Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
FOSCARNET SODIUM
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS
- QT prolongation and torsade de pointes
- FOSCAVIR has been associated with prolongation of the QT interval, an ECG abnormality that has been associated with torsades de pointes, which has been reported during postmarketing surveillance for FOSCAVIR (see ADVERSE REACTIONS section). Some of these patients had confounding risk factors such as underlying cardiac disease, electrolyte abnormalities and other concomitant medications.
- Use with caution in patients who have a history of QT prolongation, in patients who are taking medications known to prolong the QT interval (see PRECAUTIONS section), in patients with electrolyte disturbances, or in patients who have other risk factors for QT prolongation. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) and measurement of electrolytes should be obtained prior to treatment initiation and periodically during treatment with FOSCAVIR.
- PRECAUTIONS
- Drug Interactions
- Because of the risk of QT prolongation and the potential for torsades de pointes, the use of FOSCAVIR should be avoided in combination with agents known to prolong the QT interval including Class IA (e.g., quinidine or procainamide) or Class III (e.g., dofetilide, amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents, phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants, and certain macrolides and fluoroquinolones.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Adverse events that have been reported in post-marketing surveillance include: administration site extravasation, localized edema, hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylactic shock, urticaria and angioedema) (see WARNINGS section), gastrointestinal hemorrhage, increased lipase, glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, proteinuria, status epilepticus, ventricular arrhythmia, prolongation of QT interval, torsade de pointes (see WARNINGS section), gamma GT increased, diabetes insipidus (usually nephrogenic), renal calculus, Fanconi syndrome acquired, renal tubular acidosis, renal tubular necrosis, crystal-induced nephropathy, hypercalcemia, hypernatremia, esophageal ulceration and muscle disorders including myopathy, myositis, muscle weakness and rare cases of rhabdomyolysis. Cases of vesiculobullous eruptions including erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome have been reported. In most cases, patients were taking other medications that have been associated with toxic epidermal necrolysis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
3
24089
Other ADRs
2599
38378988
Odds Ratio = 1.84
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- J05AD01 - foscarnet sodium
- J05AD - Phosphonic acid derivatives
- J05A - DIRECT ACTING ANTIVIRALS
- J05 - ANTIVIRALS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- J - ANTIINFECTIVES FOR SYSTEMIC USE
Active Ingredient:foscarnet sodium
Active Ingredient UNII:964YS0OOG1
Drugbank ID:DB00529
PubChem Compound:3415
CTD ID:D017245
PharmGKB:PA449706
CAS Number:4428-95-9
Dosage Form(s):injection, solution
Route(s) Of Administrator:intravenous
Daily Dose:
- 6500.0 mg/day J05AD01
Chemical Structure: 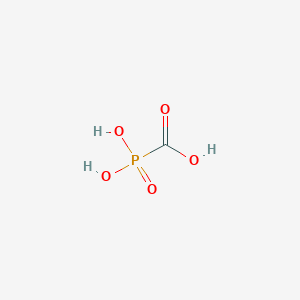

SMILE Code:
OC(=O)P(O)(O)=O
OC(=O)P(O)(O)=O
Reference
N/A
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.