Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
CHLOROQUINE PHOSPHATE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS
- Cardiac Effects
- Cases of cardiomyopathy resulting in cardiac failure, in some cases with fatal outcome, have been reported in patients treated during long term therapy at high doses with chloroquine (see ADVERSE REACTIONS and OVERDOSAGE). Monitor for signs and symptoms of cardiomyopathy and discontinue chloroquine if cardiomyopathy develops. Chronic toxicity should be considered when conduction disorders (bundle branch block / atrio-ventricular heart block) are diagnosed. If cardiotoxicity is suspected, prompt discontinuation of chloroquine may prevent life-threatening complications. QT interval prolongation, torsades de pointes, and ventricular arrhythmias have been reported. The risk is greater if chloroquine is administered at high doses. Fatal cases have been reported. Chloroquine should be used with caution in patients with cardiac disease, a history of ventricular arrhythmias, uncorrected hypokalemia and/or hypomagnesemia, or bradycardia (˂50 bpm), and during concomitant administration with QT interval prolonging agents due to potential for QT interval prolongation (see WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, DRUG INTERACTIONS, ADVERSE REACTIONS and OVERDOSAGE).
- PRECAUTIONS
- Drug Interactions
- Arrhythmogenic drugs: There may be an increased risk of inducing ventricular arrhythmias if chloroquine is used concomitantly with other arrhythmogenic drugs, such as amiodarone or moxifloxacin.
- OVERDOSAGE
- Signs and Symptoms: Chloroquine is very rapidly and completely absorbed after ingestion. Toxic doses of chloroquine can be fatal. As little as 1 g may be fatal in children. Toxic symptoms can occur within minutes. The symptoms of overdosage may include nausea, vomiting, headache, drowsiness, visual disturbances, cardiovascular collapse, convulsions, hypokalemia, rhythm and conduction disorders including QT prolongation, torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, followed by sudden potentially fatal respiratory and cardiac arrest. Immediate medical attention is required, as these effects may appear shortly after the overdose. Cases of extrapyramidal disorders have also been reported in the context of chloroquine overdose (see WARNINGS and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Cardiac arrhythmias, conduction disorders such as bundle branch block / atrio-ventricular block, QT interval prolongation, torsade de pointes, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation have been reported with therapeutic doses of chloroquine as well as with overdose. The risk is greater if chloroquine is administered at high doses. Fatal cases have been reported (see WARNINGS, CARDIAC EFFECTS and OVERDOSAGE).
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
29
24063
Other ADRs
2591
38378996
Odds Ratio = 17.852
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- P01BA01 - chloroquine phosphate
- P01BA - Aminoquinolines
- P01B - ANTIMALARIALS
- P01 - ANTIPROTOZOALS
- P - "ANTIPARASITIC PRODUCTS, INSECTICIDES AND REPELLENTS"
Active Ingredient:CHLOROQUINE PHOSPHATE
Active Ingredient UNII:6E17K3343P
Drugbank ID:DB00608
PubChem Compound:2719
CTD ID:D002738
PharmGKB:PA448948
CAS Number:54-05-7
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 500.0 mg/day P01BA01
Chemical Structure: 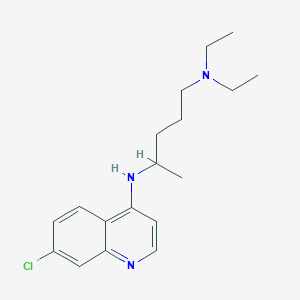

SMILE Code:
CCN(CC)CCCC(C)NC1=CC=NC2=CC(Cl)=CC=C12
CCN(CC)CCCC(C)NC1=CC=NC2=CC(Cl)=CC=C12
Reference
1: {'i': 'Torsade de Pointes', '#text': 'Lethal Arrhythmia () in COVID-19: An Event Synergistically Induced by Viral Associated Cardiac Injury, Hyperinflammatory Response, and Treatment Drug?'}
[Yasmin Kusumawardhani Nuraini,Huang Ian,Martanto Erwan,Sihite Teddy Arnold,Nugraha Eka Surya,Prodjosoewojo Susantina,Hamijoyo Laniyati,Hartantri Yovita]Clin Med Insights Case Rep,2020 Dec 14;13:1179547620972397. PMID: 33402858
2: Hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19 - A narrative review.
[Bajpai Jyoti,Pradhan Akshyaya,Singh Abhishek,Kant Surya]Indian J Tuberc,2020 Dec;67(4S):S147-S154. PMID: 33308661
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.