Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
PANOBINOSTAT
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Cardiac Toxicities
- Severe and fatal cardiac ischemic events, as well as severe arrhythmias, and electrocardiogram (ECG) changes occurred in patients receiving FARYDAK. Arrhythmias occurred in 12% of patients receiving FARYDAK, compared to 5% of patients in the control arm. Cardiac ischemic events occurred in 4% of patients treated with FARYDAK compared with 1% of patients in the control arm. Do not initiate FARYDAK treatment in patients with history of recent myocardial infarction or unstable angina.
- Electrocardiographic abnormalities such as ST-segment depression and T-wave abnormalities also occurred more frequently in patients receiving FARYDAK compared to the control arm: 22% versus 4% and 40% versus 18%, respectively. FARYDAK may prolong cardiac ventricular repolarization (QT interval). Do not initiate treatment with FARYDAK in patients with a QTcF >450 msec or clinically significant baseline ST-segment or T-wave abnormalities. Arrhythmias may be exacerbated by electrolyte abnormalities. If during treatment with FARYDAK, the QTcF increases to ≥480 msec, interrupt treatment. Correct any electrolyte abnormalities. If QT prolongation does not resolve, permanently discontinue treatment with FARYDAK.
- Obtain ECG at baseline and periodically during treatment as clinically indicated. Monitor electrolytes during treatment with FARYDAK and correct abnormalities as clinically indicated.
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Drugs that Prolong QT interval
- Concomitant use of anti-arrhythmic medicines (including, but not limited to amiodarone, disopyramide, procainamide, quinidine and sotalol) and other drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval (including, but not limited to chloroquine, halofantrine, clarithromycin, methadone, moxifloxacin, bepridil and pimozide) is not recommended. Anti-emetic drugs with known QT prolonging risk, such as dolasetron, ondansetron, and tropisetron can be used with frequent ECG monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administration and Monitoring Instructions
- Prior to the start of FARYDAK treatment and during treatment, monitoring should include:
- ECG: Perform an ECG prior to the start of therapy and repeat periodically during treatment as clinically indicated. Verify that the QTcF is less than 450 msec prior to initiation of treatment with FARYDAK. If during treatment with FARYDAK, the QTcF increases to ≥480 msec, interrupt treatment. Correct any electrolyte abnormalities. If QT prolongation does not resolve, permanently discontinue treatment with FARYDAK [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. During the clinical trial, ECGs were performed at baseline and prior to initiation of each cycle for the first 8 cycles.
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- FARYDAK may prolong cardiac ventricular repolarization (QT interval) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. In the randomized multiple myeloma trial, QTc prolongation with values between 451 msec to 480 msec occurred in 10.8% of FARYDAK treated patients. Events with values of 481 msec to 500 msec occurred in 1.3% of FARYDAK treated patients. A maximum QTcF increase from baseline of between 31 msec and 60 msec was reported in 14.5% of FARYDAK treated patients. A maximum QTcF increase from baseline of >60 msec was reported in 0.8% of FARYDAK treated patients. No episodes of QTcF prolongation >500 msec have been reported with the dose of 20 mg FARYDAK in the randomized multiple myeloma trial conducted in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone. Pooled clinical data from over 500 patients treated with single agent FARYDAK in multiple indications and at different dose levels has shown that the incidence of CTC Grade 3 QTc prolongation (QTcF >500 msec) was approximately 1% overall and 5% or more at a dose of 60 mg or higher.
- MEDICATION GUIDE
- Heart problems FARYDAK can cause severe heart problems which can lead to death. Your risk of heart problems may be increased if you have a condition called “long QT syndrome” or other heart problems. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your electrolytes and do an electrocardiogram (ECG) tests before and during treatment with FARYDAK.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
8
24084
Other ADRs
4213
38377374
Odds Ratio = 3.026
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- L01XH03 - panobinostat
- L01XH -
- L01X - OTHER ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS
- L01 - ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS
- L - ANTINEOPLASTIC AND IMMUNOMODULATING AGENTS
Active Ingredient:PANOBINOSTAT LACTATE
Active Ingredient UNII:HN0T99OO4V
Drugbank ID:DB06603
PubChem Compound:6918837
CTD ID:D000077767
PharmGKB:PA166161307
CAS Number:404950-80-7
Dosage Form(s):capsule
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
Chemical Structure: 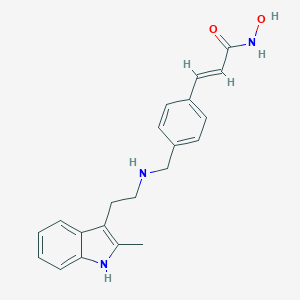

SMILE Code:
CC1=C(CCNCC2=CC=C(\C=C\C(=O)NO)C=C2)C2=CC=CC=C2N1
CC1=C(CCNCC2=CC=C(\C=C\C(=O)NO)C=C2)C2=CC=CC=C2N1
Reference
1: A phase I study of panobinostat in children with relapsed and refractory hematologic malignancies.
[Goldberg John,Sulis Maria Luisa,Bender Julia,Jeha Sima,Gardner Rebecca,Pollard Jessica,Aquino Victor,Laetsch Theodore,Winick Naomi,Fu Cecilia,Marcus Leigh,Sun Weili,Verma Anupam,Burke Michael,Ho Phoenix,Manley Thomas,Mody Rajen,Tcheng Wendy,Thomson Blythe,Park Julie,Sposto Richard,Messinger Yoav,Hijiya Nobuko,Gaynon Paul,Barredo Julio]Pediatr Hematol Oncol,2020 Sep;37(6):465-474. PMID: 32338562
2: A phase I trial of oral administration of panobinostat in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with solid tumors.
[Jones Suzanne F,Infante Jeffrey R,Thompson Dana S,Mohyuddin Adil,Bendell Johanna C,Yardley Denise A,Burris Howard A]Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,2012 Sep;70(3):471-5. PMID: 22851205
3: Clinically relevant QTc prolongation is not associated with current dose schedules of LBH589 (panobinostat).
[Zhang Lei,Lebwohl David,Masson Eric,Laird Glen,Cooper Michael R,Prince H Miles]J Clin Oncol,2008 Jan 10;26(2):332-3; discussion 333-4. PMID: 18182676
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.