Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
TOLTERODINE TARTRATE
DIR Classification
Classification:Moderate-DIQT concern
Severity Score:2.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- PRECAUTIONS
- Patients with Congenital or Acquired QT Prolongation
- In a study of the effect of tolterodine immediate release tablets on the QT interval (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY) , the effect on the QT interval appeared greater for 8 mg/day (two times the therapeutic dose) compared to 4 mg/day and was more pronounced in CYP2D6 poor metabolizers (PM) than extensive metabolizers (EMs). The effect of tolterodine 8 mg/day was not as large as that observed after four days of therapeutic dosing with the active control moxifloxacin. However, the confidence intervals overlapped. These observations should be considered in clinical decisions to prescribe tolterodine tartrate tablets for patients with a known history of QT prolongation or patients who are taking Class IA (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications (seePRECAUTIONS, DRUG INTERACTIONS) .There has been no association of Torsade de Pointes in the international post-marketing experience with tolterodine tartrate tablets or tolterodine tartrate extended-release capsules.
- OVERDOSAGE
- Management of Overdosage
- Overdosage with tolterodine tartrate tablets can potentially result in severe central anticholinergic effects and should be treated accordingly.
- ECG monitoring is recommended in the event of overdosage. In dogs, changes in the QT interval (slight prolongation of 10% to 20%) were observed at a suprapharmacologic dose of 4.5 mg/kg, which is about 68 times higher than the recommended human dose. In clinical trials of normal volunteers and patients, QT interval prolongation was observed with tolterodine immediate release at doses up to 8 mg (4 mg bid) and higher doses were not evaluated (see PRECAUTIONS, PATIENTS WITH CONGENITAL OR ACQUIRED QT PROLONGATION).
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- The effect of 2 mg BID and 4 mg BID of tolterodine immediate release (IR) on the QT interval was evaluated in a 4-way crossover, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg QD) study in healthy male (N=25) and female (N=23) volunteers aged 18–55 years. Study subjects [approximately equal representation of CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs) and poor metabolizers (PMs)] completed sequential 4-day periods of dosing with moxifloxacin 400 mg QD, tolterodine 2 mg BID, tolterodine 4 mg BID, and placebo. The 4 mg BID dose of tolterodine IR (two times the highest recommended dose) was chosen because this dose results in tolterodine exposure similar to that observed upon coadministration of tolterodine 2 mg BID with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors in patients who are CYP2D6 poor metabolizers (see PRECAUTIONS, DRUG INTERACTIONS). QT interval was measured over a 12-hour period following dosing, including the time of peak plasma concentration (Tmax) of tolterodine and at steady state (Day 4 of dosing).
- Table 2 summarizes the mean change from baseline to steady state in corrected QT interval (QTc) relative to placebo at the time of peak tolterodine (1 hour) and moxifloxacin (2 hour) concentrations. Both Fridericia's (QTcF) and a population-specific (QTcP) method were used to correct QT interval for heart rate. No single QT correction method is known to be more valid than others. QT interval was measured manually and by machine, and data from both are presented. The mean increase of heart rate associated with a 4 mg/day dose of tolterodine in this study was 2.0 beats/minute and 6.3 beats/minute with 8 mg/day tolterodine. The change in heart rate with moxifloxacin was 0.5 beats/minute.
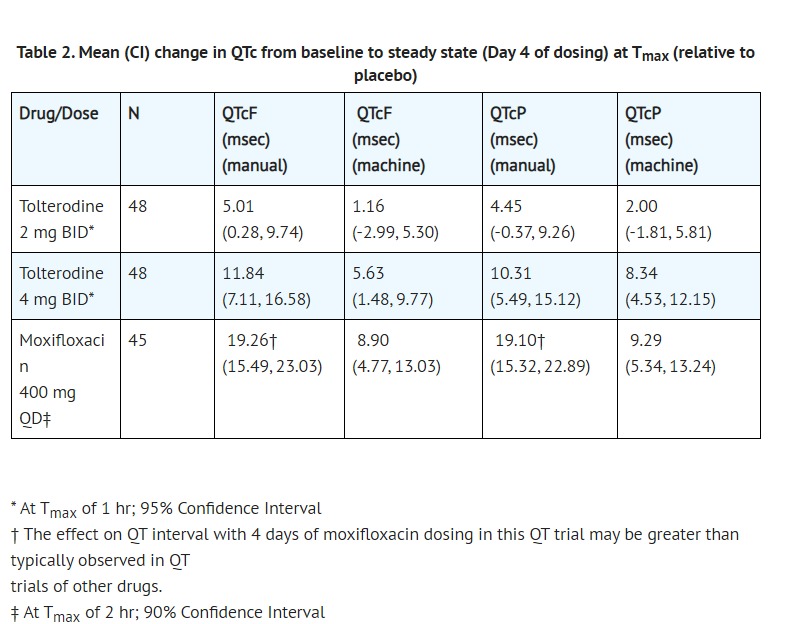
- The reason for the difference between machine and manual read of QT interval is unclear.
- The QT effect of tolterodine immediate release tablets appeared greater for 8 mg/day (two times the therapeutic dose) compared to 4 mg/day. The effect of tolterodine 8 mg/day was not as large as that observed after four days of therapeutic dosing with the active control moxifloxacin. However, the confidence intervals overlapped.
- Tolterodine's effect on QT interval was found to correlate with plasma concentration of tolterodine. There appeared to be a greater QTc interval increase in CYP2D6 poor metabolizers than in CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers after tolterodine treatment in this study.
- This study was not designed to make direct statistical comparisons between drugs or dose levels. There has been no association of Torsade de Pointes in the international post-marketing experience with tolterodine tartrate tablets or tolterodine tartrate extended-release capsules (see PRECAUTIONS, PATIENTS WITH CONGENITAL OR ACQUIRED QT PROLONGATION).
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
13
24079
Other ADRs
4587
38377000
Odds Ratio = 4.517
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- G04BD07 - tolterodine tartrate
- G04BD0 -
- G04BD - Urinary antispasmodics
- G04B - "OTHER UROLOGICALS, INCL. ANTISPASMODICS"
- G04 - UROLOGICALS
- G - GENITO URINARY SYSTEM AND SEX HORMONES
Active Ingredient:TOLTERODINE TARTRATE
Active Ingredient UNII:5T619TQR3R
Drugbank ID:DB01036
PubChem Compound:443879
CTD ID:D000068737
PharmGKB:PA164746757
CAS Number:124937-51-5
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 4.0 mg/day G04BD07
Chemical Structure: 

SMILE Code:
CC(C)N(CC[C@H](C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=C(O)C=CC(C)=C1)C(C)C
CC(C)N(CC[C@H](C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=C(O)C=CC(C)=C1)C(C)C
Reference
1: Virtual Thorough QT (TQT) Trial-Extrapolation of In Vitro Cardiac Safety Data to In Vivo Situation Using Multi-Scale Physiologically Based Ventricular Cell-wall Model Exemplified with Tolterodine and Fesoterodine.
[Patel Nikunjkumar,Wisniowska Barbara,Polak Sebastian]AAPS J,2018 Jul 11;20(5):83. PMID: 29995258
2: In vitro preclinical cardiac assessment of tolterodine and terodiline: multiple factors predict the clinical experience.
[Martin Ruth L,Su Zhi,Limberis James T,Palmatier Jason D,Cowart Marlon D,Cox Bryan F,Gintant Gary A]J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,2006 Nov;48(5):199-206. PMID: 17110801
3: Benefit-risk assessment of tolterodine in the treatment of overactive bladder in adults.
[Garely Alan D,Burrows Lara]Drug Saf,2004;27(13):1043-57. PMID: 15471509
4: Cardiac ion channel effects of tolterodine.
[Kang Jiesheng,Chen Xiao-Liang,Wang Hongge,Ji Junzhi,Reynolds William,Lim Sungtaek,Hendrix James,Rampe David]J Pharmacol Exp Ther,2004 Mar;308(3):935-40. PMID: 14711935
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.