Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
PALIPERIDONE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QT Prolongation
- Paliperidone causes a modest increase in the corrected QT (QTc) interval. The use of paliperidone should be avoided in combination with other drugs that are known to prolong QTc including Class 1A (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications, antipsychotic medications (e.g., chlorpromazine, thioridazine), antibiotics (e.g., gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin), or any other class of medications known to prolong the QTc interval. Paliperidone should also be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias.
- Certain circumstances may increase the risk of the occurrence of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with the use of drugs that prolong the QTc interval, including (1) bradycardia; (2) hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia; (3) concomitant use of other drugs that prolong the QTc interval; and (4) presence of congenital prolongation of the QT interval.
- The effects of paliperidone on the QT interval were evaluated in a double-blind, active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg single dose), multicenter QT study in adults with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder, and in three placebo- and active-controlled 6-week, fixed-dose efficacy trials in adults with schizophrenia.
- In the QT study (n = 141), the 8 mg dose of immediate-release oral paliperidone (n = 50) showed a mean placebo-subtracted increase from baseline in QTcLD of 12.3 msec (90% CI: 8.9; 15.6) on day 8 at 1.5 hours post-dose. The mean steady-state peak plasma concentration for this 8 mg dose of paliperidone immediate-release was more than twice the exposure observed with the maximum recommended 12 mg dose of paliperidone extended-release tablets (C max ss = 113 ng/mL and 45 ng/mL, respectively, when administered with a standard breakfast). In this same study, a 4 mg dose of the immediate-release oral formulation of paliperidone, for which C max ss = 35 ng/mL, showed an increased placebo-subtracted QTcLD of 6.8 msec (90% CI: 3.6; 10.1) on day 2 at 1.5 hours post-dose. None of the subjects had a change exceeding 60 msec or a QTcLD exceeding 500 msec at any time during this study.
- For the three fixed-dose efficacy studies in subjects with schizophrenia, electrocardiogram (ECG) measurements taken at various time points showed only one subject in the paliperidone extended-release tablets 12 mg group had a change exceeding 60 msec at one time-point on Day 6 (increase of 62 msec). No subject receiving paliperidone extended-release tablets had a QTcLD exceeding 500 msec at any time in any of these three studies.
- OVERDOSAGE
- Human Experience
- While experience with paliperidone overdose is limited, among the few cases of overdose reported in pre-marketing trials, the highest estimated ingestion of paliperidone extended-release tablets was 405 mg. Observed signs and symptoms included extrapyramidal symptoms and gait unsteadiness. Other potential signs and symptoms include those resulting from an exaggeration of paliperidone’s known pharmacological effects, i.e., drowsiness and somnolence, tachycardia and hypotension, and QT prolongation. Torsade de pointes and ventricular fibrillation have been reported in a patient in the setting of overdose.
- Paliperidone is the major active metabolite of risperidone. Overdose experience reported with risperidone can be found in the OVERDOSAGE section of the risperidone package insert.
- [Management of Overdosage]
- There is no specific antidote to paliperidone, therefore, appropriate supportive measures should be instituted and close medical supervision and monitoring should continue until the patient recovers. Consideration should be given to the extended-release nature of the product when assessing treatment needs and recovery. Multiple drug involvement should also be considered.
- In case of acute overdose, establish and maintain an airway and ensure adequate oxygenation and ventilation. Administration of activated charcoal together with a laxative should be considered.
- The possibility of obtundation, seizures, or dystonic reaction of the head and neck following overdose may create a risk of aspiration with induced emesis.
- Cardiovascular monitoring should commence immediately, including continuous electrocardiographic monitoring for possible arrhythmias. If antiarrhythmic therapy is administered, disopyramide, procainamide, and quinidine carry a theoretical hazard of additive QT-prolonging effects when administered in patients with an acute overdose of paliperidone. Similarly, the alpha-blocking properties of bretylium might be additive to those of paliperidone, resulting in problematic hypotension.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Overall Adverse Reaction Profile
- The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Increased mortality in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis [see BOXED WARNING and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Cerebrovascular adverse reactions, including stroke, in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)]
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.3)]
- QT prolongation [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.4)]
- Tardive dyskinesia [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5)]
- Metabolic changes [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.6)]
- Hyperprolactinemia [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.7)]
- Potential for gastrointestinal obstruction [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.8)]
- Orthostatic hypotension and syncope [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.9)]
- Falls [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.10)]
- Leukopenia, neutropenia, and agranulocytosis [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.11)]
- Potential for cognitive and motor impairment [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.12)]
- Seizures [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.13)]
- Dysphagia [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.14)]
- Priapism [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.15)]
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.16)]
- Disruption of body temperature regulation [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.17)]
- Antiemetic effect [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.18)]
- Patients with Concomitant Illness [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.19)]
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
80
24012
Other ADRs
62021
38319566
Odds Ratio = 2.059
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- N05AX13 - paliperidone
- N05AX - Other antipsychotics
- N05A - ANTIPSYCHOTICS
- N05 - PSYCHOLEPTICS
- N - NERVOUS SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:PALIPERIDONE
Active Ingredient UNII:838F01T721
Drugbank ID:DB01267
PubChem Compound:115237
CTD ID:D000068882
PharmGKB:PA163518919
CAS Number:144598-75-4
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated, extended release
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 6.0 mg/day N05AX13
Chemical Structure: 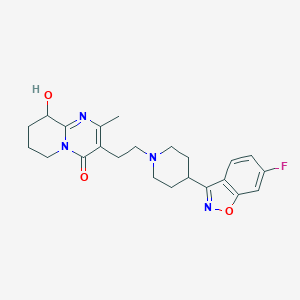

SMILE Code:
CC1=C(CCN2CCC(CC2)C2=NOC3=C2C=CC(F)=C3)C(=O)N2CCCC(O)C2=N1
CC1=C(CCN2CCC(CC2)C2=NOC3=C2C=CC(F)=C3)C(=O)N2CCCC(O)C2=N1
Reference
1: Arrhythmias related to antipsychotics and antidepressants: an analysis of the summaries of product characteristics of original products approved in Germany.
[Elsayed Mohamed,Abdel-Kahaar Emaad,Gahr Maximilian,Connemann Bernhard J,Denkinger Michael,Schönfeldt-Lecuona Carlos]Eur J Clin Pharmacol,2021 May;77(5):767-775. PMID: 33230596
2: Need for Bioequivalence Standards that Reflect the Clinical Importance of the Complex Pharmacokinetics of Paliperidone Palmitate Long-Acting Injectable Suspension.
[Procyshyn Ric M,Lamoure Joel W,Katzman Martin A,Skinner Pamela L,Sherman Stephen E]J Pharm Pharm Sci,2019;22(1):548-566. PMID: 31730504
3: Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 32 oral antipsychotics for the acute treatment of adults with multi-episode schizophrenia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.
[Huhn Maximilian,Nikolakopoulou Adriani,Schneider-Thoma Johannes,Krause Marc,Samara Myrto,Peter Natalie,Arndt Thomas,Bäckers Lio,Rothe Philipp,Cipriani Andrea,Davis John,Salanti Georgia,Leucht Stefan]Lancet,2019 Sep 14;394(10202):939-951. PMID: 31303314
4: Coprescription of QT interval-prolonging antipsychotics with potentially interacting medications in Thailand.
[Waleekhachonloet Onanong,Limwattananon Chulaporn,Rattanachotphanit Thananan]Ther Adv Drug Saf,2019 Jun 13;10:2042098619854886. PMID: 31223470
5: Maximizing response to first-line antipsychotics in schizophrenia: a review focused on finding from meta-analysis.
[Smith Robert C,Leucht Stefan,Davis John M]Psychopharmacology (Berl),2019 Feb;236(2):545-559. PMID: 30506237
6: Analysis of proarrhythmic potential of an atypical antipsychotic drug paliperidone in the halothane-anesthetized dogs.
[Chiba Koki,Wada Takeshi,Nakamura Yuji,Cao Xin,Hagiwara-Nagasawa Mihoko,Izumi-Nakaseko Hiroko,Ando Kentaro,Tanaka Koichiro,Naito Atsuhiko T,Sugiyama Atsushi]J Pharmacol Sci,2017 Aug;134(4):239-246. PMID: 28844424
7: Effect of lipid emulsion infusion on paliperidone pharmacokinetics in the acute overdose rat model: A potential emergency treatment for paliperidone intoxication.
[Enokiya Tomoyuki,Zhang Erquan,Ikemura Kenji,Muraki Yuichi,Iwashita Yoshiaki,Iwamoto Takuya,Imai Hiroshi,Maruyama Kazuo,Okuda Masahiro]Eur J Pharm Sci,2017 Nov 15;109:217-222. PMID: 28821438
8: In vivo analysis of torsadogenic potential of an antipsychotic drug paliperidone using the acute atrioventricular block rabbit as a proarrhythmia model.
[Hagiwara Mihoko,Kambayashi Ryuichi,Aimoto Megumi,Nagasawa Yoshinobu,Takahara Akira]J Pharmacol Sci,2016 Sep;132(1):48-54. PMID: 27262905
9: [The Safety of Using Long-acting Injections : From an Opposing Position-Is It Better to Administer Long-acting Injections?].
[Suzuki Yutaro]Seishin Shinkeigaku Zasshi,2016;118(8):584-588. PMID: 30620476
10: Corrected QT changes during antipsychotic treatment of children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials.
[Jensen Karsten Gjessing,Juul Klaus,Fink-Jensen Anders,Correll Christoph U,Pagsberg Anne Katrine]J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry,2015 Jan;54(1):25-36. PMID: 25524787
11: Quetiapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia.
[Asmal Laila,Flegar Srnka J,Wang Jikun,Rummel-Kluge Christine,Komossa Katja,Leucht Stefan]Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2013 Nov 18;(11):CD006625. PMID: 24249315
12: Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis.
[Leucht Stefan,Cipriani Andrea,Spineli Loukia,Mavridis Dimitris,Orey Deniz,Richter Franziska,Samara Myrto,Barbui Corrado,Engel Rolf R,Geddes John R,Kissling Werner,Stapf Marko Paul,Lässig Bettina,Salanti Georgia,Davis John M]Lancet,2013 Sep 14;382(9896):951-62. PMID: 23810019
13: Risk of cardiovascular morbidity with risperidone or paliperidone treatment: analysis of 64 randomized, double-blind trials.
[Gopal Srihari,Hough David,Karcher Keith,Nuamah Isaac,Palumbo Joseph,Berlin Jesse A,Baseman Alan,Xu Yimei,Kent Justine]J Clin Psychopharmacol,2013 Apr;33(2):157-61. PMID: 23422378
14: QT prolongation of the antipsychotic risperidone is predominantly related to its 9-hydroxy metabolite paliperidone.
[Suzuki Yutaro,Fukui Naoki,Watanabe Junzo,Ono Shin,Sugai Takuro,Tsuneyama Nobuto,Saito Mami,Inoue Yoshimasa,Someya Toshiyuki]Hum Psychopharmacol,2012 Jan;27(1):39-42. PMID: 22144033
15: In vivo and in vitro myocardial binding of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone.
[Titier Karine,Déridet Evelyne,Moore Nicholas]Toxicol Appl Pharmacol,2002 Apr 15;180(2):145-9. PMID: 11969382
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.