Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
VARDENAFIL HYDROCHLORIDE
DIR Classification
Classification:Moderate-DIQT concern
Severity Score:3.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Congenital or Acquired QT Prolongation
- In a study of the effect of vardenafil hydrochloride on QT interval in 59 healthy males [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], therapeutic (10 mg) and supratherapeutic (80 mg) doses of vardenafil and the active control moxifloxacin (400 mg) produced similar increases in QTc interval. A postmarketing study evaluating the effect of combining vardenafil hydrochloride with another drug of comparable QT effect showed an additive QT effect when compared with either drug alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. These observations should be considered in clinical decisions when prescribing vardenafil hydrochloride to patients with known history of QT prolongation or patients who are taking medications known to prolong the QT interval.
- Patients taking Class 1A (for example. quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (for example, amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications or those with congenital QT prolongation, should avoid using vardenafil hydrochloride.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The following serious adverse reactions with the use of vardenafil hydrochloride are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Effects [see Contraindications (4.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Effects on Eye [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Sudden Hearing Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- QT Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Effects on Cardiac Electrophysiology
- The effect of 10 mg and 80 mg vardenafil on QT interval was evaluated in a single-dose, double-blind, randomized, placebo- and active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) crossover study in 59 healthy males (81% White, 12% Black, 7% Hispanic) aged 45 to 60 years. The QT interval was measured at one hour post dose because this time point approximates the average time of peak vardenafil concentration. The 80 mg dose of vardenafil hydrochloride (four times the highest recommended dose) was chosen because this dose yields plasma concentrations covering those observed upon co-administration of a low-dose of vardenafil hydrochloride (5 mg) and 600 mg BID of ritonavir. Of the CYP3A4 inhibitors that have been studied, ritonavir causes the most significant drug-drug interaction with vardenafil. Table 6 summarizes the effect on mean uncorrected QT and mean corrected QT interval (QTc) with different methods of correction (Fridericia and a linear individual correction method) at one hour post-dose. No single correction method is known to be more valid than the other. In this study, the mean increase in heart rate associated with a 10 mg dose of vardenafil hydrochloride compared to placebo was 5beats/minute and with an 80 mg dose of vardenafil hydrochloride the mean increase was 6 beats/minute.
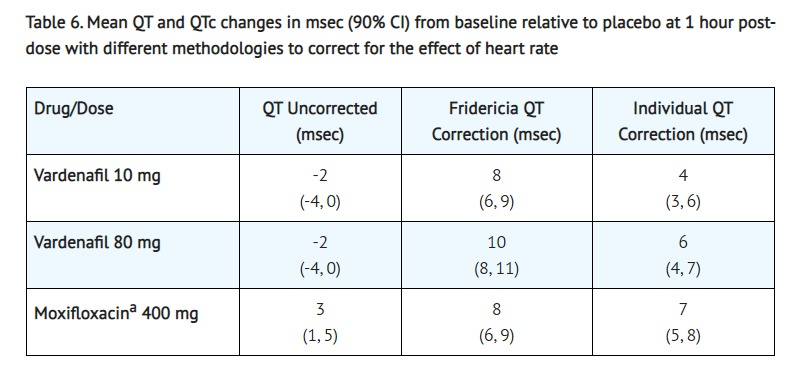
- Active control (drug known to prolong QT)
- Therapeutic and supratherapeutic doses of vardenafil and the active control moxifloxacin produced similar increases in QTc interval. This study, however, was not designed to make direct statistical comparisons between the drug or the dose levels. The clinical impact of these QTc changes is unknown [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
- In a separate postmarketing study of 44 healthy volunteers, single doses of 10 mg vardenafil hydrochloride resulted in a placebo-subtracted mean change from baseline of QTcF (Fridericia correction) of 5 msec (90% CI: 2,8). Single doses of gatifloxacin 400mg resulted in a placebo-subtracted mean change from baseline QTcF of 4 msec (90% CI: 1,7). When vardenafil hydrochloride 10mg and gatifloxacin 400 mg were co-administered, the mean QTcF change from baseline was additive when compared to either drug alone and produced a mean QTcF change of 9 msec from baseline (90% CI: 6,11). The clinical impact of these QT changes is unknown [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
3
24089
Other ADRs
10436
38371151
Odds Ratio = 0.458
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- G04BE09 - vardenafil hydrochloride
- G04BE - Drugs used in erectile dysfunction
- G04B - "OTHER UROLOGICALS, INCL. ANTISPASMODICS"
- G04 - UROLOGICALS
- G - GENITO URINARY SYSTEM AND SEX HORMONES
Active Ingredient:VARDENAFIL HYDROCHLORIDE
Active Ingredient UNII:5M8S2CU0TS
Drugbank ID:DB00862
PubChem Compound:110634
CTD ID:D000069058
PharmGKB:PA10229
CAS Number:224785-90-4
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 10.0 mg/day G04BE09
Chemical Structure: 

SMILE Code:
CCCC1=NC(C)=C2N1NC(=NC2=O)C1=C(OCC)C=CC(=C1)S(=O)(=O)N1CCN(CC)CC1
CCCC1=NC(C)=C2N1NC(=NC2=O)C1=C(OCC)C=CC(=C1)S(=O)(=O)N1CCN(CC)CC1
Reference
N/A
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.