Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
ALFUZOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE
DIR Classification
Classification:Ambiguous
Severity Score:1.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Patients with Congenital or Acquired QT Prolongation
- Use with caution in patients with acquired or congenital QT prolongation or who are taking medications that prolong the QT interval [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.2)].
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- The effect of 10 mg and 40 mg alfuzosin on QT interval was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized, placebo and active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg), 4-way crossover single dose study in 45 healthy white male subjects aged 19 to 45 years. The QT interval was measured at the time of peak alfuzosin plasma concentrations. The 40 mg dose of alfuzosin was chosen because this dose achieves higher blood levels than those achieved with the co-administration of alfuzosin hydrochloride extended-release tablets and ketoconazole 400 mg. Table 3 summarizes the effect on uncorrected QT and mean corrected QT interval (QTc) with different methods of correction (Fridericia, population-specific and subject-specific correction methods) at the time of peak alfuzosin plasma concentrations. No single one of these correction methodologies is known to be more valid. The mean change of heart rate associated with a 10 mg dose of alfuzosin in this study was 5.2 beats/minute and 5.8 beats/minute with 40 mg alfuzosin. The change in heart rate with moxifloxacin was 2.8 beats/minute.
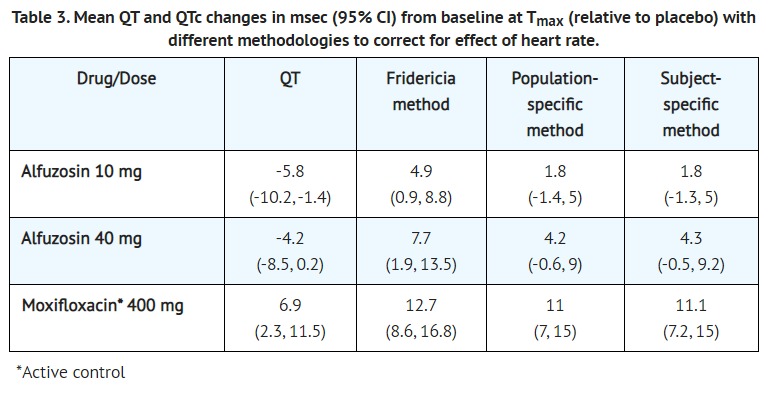
- The QT effect appeared greater for 40 mg compared to 10 mg alfuzosin. The effect of the highest alfuzosin dose (four times the therapeutic dose) studied did not appear as large as that of the active control moxifloxacin at its therapeutic dose. This study, however, was not designed to make direct statistical comparisons between the drugs or the dose levels. There has been no signal of Torsade de Pointes in the extensive post-marketing experience with alfuzosin outside the United States.
- A separate post-marketing QT study evaluated the effect of the co-administration of 10 mg alfuzosin with a drug of similar QT effect size. In this study, the mean placebo-subtracted QTcF increase of alfuzosin 10 mg alone was 1.9 msec (upperbound 95% CI, 5.5 msec). The concomitant administration of the two drugs showed an increased QT effect when compared with either drug alone. This QTcF increase [5.9 msec (UB 95% CI, 9.4 msec)] was not more than additive. Although this study was not designed to make direct statistical comparisons between drugs, the QT increase with both drugs given together appeared to be lower than the QTcF increase seen with the positive control moxifloxacin 400 mg [10.2 msec (UB 95% CI, 13.8 msec)]. The clinical impact of these QTc changes is unknown.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
10
24082
Other ADRs
4109
38377478
Odds Ratio = 3.879
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- G04CA01 - alfuzosin hydrochloride
- G04CA - Alpha-adrenoreceptor antagonists
- G04C - DRUGS USED IN BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY
- G04 - UROLOGICALS
- G - GENITO URINARY SYSTEM AND SEX HORMONES
Active Ingredient:ALFUZOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE
Active Ingredient UNII:75046A1XTN
Drugbank ID:DB00346
PubChem Compound:2092
CTD ID: C047638
PharmGKB:PA164774795
CAS Number:81403-80-7
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated, extended release
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 7.5 mg/day G04CA01
Chemical Structure: 

SMILE Code:
COC1=CC2=C(C=C1OC)C(N)=NC(=N2)N(C)CCCNC(=O)C1CCCO1
COC1=CC2=C(C=C1OC)C(N)=NC(=N2)N(C)CCCNC(=O)C1CCCO1
Reference
N/A
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.