Search for drugs:
Typing the drug name to query
TOREMIFENE CITRATE
DIR Classification
Classification:Most-DIQT concern
Severity Score:5.0
Description in Drug Labeling: View Full Labeling: SPL in DailyMed | PDF
- BOXED WARNING
- WARNING: QT PROLONGATION
- Toremifene citrate has been shown to prolong the QTc interval in a dose- and concentration-related manner [SEE CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.2)].Prolongation of the QT interval can result in a type of ventricular tachycardia called Torsade de pointes, which may result in syncope, seizure, and/or death. Toremifene should not be prescribed to patients with congenital/acquired QT prolongation, uncorrected hypokalemia or uncorrected hypomagnesemia. Drugs known to prolong the QT interval and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors should be avoided[SEE WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Prolongation of the QT Interval
- Toremifene has been shown to prolong the QTc interval in a dose- and concentration-related manner[SEE CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.2)] .Prolongation of the QT interval can result in a type of ventricular tachycardia called Torsade de pointes, which may result in syncope, seizure, and/or death.
- Toremifene should be avoided in patients with long QT syndrome. Caution should be exercised in patients with congestive heart failure, hepatic impairment and electrolyte abnormalities. Hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia must be corrected prior to initiating toremifene and these electrolytes should be monitored periodically during therapy. Drugs that prolong the QT interval should be avoided. In patients at increased risk, electrocardiograms (ECGs) should be obtained at baseline and as clinically indicated [SEE DRUG INTERACTIONS (7.2) and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.2)].
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Agents that Prolong QT
- The administration of toremifene citrate with agents that have demonstrated QT prolongation as one of their pharmacodynamic effects should be avoided. Should treatment with any of these agents be required, it is recommended that therapy with toremifene citrate be interrupted. If interruption of treatment with toremifene citrate is not possible, patients who require treatment with a drug that prolongs QT should be closely monitored for prolongation of the QT interval. Agents generally accepted to prolong QT interval include Class 1A (e.g., quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide) and Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol, ibutilide, dofetilide) antiarrhythmics; certain antipsychotics (e.g., thioridazine, haloperidol); certain antidepressants (e.g., venlafaxine, amitriptyline); certain antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin, clarithromycin, levofloxacin, ofloxacin); and certain anti-emetics (e.g., ondansetron, granisetron). In patients at increased risk, electrocardiograms (ECGs) should be obtained and patients monitored as clinically indicated [SEE BOXED WARNINGand WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
- [Effect of Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors on Toremifene]
- In a study of 18 healthy subjects, 80 mg toremifene once daily coadministered with 200 mg of ketoconazole twice daily increased the toremifene Cmax and AUC by 1.4- and 2.9-fold, respectively. N-demethyltoremifene Cmax and AUC were reduced by 56% and 20%, respectively.
- The administration of toremifene citrate with agents that are strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, indinavir, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, and voriconazole) increase the steady-state concentration in serum and should be avoided. Grapefruit juice may also increase plasma concentrations of toremifene and should be avoided. Should treatment with any of these agents be required, it is recommended that therapy with toremifene citrate be interrupted. If interruption of treatment with toremifene citrate is not possible, patients who require treatment with a drug that strongly inhibits CYP3A4 should be closely monitored for prolongation of the QT interval [SEE BOXED WARNINGand WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- QT Prolongation, Hypokalemia, Hypomagnesemia
- Toremifene should not be prescribed to patients with congenital/acquired QT prolongation (long QT syndrome), uncorrected hypokalemia, or uncorrected hypomagnesemia.
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacodynamics
- Effects on Cardiac Electrophysiology
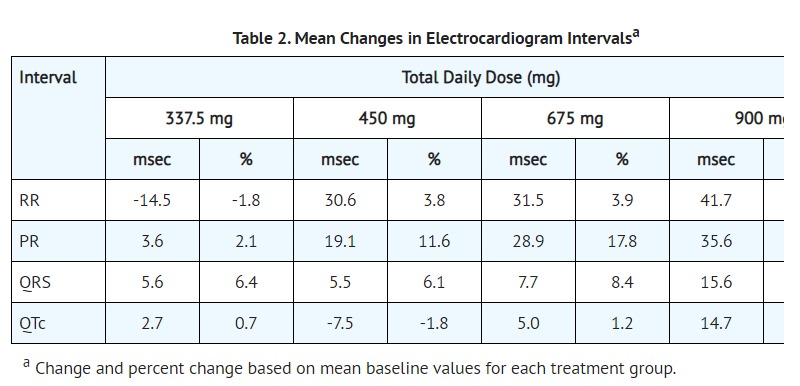
- The effect of 20 mg, 80 mg, and 300 mg of toremifene on QT interval was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized study in healthy male subjects aged 18 to 45 years. The QT interval was measured at steady state of toremifene (Day 5 of dosing), including the time of peak plasma concentration (Tmax), at 13 time points (4 ECGs/time point) over 24 hours post dose in a time matched analysis. The 300 mg dose of toremifene (approximately five times the highest recommended dose 60 mg) was chosen because this dose produces exposure to toremifene that will cover the expected exposures that may result from potential drug interactions and hepatic impairment [SEE DRUG INTERACTIONS (7.2)].
- Dose and concentration-related increases in the QTc interval and T wave changes were observed (see Table 1). These effects are believed to be caused by toremifene and N-demethyltoremifene. Toremifene had no effects on heart rate, PR and QRS interval duration [SEE BOXED WARNINGand WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
- PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Patients who must take medications known to prolong the QT interval, or potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, should be informed of the effect of toremifene on QT interval. Toremifene has been shown to prolong the QTc interval in a dose-related manner [SEE BOXED WARNING, WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1),and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.2)].
Postmarketing Surveillance
Contingency Table:
Current Drug
Other Drugs
QT Prolongation
3
24089
Other ADRs
662
38380925
Odds Ratio = 7.221
Drug Property Information
ATC Code(s):
- L02BA02 - toremifene citrate
- L02BA - Anti-estrogens
- L02B - HORMONE ANTAGONISTS AND RELATED AGENTS
- L02 - ENDOCRINE THERAPY
- L - ANTINEOPLASTIC AND IMMUNOMODULATING AGENTS
Active Ingredient:TOREMIFENE CITRATE
Active Ingredient UNII:2498Y783QT
Drugbank ID:DB00539
PubChem Compound:3005573
CTD ID:D017312
PharmGKB:PA451731
CAS Number:89778-26-7
Dosage Form(s):tablet
Route(s) Of Administrator:oral
Daily Dose:
- 60.0 mg/day L02BA02
Chemical Structure: 

SMILE Code:
CN(C)CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=C(\CCCl)C1=CC=CC=C1)\C1=CC=CC=C1
CN(C)CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=C(\CCCl)C1=CC=CC=C1)\C1=CC=CC=C1
Reference
N/A
Disclaimer:
The content of this database of QT prolongation is intended for educational and scientific research purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Any mention of commercial products is for clarification and not intended as endorsement.