Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
DOLASETRON MESYLATE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- WARNINGS
- QT Interval Prolongation
- ANZEMET prolongs the QT interval in a dose dependent fashion. Torsade de Pointes has been reported during post-marketing experience. Avoid ANZEMET in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, hypomagnesemia, or hypokalemia. Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia must be corrected prior to ANZEMET administration. Monitor these electrolytes after administration as clinically indicated. Use ECG monitoring in patients with congestive heart failure, bradycardia, renal impairment, and elderly patients (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
- [PR and QRS Interval Prolongation]
- ANZEMET has been shown to cause dose dependent prolongation of the PR and QRS interval and reports of second or third degree atrioventricular block, cardiac arrest and serious ventricular arrhythmias including fatalities in both adult and pediatric patients. At particular risk are patients with underlying structural heart disease and preexisting conduction system abnormalities, elderly, patients with sick sinus syndrome, patients with atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response, patients with myocardial ischemia or patients receiving drugs known to prolong the PR interval (such as verapamil) and QRS interval (e.g., flecainide or quinidine). ANZEMET should be used with caution and with ECG monitoring in these patients. ANZEMET should be avoided in patients with complete heart block or at risk for complete heart block, unless they have an implanted pacemaker (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
- PRECAUTIONS
- General
- Dolasetron should be administered with caution in patients who have or may develop prolongation of cardiac conduction intervals, particularly QTc. These include patients with hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, patients taking diuretics with potential for inducing electrolyte abnormalities, patients with congenital QT syndrome, patients taking anti-arrhythmic drugs or other drugs which lead to QT prolongation, and cumulative high dose anthracycline therapy.
- Cross hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients who received other selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. These reactions have not been seen with dolasetron mesylate.
- [Drug Interactions]
- The potential for clinically significant drug-drug interactions posed by dolasetron and hydrodolasetron appears to be low for drugs commonly used in chemotherapy because hydrodolasetron is eliminated by multiple routes. See PRECAUTIONS, GENERAL for information about potential interaction with other drugs that prolong the QTc interval.
- [Geriatric Use]
- Elderly patients are at particular risk for prolongation of the PR, QRS, and QT interval; therefore, caution should be exercised and ECG monitoring should be performed when using ANZEMET in this population (see WARNINGS).
- OVERDOSAGE
- A 59-year-old man with metastatic melanoma and no known pre-existing cardiac conditions developed severe hypotension and dizziness 40 minutes after receiving a 15 minute intravenous infusion of 1000 mg (13 mg/kg) of dolasetron mesylate. Treatment for the overdose consisted of infusion of 500 mL of a plasma expander, dopamine, and atropine. The patient had normal sinus rhythm and prolongation of PR, QRS and QTc intervals on an ECG recorded 2 hours after the infusion. The patient’s blood pressure was normal 3 hours after the event and the ECG intervals returned to baseline on follow-up. The patient was released from the hospital 6 hours after the event.
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- In children for whom the 100 mg tablet is not appropriate based on their weight or ability to swallow tablets, the ANZEMET Injection solution may be mixed into apple or apple-grape juice for oral dosing in pediatric patients. The diluted product may be kept up to 2 hours at room temperature before use. However, ANZEMET Injection solution when administered intravenously is contraindicated in adult and pediatric patients for the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of emetogenic cancer chemotherapy due to dose dependent QT prolongation.
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Effects on Electrocardiogram
- QTcF interval was evaluated in a randomized, placebo and active (moxifloxacin 400 mg once-daily) controlled crossover study in 80 healthy adults, with 14 measurements over 24 hours on Day 4. The maximum mean (95% upper confidence bound) differences in QTcF from placebo after baseline-correction were 14.1 (16.1) ms and 36.6 (38.6) ms for 100 mg and supratherapeutic 300 mg ANZEMET, administered intravenously, respectively. ANZEMET 300 mg once daily resulted in approximately 3-fold higher mean Cmax values of dolasetron mesylate and its active metabolite hydrodolasetron on Day 4 compared to those observed with the therapeutic 100 mg ANZEMET dose.
- Based on exposure-response analysis in healthy volunteers, QTc interval prolongations appear to be associated with concentrations of hydrodolasetron. Using the established exposure-response relationship, the mean predicted increase (95% upper prediction interval) in QTcF intervals were 16.0 (17.1) ms and 17.9 (19.1) ms for renally impaired and elderly subjects following an oral dose of 100 mg.
- In the thorough QT study, exposure dependent prolongation of the PR and QRS interval was also noted in healthy subjects receiving ANZEMET. The maximum mean (95% upper confidence bound) difference in PR from placebo after baseline-correction was 9.8 (11.6) ms and 33.1 (34.9) ms for 100 mg and supratherapeutic 300 mg ANZEMET, respectively. The maximum mean (95% upper confidence bound) difference in QRS from placebo after baseline-correction was 3.5 (4.5) ms and 13 (14.5) ms for 100 mg and supratherapeutic 300 mg ANZEMET, respectively. Over one-fourth of the subjects treated with the 300 mg dose had an absolute PR over 200 ms and absolute QRS of over 110 ms post-treatment. A change from baseline ≥ 25% was noted in several of these subjects (see WARNINGS).
- PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Patients should be informed that ANZEMET may cause serious cardiac arrhythmias such as QT prolongation or heart block. Patients should be instructed to tell their health care provider right away if they perceive a change in their heart rate, if they feel lightheaded, or if they have a syncopal episode.
- Patients should be informed that the chances of developing serious cardiac arrhythmias such as QT prolongation and Torsade de Pointes or heart block are higher in the following people:
- Patients with a personal or family history of abnormal heart rhythms, such as congenital long QT syndrome
- Patients with a personal history of sick sinus syndrome, atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response or myocardial ischemia
- Patients who take medications that may prolong the PR interval, such as certain antihypertensives or medications that may prolong the QRS interval, such as antiarrythmic medications
- Patients who take medications, such as diuretics, which may cause electrolyte abnormalities
- Patients with hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia. Some types of chemotherapy cause hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia
- Elderly patients and renally impaired patients
- ANZEMET should be avoided in these patients, since they may be more at risk for cardiac arrhythmias such as QT prolongation and Torsade de Pointes.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
1
24091
Other ADRs
178
38381409
Odds Ratio = 8.951
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- A04AA04 - dolasetron mesylate
- A04AA - Serotonin (5HT3) antagonists
- A04A - ANTIEMETICS AND ANTINAUSEANTS
- A04 - ANTIEMETICS AND ANTINAUSEANTS
- A - ALIMENTARY TRACT AND METABOLISM
Active Ingredient:DOLASETRON MESYLATE
Active Ingredient UNII:U3C8E5BWKR
Drugbank ID:DB00757
PubChem Compound:3033818
CTD ID: C060344
PharmGKB:PA449390
CAS Number:115956-12-2
Dosage Form(s):tablet, film coated
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 200.0 mg/day A04AA04
Chemical Structure: 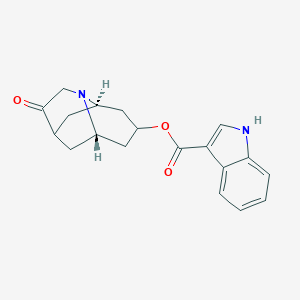

SMILE Code:
[H][C@@]1(C[C@@]2([H])C[C@]3([H])C[C@@]([H])(C1)N2CC3=O)OC(=O)C1=CNC2=C1C=CC=C2
[H][C@@]1(C[C@@]2([H])C[C@]3([H])C[C@@]([H])(C1)N2CC3=O)OC(=O)C1=CNC2=C1C=CC=C2
Reference
1: Dolasetron overdose resulting in prolonged QTc interval and severe hypotension: a case report and literature review.
[Rochford Martin,Kiernan Thomas J,Aziz Amjed]Emerg Med J,2007 Jul;24(7):515-7. PMID: 17582056
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.