Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
CETIRIZINE HYDROCHLORIDE
DIR Classification
Classification:Ambiguous
Severity Score:1.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- In four clinical studies in healthy adult males, no clinically significant mean increases in QTc were observed in cetirizine hydrochloride treated subjects. In the first study, a placebo-controlled crossover trial, cetirizine hydrochloride was given at doses up to 60 mg per day, 6 times the maximum clinical dose, for 1 week, and no significant mean QTc prolongation occurred. In the second study, a crossover trial, cetirizine hydrochloride 20 mg and erythromycin (500 mg every 8 hours) were given alone and in combination. There was no significant effect on QTc with the combination or with cetirizine hydrochloride alone. In the third trial, also a crossover study, cetirizine hydrochloride 20 mg and ketoconazole (400 mg per day) were given alone and in combination. Cetirizine hydrochloride caused a mean increase in QTc of 9.1 msec from baseline after 10 days of therapy. Ketoconazole also increased QTc by 8.3 msec. The combination caused an increase of 17.4 msec, equal to the sum of the individual effects. Thus, there was no significant drug interaction on QTc with the combination of cetirizine hydrochloride and ketoconazole. In the fourth study, a placebo-controlled parallel trial, cetirizine hydrochloride 20 mg was given alone or in combination with azithromycin (500 mg as a single dose on the first day followed by 250 mg once daily). There was no significant increase in QTc with cetirizine hydrochloride 20 mg alone or in combination with azithromycin.
- In a four-week clinical trial in pediatric patients aged 6 to 11 years, results of randomly obtained ECG measurements before treatment and after 2 weeks of treatment showed that cetirizine hydrochloride 5 or 10 mg did not increase QTc versus placebo. In a one week clinical trial (N=86) of cetirizine hydrochloride oral solution (0.25 mg/kg bid) compared with placebo in pediatric patients 6 to 11 months of age, ECG measurements taken within 3 hours of the last dose did not show any ECG abnormalities or increases in QTc interval in either group compare
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
84
24008
Other ADRs
54767
38326820
Odds Ratio = 2.449
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- R06AE07 - cetirizine hydrochloride
- R06AE - Piperazine derivatives
- R06A - ANTIHISTAMINES FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- R06 - ANTIHISTAMINES FOR SYSTEMIC USE
- R - RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:Cetirizine Hydrochloride
Active Ingredient UNII:64O047KTOA
Drugbank ID:DB00341
PubChem Compound:2678
CTD ID:D017332
PharmGKB:PA448905
CAS Number:83881-51-0
Dosage Form(s):solution
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 10.0 mg/day R06AE07
Chemical Structure: 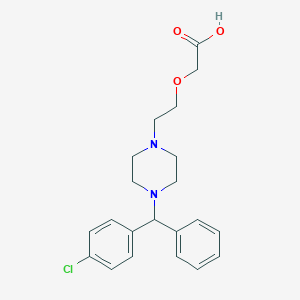

SMILE Code:
OC(=O)COCCN1CCN(CC1)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1
OC(=O)COCCN1CCN(CC1)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1
Reference
1: Comparative analysis of the cardiotoxicity proclivities of second generation antihistamines in an experimental model predictive of adverse clinical ECG effects.
[Hey J A,del Prado M,Sherwood J,Kreutner W,Egan R W]Arzneimittelforschung,1996 Feb;46(2):153-8. PMID: 8720304
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.