Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
SOLIFENACIN SUCCINATE
DIR Classification
Classification:Moderate-DIQT concern
Severity Score:3.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QT Prolongation in Patients at High Risk of QT Prolongation
- In a study of the effect of solifenacin succinate on the QT interval conducted in 76 healthy women [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.2)] , solifenacin succinate 30 mg (three times the largest maximum recommended dose in adult patients) was associated with a mean increase in the Fridericia-corrected QT interval of 8 msec (90% CI, 4, 13). The QT prolonging effect appeared less with solifenacin succinate 10 mg than with solifenacin succinate 30 mg, and the effect of solifenacin succinate 30 mg did not appear as large as that of the positive control moxifloxacin at its therapeutic dose.
- The use of solifenacin succinate is not recommended in patients at high risk of QT prolongation, including patients with a known history of QT prolongation and patients who are taking medications known to prolong the QT interval.
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
- Solifenacin is a substrate of CYP3A4. Concomitant use of ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, significantly increased the exposure of solifenacin [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.3)] . The dosage of solifenacin succinate greater than 5 mg once daily is not recommended when concomitantly used with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.4)] .
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Post-Marketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of solifenacin succinate in the U.S. and/or outside of the U.S. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Cardiac disorders: QT prolongation, Torsade de Pointes, atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, palpitations;
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- The effect of 10 mg and 30 mg solifenacin succinate (three times the maximum recommended dose) on the QT interval was evaluated at the time of peak plasma concentration of solifenacin in a multi-dose, randomized, double-blind, placebo and positive-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) trial [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.6)]. After receiving placebo and moxifloxacin sequentially, subjects were randomized to one of two treatment groups. One group (n=51) completed 3 additional sequential periods of dosing with solifenacin succinate 10 mg, 20 mg, and 30 mg while the second group (n=25) in parallel completed a sequence of placebo and moxifloxacin. Study subjects were female volunteers aged 19 to 79 years. The 30 mg dose of solifenacin succinate (three times the highest recommended dose) was chosen for use in this study because this dose results in a solifenacin exposure that covers those observed upon coadministration of 10 mg solifenacin succinate with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, 400 mg). Due to the sequential dose escalating nature of the study, baseline ECG measurements were separated from the final QT assessment (of the 30 mg dose level) by 33 days.
- The median difference from baseline in heart rate associated with the 10 and 30 mg doses of solifenacin succinate compared to placebo was -2 and 0 beats/minute, respectively. Because a significant period effect on QTc was observed, the QTc effects were analyzed utilizing the parallel placebo control arm rather than the pre-specified intra-patient analysis. Representative results are shown in Table 2.
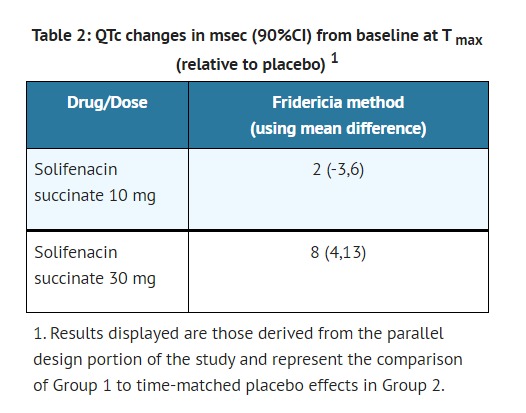
- Moxifloxacin was included as a positive control in this study and, given the length of the study, its effect on the QT interval was evaluated in 3 different sessions. The placebo-subtracted mean changes (90% CI) in QTcF for moxifloxacin in the three sessions were 11 (7, 14), 12 (8, 17), and 16 (12, 21), respectively.
- The QT interval prolonging effect of the highest solifenacin succinate dose (three times the maximum therapeutic dose) studied was not as large as that of the positive control moxifloxacin at its recommended dose. However, the confidence intervals overlapped, and this study was not designed to draw direct statistical conclusions between the drugs or the dose levels.
- PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
- What should I tell my doctor before taking solifenacin succinate?
- Before you take solifenacin succinate, tell your doctor if you:
- have a rare heart problem called QT prolongation
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
37
24055
Other ADRs
24320
38357267
Odds Ratio = 2.426
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- G04BD08 - solifenacin succinate
- G04BD - Urinary antispasmodics
- G04B - "OTHER UROLOGICALS, INCL. ANTISPASMODICS"
- G04 - UROLOGICALS
- G - GENITO URINARY SYSTEM AND SEX HORMONES
Active Ingredient:SOLIFENACIN SUCCINATE
Active Ingredient UNII:KKA5DLD701
Drugbank ID:DB01591
PubChem Compound:154059
CTD ID:D000069464
PharmGKB:PA164783810
CAS Number:242478-37-1
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 5.0 mg/day G04BD08
Chemical Structure: 

SMILE Code:
O=C(O[C@H]1CN2CCC1CC2)N1CCC2=CC=CC=C2[C@@H]1C1=CC=CC=C1
O=C(O[C@H]1CN2CCC1CC2)N1CCC2=CC=CC=C2[C@@H]1C1=CC=CC=C1
Reference
1: Cardiovascular safety in refractory incontinent patients with overactive bladder receiving add-on mirabegron therapy to solifenacin (BESIDE).
[Drake Marcus J,MacDiarmid Scott,Chapple Christopher R,Esen Adil,Athanasiou Stavros,Cambronero Santos Javier,Mitcheson David,Herschorn Sender,Siddiqui Emad,Huang Moses,Stoelzel Matthias]Int J Clin Pract,2017 May;71(5):e12944. PMID: 28419650
2: [Case Report; A case of QT prolongation and torsade de pointes associated with Solifenacin].
[Yoshida Fumina,Okusu Yasuo,Wada Atsushi,Hiroe Yoshitaka,Yano Hideto,Miyazaki Takahiro,Ishikawa Hiroyuki,Nakamura Masashi,Mochizuki Takatoshi]Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi,2014 Nov 10;103(11):2804-6. PMID: 27522821
3: QT prolongation and torsade de pointes associated with solifenacin in an 81-year-old woman.
[Asajima Hiroshi,Sekiguchi Yohei,Matsushima Shoji,Saito Naotaka,Saito Takahiko]Br J Clin Pharmacol,2008 Dec;66(6):896-7. PMID: 18823303
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.