Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
RIBOCICLIB
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QT Interval Prolongation
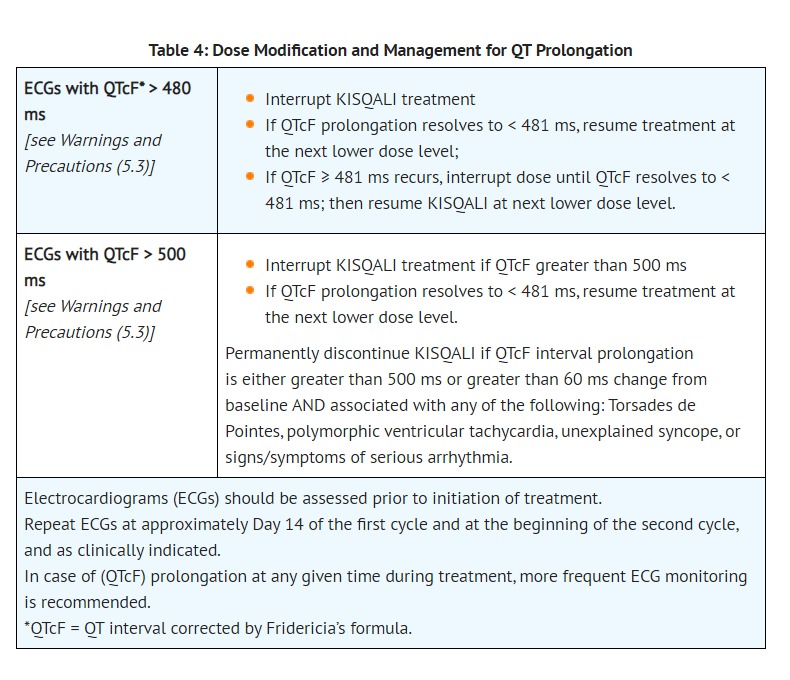
- KISQALI has been shown to prolong the QT interval in a concentration-dependent manner [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Based on the observed QT prolongation during treatment, KISQALI may require dose interruption, reduction or discontinuation as described in Table 4 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Drug Interactions (7.4)].
- Across MONALEESA-2, MONALEESA-7, and MONALEESA-3 in patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer who received the combination of KISQALI plus an aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant, 14 out of 1054 patients (1%) had a > 500 ms post-baseline QTcF value, and 59 out of 1054 patients (6%) had a > 60 ms increase from baseline in QTcF intervals.
- These ECG changes were reversible with dose interruption and the majority occurred within the first four weeks of treatment. There were no reported cases of Torsades de Pointes.
- In MONALEESA-2, on the KISQALI plus letrozole treatment arm, there was one (0.3%) sudden death in a patient with Grade 3 hypokalemia and Grade 2 QT prolongation. No cases of sudden death were reported in MONALEESA-7 or MONALEESA-3 [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
- Assess ECG prior to initiation of treatment. Initiate treatment with KISQALI only in patients with QTcF values less than 450 ms. Repeat ECG at approximately Day 14 of the first cycle and the beginning of the second cycle, and as clinically indicated.
- Monitor serum electrolytes (including potassium, calcium, phosphorous and magnesium) prior to the initiation of treatment, at the beginning of the first 6 cycles, and as clinically indicated. Correct any abnormality before starting KISQALI therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Avoid the use of KISQALI in patients who already have or who are at significant risk of developing QT prolongation, including patients with:long QT syndrome
- uncontrolled or significant cardiac disease including recent myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, unstable angina, and bradyarrhythmias
- electrolyte abnormalities
- Avoid using KISQALI with drugs known to prolong QT interval and/or strong CYP3A inhibitors as this may lead to prolongation of the QTcF interval.
- [Increased QT Prolongation With Concomitant Use of Tamoxifen]
- KISQALI is not indicated for concomitant use with tamoxifen. In MONALEESA-7, the observed mean QTcF increase from baseline was > 10 ms higher in the tamoxifen plus placebo subgroup compared with the non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors (NSAIs) plus placebo subgroup. In the placebo arm, an increase of > 60 ms from baseline occurred in 6/90 (7%) of patients receiving tamoxifen, and in no patients receiving an NSAI. An increase of > 60 ms from baseline in the QTcF interval was observed in 14/87 (16%) of patients in the KISQALI and tamoxifen combination and in 18/245 (7%) of patients receiving KISQALI plus an NSAI [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Drugs That Prolong the QT Interval
- Avoid coadministration of KISQALI with medicinal products with a known potential to prolong QT, such as antiarrhythmic medicines (including, but not limited to amiodarone, disopyramide, procainamide, quinidine, and sotalol), and other drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval (including, but not limited to, chloroquine, halofantrine, clarithromycin, haloperidol, methadone, moxifloxacin, bepridil, pimozide, and ondansetron) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- QT Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)]
- Hepatobiliary Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- [Clinical Trials Experience]
- On-treatment deaths, regardless of causality, were reported in three cases (0.9%) of KISQALI plus letrozole treated patients vs. one case (0.3%) of placebo plus letrozole treated patients. Causes of death on KISQALI plus letrozole included one case each of the following: progressive disease, death (cause unknown), and sudden death (in the setting of Grade 3 hypokalemia and Grade 2 QT prolongation).
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- Serial, triplicate ECGs were collected following a single dose and at steady-state to evaluate the effect of ribociclib on the QTcF interval in patients with advanced cancer. A pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis included a total of 997 patients treated with ribociclib at doses ranging from 50 to 1200 mg. The analysis suggested that ribociclib causes concentration-dependent increases in the QTcF interval. The estimated mean change from baseline in QTcF for KISQALI 600 mg in combination with aromatase inhibitors or fulvestrant was 22.0 ms (90% CI: 20.6, 23.4) and 23.7 ms (90% CI: 22.3, 25.1), respectively, and was 34.7 ms (90% CI: 31.6, 37.8) in combination with tamoxifen at the geometric mean Cmax at steady-state [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
- PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- QT Prolongation
- Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of QT prolongation. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of QT prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4)].
- [Drug Interactions]
- Inform patients to avoid grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking KISQALI [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
- Inform patients to avoid strong CYP3A inhibitors, strong CYP3A inducers, and drugs known to prolong the QT interval [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2, 7.4)].
- PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
- KISQALI may cause serious side effects, including:
- Heart rhythm problems (QT prolongation). KISQALI can cause a heart problem known as QT prolongation. This condition can cause an abnormal heartbeat and may lead to death. Your healthcare provider should check your heart and do blood tests before and during treatment with KISQALI. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have a change in your heartbeat (a fast or irregular heartbeat), or if you feel dizzy or faint.
- NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
- In vivo cardiac safety studies in dogs demonstrated dose and concentration related QTc interval prolongation at an exposure similar to patients receiving the recommended dose of 600 mg. There is a potential to induce incidences of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) at elevated exposures (approximately 5-fold the anticipated clinical Cmax).
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
188
23904
Other ADRs
19936
38361651
Odds Ratio = 15.134
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- L01EF02 - ribociclib
- L01EF -
- L01E -
- L01 - ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS
- L - ANTINEOPLASTIC AND IMMUNOMODULATING AGENTS
Active Ingredient:RIBOCICLIB
Active Ingredient UNII:TK8ERE8P56
Drugbank ID:DB11730
PubChem Compound:44631912
CTD ID:C000589651
PharmGKB:PA166153470
CAS Number:1211441-98-3
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
Chemical Structure: 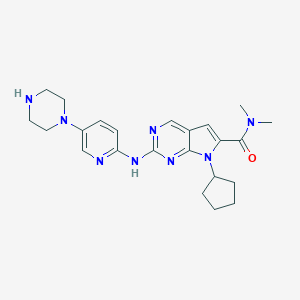

SMILE Code:
CN(C)C(=O)C1=CC2=CN=C(NC3=CC=C(C=N3)N3CCNCC3)N=C2N1C1CCCC1
CN(C)C(=O)C1=CC2=CN=C(NC3=CC=C(C=N3)N3CCNCC3)N=C2N1C1CCCC1
Reference
1: Phase I/II trial of exemestane, ribociclib, and everolimus in women with HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer after progression on CDK4/6 inhibitors (TRINITI-1).
[Bardia Aditya,Hurvitz Sara A,DeMichele Angela,Clark Amy S,Zelnak Amelia,Yardley Denise,Karuturi Meghan Sri,Sanft Tara,Blau Sibel,Hart Lowell,Ma Cynthia X,Rugo Hope S,Purkayastha Das,Moulder-Thompson Stacy]Clin Cancer Res,2021 Mar 15;clincanres.2114.2020. PMID: 33722897
2: Cardiovascular Disease Amongst Women Treated for Breast Cancer: Traditional Cytotoxic Chemotherapy, Targeted Therapy, and Radiation Therapy.
[Chen Daniel H,Tyebally Sara,Malloupas Michael,Roylance Rebecca,Spurrell Emma,Raja Fharat,Ghosh Arjun K]Curr Cardiol Rep,2021 Jan 26;23(3):16. PMID: 33501515
3: CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: differences in toxicity profiles and impact on agent choice. A systematic review and meta-analysis.
[Onesti Concetta E,Jerusalem Guy]Expert Rev Anticancer Ther,2021 Mar;21(3):283-298. PMID: 33233970
4: Ribociclib plus fulvestrant in the treatment of breast cancer.
[Neven Patrick,Sonke Gabe S,Jerusalem Guy]Expert Rev Anticancer Ther,2021 Jan;21(1):93-106. PMID: 33085548
5: Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 and 6 Inhibitors Palbociclib, Ribociclib, and Abemaciclib.
[Groenland Stefanie L,Martínez-Chávez Alejandra,van Dongen Marloes G J,Beijnen Jos H,Schinkel Alfred H,Huitema Alwin D R,Steeghs Neeltje]Clin Pharmacokinet,2020 Dec;59(12):1501-1520. PMID: 33029704
6: Increased risk of cardiac conduction abnormalities with ribociclib in patients with metastatic breast cancer: A combined analysis of phase III randomized controlled trials.
[Ball Somedeb,Swarup Sriman,Sultan Anita,Thein Kyaw Zin]Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther,2020 May 5;S1658-3876(20)30047-9. PMID: 32413420
7: Ribociclib Plus Trastuzumab in Advanced HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: Results of a Phase 1b/2 Trial.
[Goel Shom,Pernas Sonia,Tan-Wasielewski Zhenying,Barry William T,Bardia Aditya,Rees Rebecca,Andrews Chelsea,Tahara Rie Kawabori,Trippa Lorenzo,Mayer Erica L,Winer Eric P,Spring Laura M,Tolaney Sara M]Clin Breast Cancer,2019 Dec;19(6):399-404. PMID: 31235441
8: Cardiac arrhythmia considerations of hormone cancer therapies.
[Barber Mary,Nguyen Lee S,Wassermann Johanna,Spano Jean-Philippe,Funck-Brentano Christian,Salem Joe-Elie]Cardiovasc Res,2019 Apr 15;115(5):878-894. PMID: 30698686
9: Comparative efficacy of palbociclib, ribociclib and abemaciclib for ER+ metastatic breast cancer: an adjusted indirect analysis of randomized controlled trials.
[Petrelli Fausto,Ghidini Antonio,Pedersini Rebecca,Cabiddu Mary,Borgonovo Karen,Parati Maria Chiara,Ghilardi Mara,Amoroso Vito,Berruti Alfredo,Barni Sandro]Breast Cancer Res Treat,2019 Apr;174(3):597-604. PMID: 30659432
10: Ribociclib in HR+/HER2- Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients.
[Rascon Kaitlin,Flajc Goran,De Angelis Carmine,Liu Xinli,Trivedi Meghana V,Ekinci Ekim]Ann Pharmacother,2019 May;53(5):501-509. PMID: 30522347
11: Management of adverse events during cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor-based treatment in breast cancer.
[Thill Marc,Schmidt Marcus]Ther Adv Med Oncol,2018 Sep 3;10:1758835918793326. PMID: 30202447
12: A Phase I Study of the CDK4/6 Inhibitor Ribociclib (LEE011) in Pediatric Patients with Malignant Rhabdoid Tumors, Neuroblastoma, and Other Solid Tumors.
[Geoerger Birgit,Bourdeaut Franck,DuBois Steven G,Fischer Matthias,Geller James I,Gottardo Nicholas G,Marabelle Aurélien,Pearson Andrew D J,Modak Shakeel,Cash Thomas,Robinson Giles W,Motta Marlyane,Matano Alessandro,Bhansali Suraj G,Dobson Jason R,Parasuraman Sudha,Chi Susan N]Clin Cancer Res,2017 May 15;23(10):2433-2441. PMID: 28432176
13: A Phase I Study of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor Ribociclib (LEE011) in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors and Lymphomas.
[Infante Jeffrey R,Cassier Philippe A,Gerecitano John F,Witteveen Petronella O,Chugh Rashmi,Ribrag Vincent,Chakraborty Abhijit,Matano Alessandro,Dobson Jason R,Crystal Adam S,Parasuraman Sudha,Shapiro Geoffrey I]Clin Cancer Res,2016 Dec 1;22(23):5696-5705. PMID: 27542767
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.