; discussion 787-8. PMID: 12383035
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.