Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
PROCAINAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:4.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- PRECAUTIONS
- General
- After achieving and maintaining therapeutic plasma concentrations and satisfactory electrocardiographic and clinical responses, continued frequent periodic monitoring of vital signs and electrocardiograms is advised. If evidence of QRS widening of more than 25 percent or marked prolongation of the Q-T interval occurs, concern for overdosage is appropriate, and interruption of the PA infusion is advisable if a 50 percent increase occurs. Elevated serum creatinine or urea nitrogen, reduced creatinine clearance or history of renal insufficiency, as well as use in older patients (over age 50), provide grounds to anticipate that less than the usual dosage or infusion rate may suffice, since the urinary elimination of PA and NAPA may be reduced, leading to gradual accumulation beyond normally-predicted amounts. If facilities are available for measurement of plasma PA and NAPA, or acetylation capability, individual dose adjustment for optimal therapeutic levels may be easier, but close observation of clinical effectiveness is the most important criterion.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Torsades de Pointes: In the unusual ventricular arrhythmia called "les torsades de pointes" (twistings of the points), characterized by alternation of one or more ventricular premature beats in the directions of the QRS complexes on ECG in persons with prolonged Q-T and often enhanced U waves, Group 1A antiarrhythmic drugs are contraindicated. Administration of PA in such cases may aggravate this special type of ventricular extrasystole or tachycardia instead of suppressing it.
- OVERDOSAGE
- Progressive widening of the QRS complex, prolonged Q-T and P-R intervals, lowering of the R and T waves, as well as increasing A-V block, may be seen with doses which are excessive for a given patient. Increased ventricular extrasystoles, or even ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation may occur. After intravenous administration but seldom after oral therapy, transient high plasma levels of PA may induce hypotension, affecting systolic more than diastolic pressures, especially in hypertensive patients. Such high levels may also produce central nervous depression, tremor, and even respiratory depression.
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- The electrocardiogram may reflect these effects by showing slight sinus tachycardia (due to the anticholinergic action) and widened QRS complexes and, less regularly, prolonged Q-T and P-R intervals (due to longer systole and slower conduction), as well as some decrease in QRS and T wave amplitude. These direct effects of PA on electrical activity, conduction, responsiveness, excitability and automaticity are characteristic of a Group 1A antiarrhythmic agent, the prototype for which is quinidine; PA effects are very similar. However, PA has weaker vagal blocking action than does quinidine, does not induce alpha-adrenergic blockade, and is less depressing to cardiac contractility.
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
5
24087
Other ADRs
134
38381453
Odds Ratio = 59.458
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- C01BA02 - procainamide hydrochloride
- C01BA - "Antiarrhythmics, class Ia"
- C01B - "ANTIARRHYTHMICS, CLASS I AND III"
- C01 - CARDIAC THERAPY
- C - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Active Ingredient:PROCAINAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
Active Ingredient UNII:SI4064O0LX
Drugbank ID:DB01035
PubChem Compound:4913
CTD ID:D011342
PharmGKB:PA451108
CAS Number:51-06-9
Dosage Form(s):injection, solution
Route(s) Of Administrator:intramuscular; intravenous
Daily Dose:
- 300.0 mg/day C01BA02
Chemical Structure: 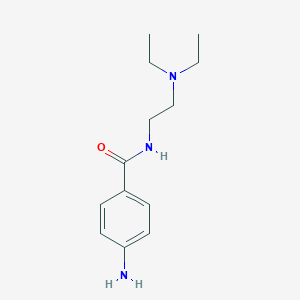

SMILE Code:
CCN(CC)CCNC(=O)C1=CC=C(N)C=C1
CCN(CC)CCNC(=O)C1=CC=C(N)C=C1
Reference
1: Female gender as a risk factor for torsades de pointes associated with cardiovascular drugs.
[Makkar R R,Fromm B S,Steinman R T,Meissner M D,Lehmann M H]JAMA,1993 Dec 1;270(21):2590-7. PMID: 8230644
2: Drug-induced torsade de pointes.
[Raehl C L,Patel A K,LeRoy M]Clin Pharm,Nov-Dec 1985;4(6):675-90. PMID: 2416504
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.