Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
MIRABEGRON
DIR Classification
Classification:Ambiguous
Severity Score:1.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- The effect of multiple doses of MYRBETRIQ 50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg once daily on QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized, placebo- and active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg), four-treatment-arm, parallel crossover study in 352 healthy subjects. In a study with demonstrated ability to detect small effects, the upper bound of the one-sided 95% confidence interval for the largest placebo-adjusted, baseline-corrected QTc based on individual correction method (QTcI) was below 10 msec. For the 50 mg MYRBETRIQ dose group (the maximum approved dosage), the mean difference from placebo on QTcI interval at 4 to 5 hours post-dose was 3.7 msec (upper bound of the 95% CI 5.1 msec).
- For the MYRBETRIQ 100 mg and 200 mg doses groups (dosages greater than the maximum approved dose and resulting in substantial multiples of the anticipated maximum blood levels at 50 mg), the mean differences from placebo in QTcI interval at 4 to 5 hours post-dose were 6.1 msec (upper bound of the 95% CI 7.6 msec) and 8.1 msec (upper bound of the 95% CI 9.8 msec), respectively. At the MYRBETRIQ 200 mg dose, in females, the mean effect was 10.4 msec (upper bound of the 95% CI 13.4 msec).
- In this thorough QT study, MYRBETRIQ increased heart rate on ECG in a dose-dependent manner. Maximum mean increases from baseline in heart rate for the 50 mg, 100 mg, and 200 mg dose groups compared to placebo were 6.7 beats per minutes (bpm), 11 bpm, and 17 bpm, respectively. In the clinical efficacy and safety studies, the change from baseline in mean pulse rate for MYRBETRIQ 50 mg was approximately 1 bpm. In this thorough QT study, MYRBETRIQ also increased blood pressure in a dose-dependent manner (see Effects on Blood Pressure).
- [Effects on Blood Pressure]
- In a study of 352 healthy subjects assessing the effect of multiple daily doses of 50 mg, 100 mg, and 200 mg of MYRBETRIQ for 10 days on the QTc interval, the maximum mean increase in supine systolic blood pressure (SBP)/diastolic blood pressure (DBP) at the maximum recommended dose of 50 mg was approximately 4.0/1.6 mm Hg greater than placebo. The 24-hour average increases in SBP compared to placebo were 3.0, 5.5, and 9.7 mm Hg at MYRBETRIQ doses of 50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg, respectively. Increases in DBP were also dose-dependent, but were smaller than SBP.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
34
24058
Other ADRs
34758
38346829
Odds Ratio = 1.56
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- G04BD12 - mirabegron
- G04BD1 -
- G04BD - Urinary antispasmodics
- G04B - "OTHER UROLOGICALS, INCL. ANTISPASMODICS"
- G04 - UROLOGICALS
- G - GENITO URINARY SYSTEM AND SEX HORMONES
Active Ingredient:MIRABEGRON
Active Ingredient UNII:MVR3JL3B2V
Drugbank ID:DB08893
PubChem Compound:9865528
CTD ID:C520025
CAS Number:223673-61-8
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated, extended release
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 50.0 mg/day G04BD12
Chemical Structure: 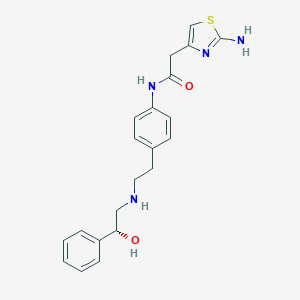

SMILE Code:
NC1=NC(CC(=O)NC2=CC=C(CCNC[C@H](O)C3=CC=CC=C3)C=C2)=CS1
NC1=NC(CC(=O)NC2=CC=C(CCNC[C@H](O)C3=CC=CC=C3)C=C2)=CS1
Reference
1: Cardiovascular effects of antimuscarinic agents and beta3-adrenergic receptor agonist for the treatment of overactive bladder.
[Rosa Gian Marco,Baccino Danilo,Valbusa Alberto,Scala Carolina,Barra Fabio,Brunelli Claudio,Ferrero Simone]Expert Opin Drug Saf,2018 May;17(5):487-497. PMID: 29542337
2: Cardiovascular safety in refractory incontinent patients with overactive bladder receiving add-on mirabegron therapy to solifenacin (BESIDE).
[Drake Marcus J,MacDiarmid Scott,Chapple Christopher R,Esen Adil,Athanasiou Stavros,Cambronero Santos Javier,Mitcheson David,Herschorn Sender,Siddiqui Emad,Huang Moses,Stoelzel Matthias]Int J Clin Pract,2017 May;71(5):e12944. PMID: 28419650
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.