Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
RYDAPT
DIR Classification
Classification:Moderate-DIQT concern
Severity Score:3.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended Administration
- Administer prophylactic anti-emetics before treatment with RYDAPT to reduce the risk of nausea and vomiting.
- Administer RYDAPT orally with food, twice daily at approximately 12-hour intervals [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Do not open or crush RYDAPT capsules.
- If a dose of RYDAPT is missed or vomited, do not make up the dose; take the next dose at the usual scheduled time.
- Consider interval assessments of QT by EKG if RYDAPT is taken concurrently with medications that can prolong the QT interval.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Systemic Mastocytosis
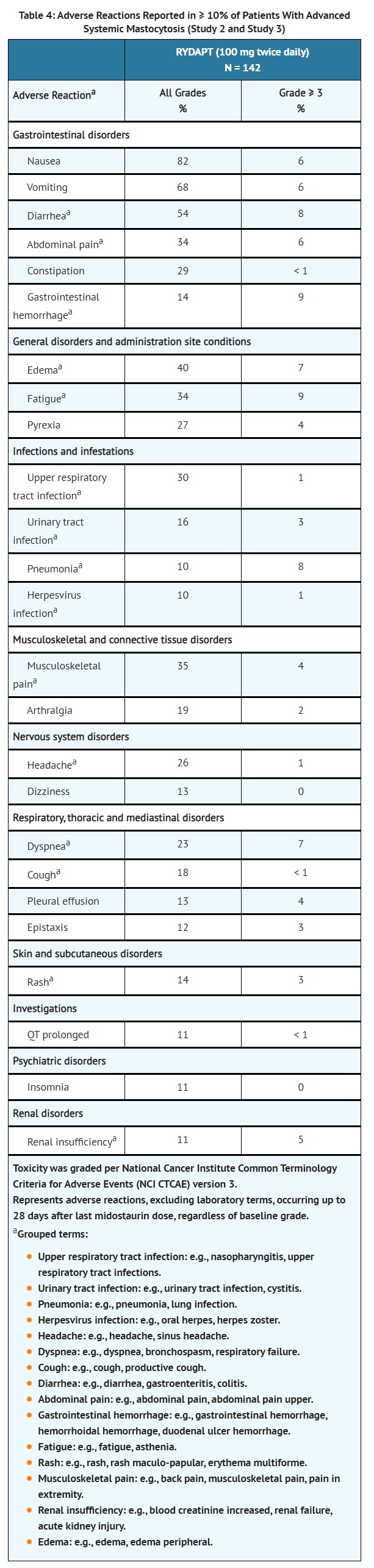
- Two single-arm, open-label multicenter trials (Study 2 and Study 3) evaluated the safety of RYDAPT (100 mg twice daily with food) as a single agent in 142 adult patients total with ASM, SM-AHN, or MCL. The median age was 63 (range 24 to 82), 63% had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1, and 75% had no hepatic impairment (bilirubin and AST ≤ ULN) at baseline. The median duration of exposure to RYDAPT was 11.4 months (range 0 to 81 months), with 34% treated for ≥ 24 months.
- The most frequent adverse reactions (≥ 20%), excluding laboratory terms, were nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, edema, musculoskeletal pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, upper respiratory tract infection, constipation, pyrexia, headache, and dyspnea (Table 4). Grade ≥ 3 adverse reactions reported in ≥ 5%, excluding laboratory terms, were fatigue, sepsis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, pneumonia, diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, edema, dyspnea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and renal insufficiency (Table 4).
- Adverse reactions led to dose modifications (interruption or reduction) in 56% of patients. Among these, the most frequent adverse reactions (> 5%) were gastrointestinal symptoms, QT prolongation, neutropenia, pyrexia, thrombocytopenia, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, lipase increase, and fatigue. The median time to first dose modification for toxicity was 1.6 months, with 75% of dose modifications first occurring within 5 months of starting treatment.
- Treatment discontinuation due to adverse reactions occurred in 21% of patients. The most frequent adverse reactions causing treatment discontinuation included infection, nausea or vomiting, QT prolongation, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Cardiac Electrophysiology
- The effect of RYDAPT (75 mg twice daily for 3 days) on the QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized, placebo and moxifloxacin controlled, multiple-dose, blinded, parallel study. There was no clinically significant prolongation of QTc interval or relationship between changes in QTc and concentrations for midostaurin and its active metabolites (CGP62221 and CGP52421). The study duration was not long enough to estimate the effects of the metabolite CGP52421 on the QT/QTc interval.
- In pooled clinical studies in patients with advanced SM, 4.7% patients had a post-baseline QTcF > 480 ms, no patients had a QTcF > 500 ms, and 6.3% patients had a QTcF > 60 ms compared to baseline.
- In a randomized placebo-controlled study in patients with AML, the proportion of patients with QTc prolongation was higher in patients randomized to midostaurin as compared to placebo (QTcF > 480 ms: 10.1% vs 5.7%; QTcF > 500 ms: 6.2% vs 2.6%; QTcF > 60 ms: 18.4% vs 10.7%).
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
0
24092
Other ADRs
0
38381587
Odds Ratio = N/A
Drug Property Information
SMILE Code:
CO[C@@H]1[C@@H](C[C@H]2O[C@]1(C)N1C3=C(C=CC=C3)C3=C1C1=C(C4=C(C=CC=C4)N21)C1=C3CNC1=O)N(C)C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1
CO[C@@H]1[C@@H](C[C@H]2O[C@]1(C)N1C3=C(C=CC=C3)C3=C1C1=C(C4=C(C=CC=C4)N21)C1=C3CNC1=O)N(C)C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1
Reference
N/A
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.