Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:5.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- BOXED WARNING
- Life-Threatening QT Prolongation
- QT interval prolongation and serious arrhythmia (torsades de pointes) have occurred during treatment with methadone. Most cases involve patients being treated for pain with large, multiple daily doses of methadone hydrochloride, although cases have been reported in patients receiving doses commonly used for maintenance treatment of opioid addiction. Closely monitor patients with risk factors for development of prolonged QT interval, a history of cardiac conduction abnormalities, and those taking medications affecting cardiac conduction for changes in cardiac rhythm during initiation and titration of Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Life-Threatening QT Prolongation
- Cases of QT interval prolongation and serious arrhythmia (torsades de pointes) have been observed during treatment with methadone. These cases appear to be more commonly associated with, but not limited to, higher dose treatment (> 200 mg/day). Most cases involve patients being treated for pain with large, multiple daily doses of methadone, although cases have been reported in patients receiving doses commonly used for maintenance treatment of opioid addiction. In most patients on the lower doses typically used for maintenance, concomitant medications and/or clinical conditions such as hypokalemia were noted as contributing factors. However, the evidence strongly suggests that methadone possesses the potential for adverse cardiac conduction effects in some patients. The effects of methadone on the QT interval have been confirmed in in vivo laboratory studies, and methadone has been shown to inhibit cardiac potassium channels in in vitro studies.
- Closely monitor patients with risk factors for development of prolonged QT interval (e.g., cardiac hypertrophy, concomitant diuretic use, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia), a history of cardiac conduction abnormalities, and those taking medications affecting cardiac conduction. QT prolongation has also been reported in patients with no prior cardiac history who have received high doses of methadone.
- Evaluate patients developing QT prolongation while on methadone treatment for the presence of modifiable risk factors, such as concomitant medications with cardiac effects, drugs that might cause electrolyte abnormalities, and drugs that might act as inhibitors of methadone metabolism.
- Only initiate Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets therapy for pain in patients for whom the anticipated benefit outweighs the risk of QT prolongation and development of dysrhythmias that have been reported with high doses of methadone.
- The use of methadone in patients already known to have a prolonged QT interval has not been systematically studied.
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Cardiovascular: arrhythmias, bigeminal rhythms, bradycardia, cardiomyopathy, ECG abnormalities, extrasystoles, flushing, heart failure, hypotension, palpitations, phlebitis, QT interval prolongation, syncope, T-wave inversion, tachycardia, torsades de pointes, ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacokinetics
- Cytochrome P450 Inhibitors:
- Voriconazole: Voriconazole can inhibit the activity of CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19. Repeat dose administration of oral voriconazole (400 mg every 12 hours for 1 day, then 200 mg every 12 hours for 4 days) increased the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) and AUC of (R)-methadone by 31% and 47%, respectively, in subjects receiving a methadone maintenance dose (30 to 100 mg) daily. The Cmax and AUC of (S)-methadone increased by 65% and 103%, respectively. Increased plasma concentrations of methadone have been associated with toxicity including QT prolongation. Frequent monitoring for adverse events and toxicity related to methadone is recommended during co-administration. Dose reduction of methadone may be needed [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
363
23729
Other ADRs
25219
38356368
Odds Ratio = 23.267
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- N07BC02 - methadone hydrochloride
- N07BC - Drugs used in opioid dependence
- N07B - DRUGS USED IN ADDICTIVE DISORDERS
- N07 - OTHER NERVOUS SYSTEM DRUGS
- N - NERVOUS SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE
Active Ingredient UNII:229809935B
Drugbank ID:DB00333
PubChem Compound:4095
CTD ID:D008691
PharmGKB:PA450401
CAS Number:76-99-3
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 25.0 mg/day N07BC02
Chemical Structure: 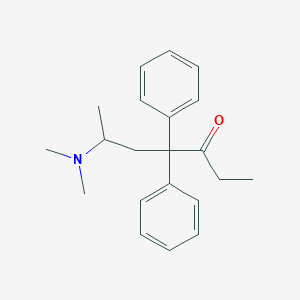

SMILE Code:
CCC(=O)C(CC(C)N(C)C)(C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1
CCC(=O)C(CC(C)N(C)C)(C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1
Reference
1: QT-interval effects of methadone, levomethadyl, and buprenorphine in a randomized trial.
[Wedam Erich F,Bigelow George E,Johnson Rolley E,Nuzzo Paul A,Haigney Mark C P]Arch Intern Med,2007 Dec 10;167(22):2469-75. PMID: 18071169
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.