Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:5.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- BOXED WARNING
- WARNING: LIFE THREATENING PROARRHYTHMIA
- To minimize the risk of drug-induced arrhythmia, initiate or reinitiate oral sotalol in a facility that can provide cardiac resuscitation and continuous electrocardiographic monitoring.
- Sotalol can cause life threatening ventricular tachycardia associated with QT interval prolongation.
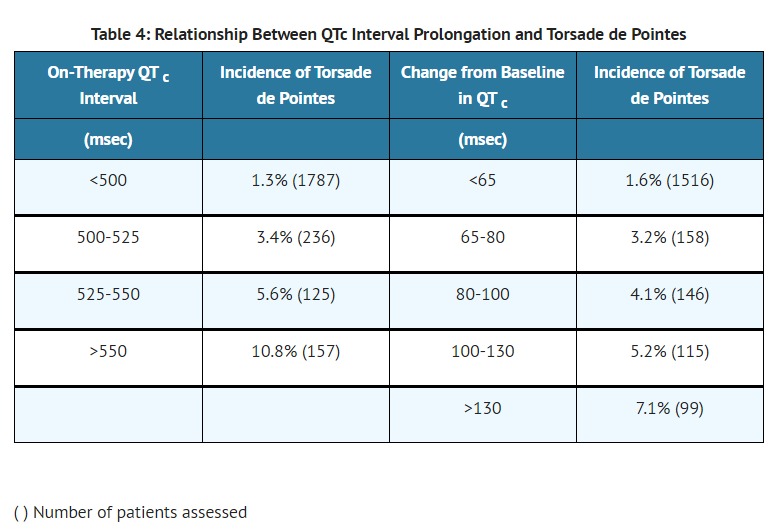
- If the QT interval prolongs to 500 msec or greater, reduce the dose, lengthen the dosing interval, or discontinue the drug.
- Calculate creatinine clearance to determine appropriate dosing [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.5)].
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QT Prolongation and Proarrhythmia
- Sotalol hydrochloride/Sotalol hydrochloride AF can cause serious and potentially fatal ventricular arrhythmias such as sustained VT/VF, primarily Torsade de Pointes (TdP) type ventricular tachycardia, a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with QT interval prolongation. Factors such as reduced creatinine clearance, female sex, higher doses, reduced heart rate and history of sustained VT/VF or heart failure increase the risk of TdP. The risk of TdP can be reduced by adjustment of the sotalol dose according to creatinine clearance and by monitoring the ECG for excessive increases in the QT interval [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1)].
- Correct hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia prior to initiating sotalol hydrochloride/sotalol hydrochloride AF, as these conditions can exaggerate the degree of QT prolongation, and increase the potential for Torsade de Pointes. Special attention should be given to electrolyte and acid-base balance in patients experiencing severe or prolonged diarrhea or patients receiving concomitant diuretic drugs.
- Proarrhythmic events must be anticipated not only on initiating therapy, but with every upward dose adjustment [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1)].
- In general, do not use sotalol with other drugs known to cause QT prolongation [see Drug Interactions ( 7.1)].
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Antiarrhythmics and other QT Prolonging Drugs
- Sotalol has not been studied with other drugs that prolong the QT interval such as antiarrhythmics, some phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants, certain oral macrolides and certain quinolone antibiotics. Discontinue Class I or Class III antiarrhythmic agents for at least three half-lives prior to dosing with sotalol. Class Ia antiarrhythmic drugs, such as disopyramide, quinidine and procainamide and other Class III drugs (for example, amiodarone) are not recommended as concomitant therapy with sotalol hydrochloride/sotalol hydrochloride AF, because of their potential to prolong refractoriness [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)]. There is only limited experience with the concomitant use of Class Ib or Ic antiarrhythmics. Additive Class II effects would also be anticipated with the use of other beta-blocking agents concomitantly with sotalol hydrochloride/sotalol hydrochloride AF.
- OVERDOSAGE
- Intentional or accidental over dosage with sotalol has resulted in death.
- Symptoms and Treatment of Over dosage
- The most common signs to be expected are bradycardia, congestive heart failure, hypotension, bronchospasm and hypoglycemia. In cases of massive intentional over dosage (2 to 16 grams) of sotalol the following clinical findings were seen: hypotension, bradycardia, cardiac asystole, prolongation of QT interval, Torsade de Pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and premature ventricular complexes. If over dosage occurs, therapy with sotalol should be discontinued and the patient observed closely. Because of the lack of protein binding, hemodialysis is useful for reducing sotalol plasma concentrations. Patients should be carefully observed until QT intervals are normalized and the heart rate returns to levels >50 bpm.
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- General Safety Measures for Initiation of Oral Sotalol Therapy
- Hospitalize patients initiated or re-initiated on sotalol for at least 3 days or until steady-state drug levels are achieved, in a facility that can provide cardiac resuscitation and continuous electrocardiographic monitoring. Initiate oral sotalol therapy in the presence of personnel trained in the management of serious arrhythmias. Perform a baseline ECG to determine the QT interval and measure and normalize serum potassium and magnesium levels before initiating therapy.
- Measure serum creatinine and calculate an estimated creatinine clearance in order to establish the appropriate dosing interval (insert cross ref to renal dosing). Continually monitor patients with each up-titration in dose, until they reach steady state. Determine QTc 2 to 4 hours after every dose.
- [Adult Dose for Ventricular Arrhythmias]
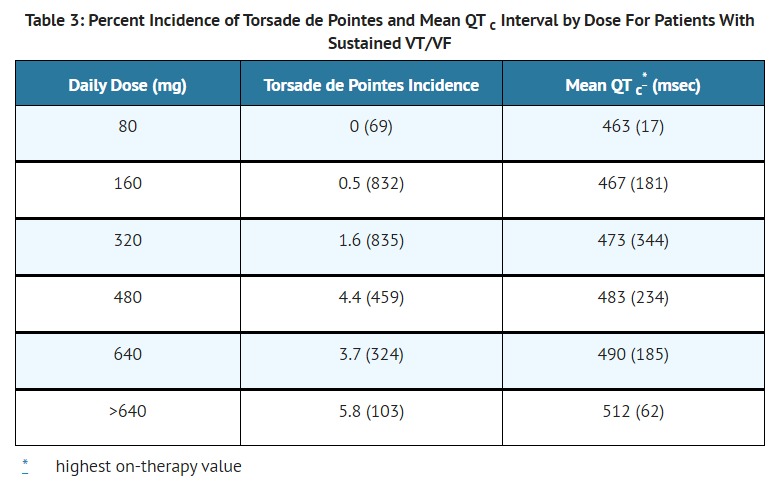
- The recommended initial dose is 80 mg twice daily. This dose may be increased in increments of 80 mg per day every 3 days provided the QTc <500 msec [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)]. Continually monitor patients until steady state blood levels are achieved. In most patients, a therapeutic response is obtained at a total daily dose of 160 to 320 mg/day, given in two or three divided doses (because of the long terminal elimination half- life of sotalol, dosing more than a two times a day is usually not necessary). Oral doses as high as 480 to 640 mg/day have been utilized in patients with refractory life-threatening arrhythmias.
- [Adult Dose for Prevention of Recurrence of AFIB/AFL]
- The recommended initial dose is 80 mg twice daily. This dose may be increased in increments of 80 mg per day every 3 days provided the QTc <500 msec [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)]. Continually monitor patients until steady state blood levels are achieved. Most patients will have satisfactory response with 120 mg twice daily. Initiation of sotalol in patients with creatinine clearance < 40 ml/min or QTc >450 is contraindicated [see Contraindication ( 4)].
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Clinical Trials Experience
- Pediatric Patients
- In an unblinded multicenter trial of 25 pediatric patients with SVT and/or VT receiving daily doses of 30, 90 and 210 mg/m 2 with dosing every 8 hours for a total of 9 doses, no Torsade de Pointes or other serious new arrhythmias were observed. One (1) patient, receiving 30 mg/m 2 daily, was discontinued because of increased frequency of sinus pauses/bradycardia. Additional cardiovascular AEs were seen at the 90 and 210 mg/m 2 daily dose levels. They included QT prolongation (2 patients), sinus pauses/bradycardia (1 patient), increased severity of atrial flutter and reported chest pain (1 patient). Values for QT c ≥ 525 msec were seen in 2 patients at the 210 mg/m 2 daily dose level. Serious adverse events including death, Torsade de Pointes, other proarrhythmias, high-degree A-V blocks, and bradycardia have been reported in infants and/or children.
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiological Effects
- Sotalol hydrochloride prolongs the plateau phase of the cardiac action potential in the isolated myocyte, as well as in isolated tissue preparations of ventricular or atrial muscle (Class III activity). In intact animals it slows heart rate, decreases AV nodal conduction and increases the refractory periods of atrial and ventricular muscle and conduction tissue.
- In man, the Class II (beta-blockade) electrophysiological effects of sotalol are manifested by increased sinus cycle length (slowed heart rate), decreased AV nodal conduction and increased AV nodal refractoriness. The Class III electrophysiological effects in man include prolongation of the atrial and ventricular monophasic action potentials, and effective refractory period prolongation of atrial muscle, ventricular muscle, and atrio ventricular accessory pathways (where present) in both the anterograde and retrograde directions. With oral doses of 160 to 640 mg/day, the surface ECG shows dose-related mean increases of 40 to 100 msec in QT and 10 to 40 msec in QTc [See Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)]. No significant alteration in QRS interval is observed.
- In a small study (n=25) of patients with implanted defibrillators treated concurrently with sotalol hydrochloride, the average defibrillatory threshold was 6 joules (range 2 to 15 joules) compared to a mean of 16 joules for a nonrandomized comparative group primarily receiving amiodarone.
- Twenty-five children in an unblinded, multicenter trial with SVT and/or ventricular tachyarrhythmias, aged between 3 days and 12 years (mostly neonates and infants), received an ascending titration regimen with daily doses of 30, 90 and 210 mg/m 2 with dosing every 8 hours for a total 9 doses. During steady-state, the respective average increases above baseline of the QTc interval were 2, 14, and 29 msec at the 3 dose levels. The respective mean maximum increases above baseline of the QTc interval were 23, 36, and 55 msec at the 3 dose levels. The steady-state percent increases in the RR interval were 3, 9 and 12%. The smallest children (BSA<0.33 m 2) showed a tendency for larger Class III effects (ΔQTc) and an increased frequency of prolongations of the QTc interval as compared with larger children (BSA ≥0.33 m 2). The beta-blocking effects also tended to be greater in the smaller children (BSA <0.33 m 2). Both the Class III and beta-blocking effects of sotalol were linearly related to the plasma concentrations.
- CLINICAL STUDIES
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
134
23958
Other ADRs
4990
38376597
Odds Ratio = 43.016
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- C07AA07 - sotalol hydrochloride
- C07AA - "Beta blocking agents, non-selective"
- C07A - BETA BLOCKING AGENTS
- C07 - BETA BLOCKING AGENTS
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE
Active Ingredient UNII:HEC37C70XX
Drugbank ID:DB00489
PubChem Compound:5253
CTD ID:D013015
PharmGKB:PA451457
CAS Number:3930-20-9
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 160.0 mg/day C07AA07
Chemical Structure: 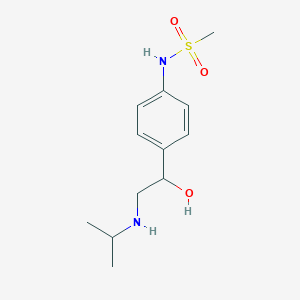

SMILE Code:
CC(C)NCC(O)C1=CC=C(NS(C)(=O)=O)C=C1
CC(C)NCC(O)C1=CC=C(NS(C)(=O)=O)C=C1
Reference
1: Intravenous Sotalol - Reintroducing a Forgotten Agent to the Electrophysiology Therapeutic Arsenal.
[Batul Syeda Atiqa,Gopinathannair Rakesh]J Atr Fibrillation,2017 Feb 28;9(5):1499. PMID: 29250266
2: Torsade de pointes and prolonged QT interval from surreptitious use of sotalol: use of drug levels in diagnosis.
[Link M S,Foote C B,Sloan S B,Homoud M K,Wang P J,Estes N A]Chest,1997 Aug;112(2):556-7. PMID: 9266902
3: Arrhythmogenic effect of beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drugs in Purkinje fibres of guinea-pig hearts.
[Lemmens-Gruber R,Zilberszac A,Heistracher P]Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther,Jan-Feb 1996;331(1):46-58. PMID: 8896710
4: Female gender as a risk factor for torsades de pointes associated with cardiovascular drugs.
[Makkar R R,Fromm B S,Steinman R T,Meissner M D,Lehmann M H]JAMA,1993 Dec 1;270(21):2590-7. PMID: 8230644
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.